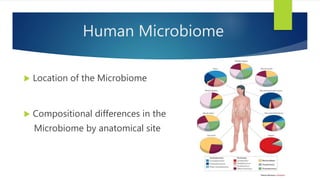
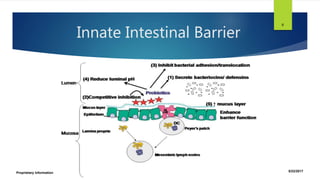
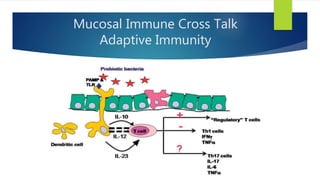
The document discusses the human microbiome, its definition, and significance, highlighting its composition and the findings from the Human Microbiome Project. It emphasizes the importance of the gut microbiome, its development from birth, and factors that can negatively affect it, such as diet and stress. Additionally, it describes the consequences of dysbiosis and its association with various health issues, aligning with the ancient belief that all disease begins in the gut.