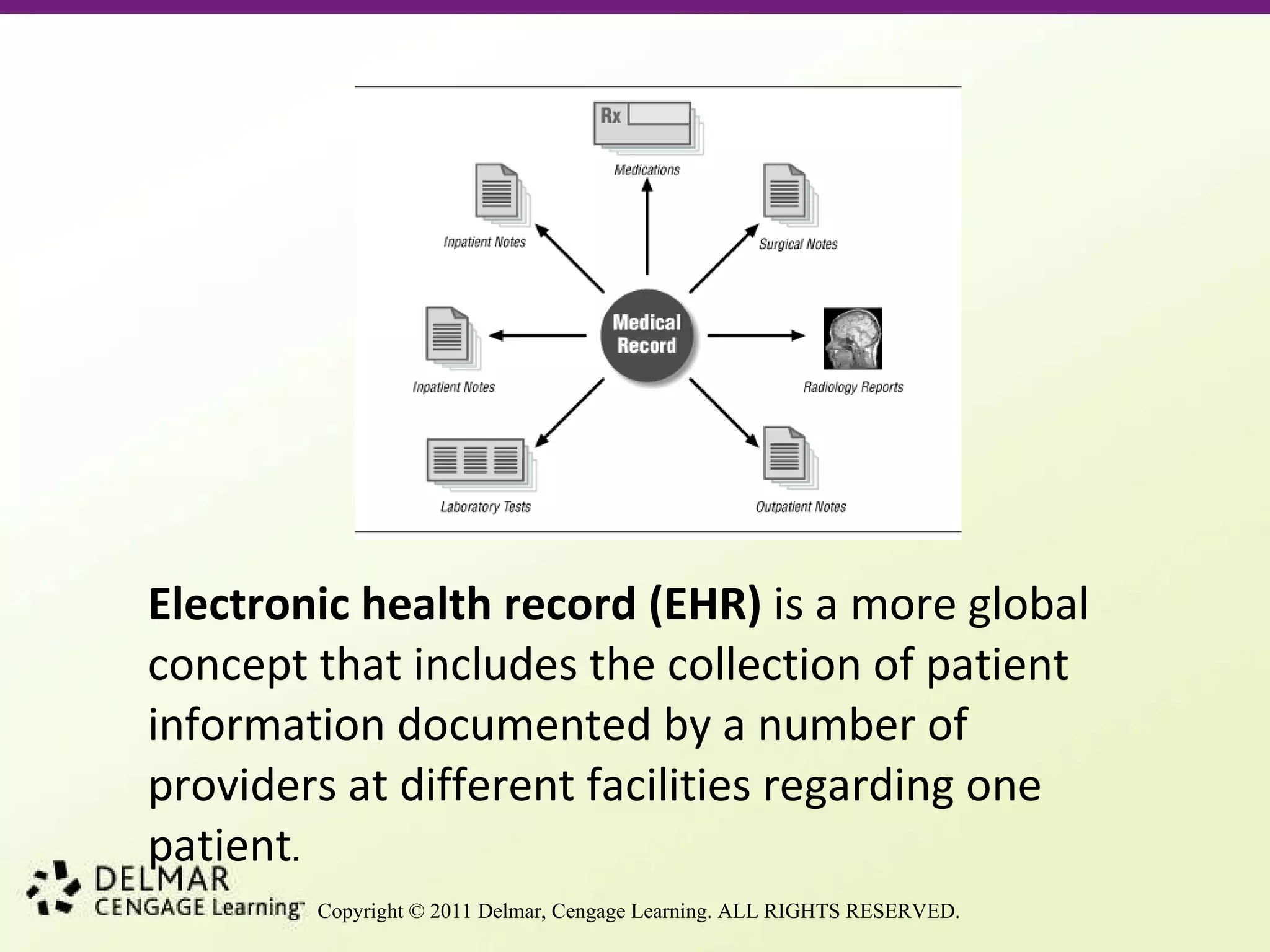
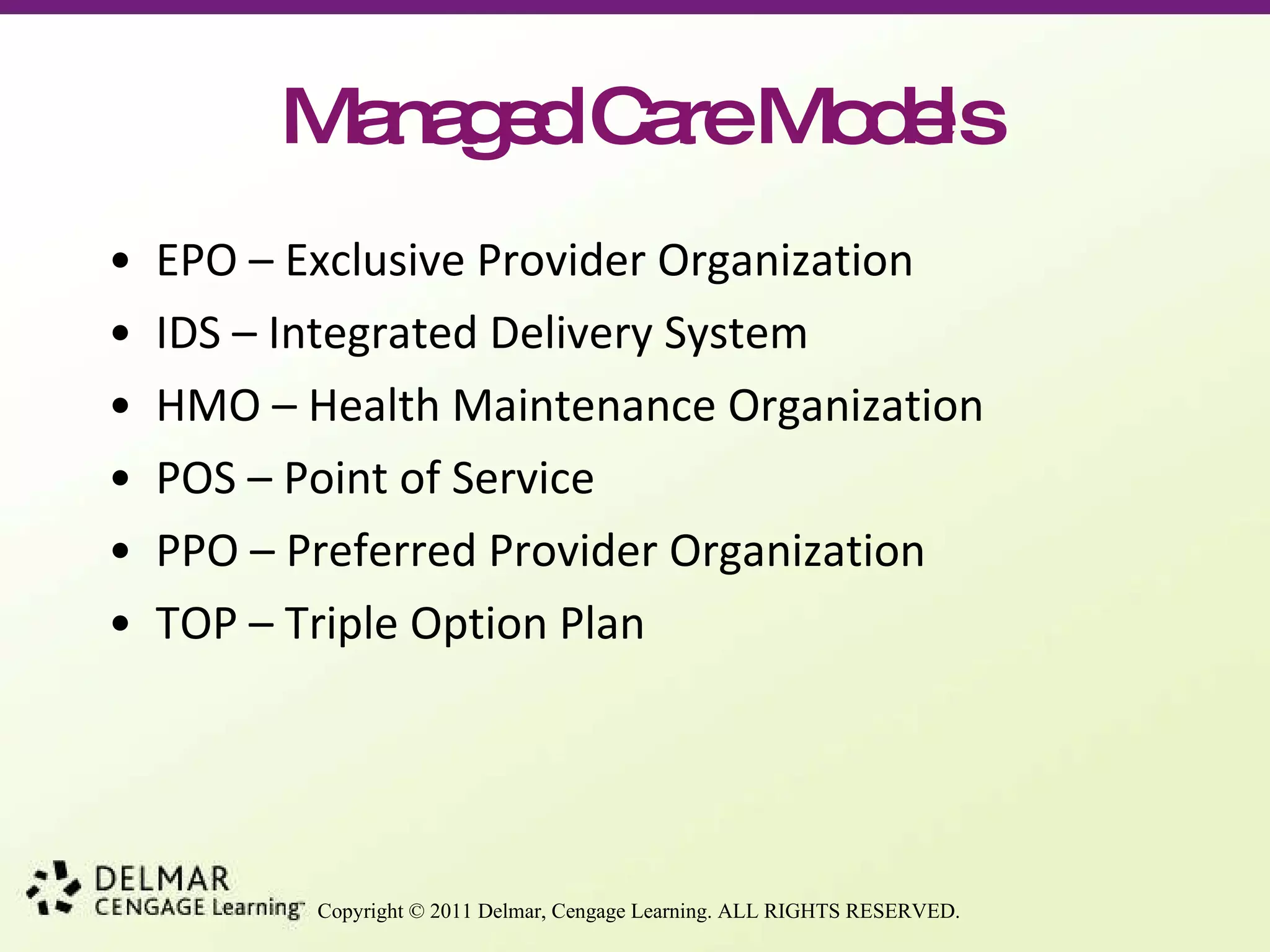
This document provides an overview of key concepts in health insurance and managed care. It defines health insurance and managed care, discusses primary care providers and their gatekeeping role. It also outlines different managed care models like HMOs, PPOs, and consumer-directed health plans. Quality assurance and utilization management processes are described as ways to control costs and ensure quality of care. Medical documentation standards and the use of electronic health records are also summarized.