The document provides information about the theory of production and the factors of production.
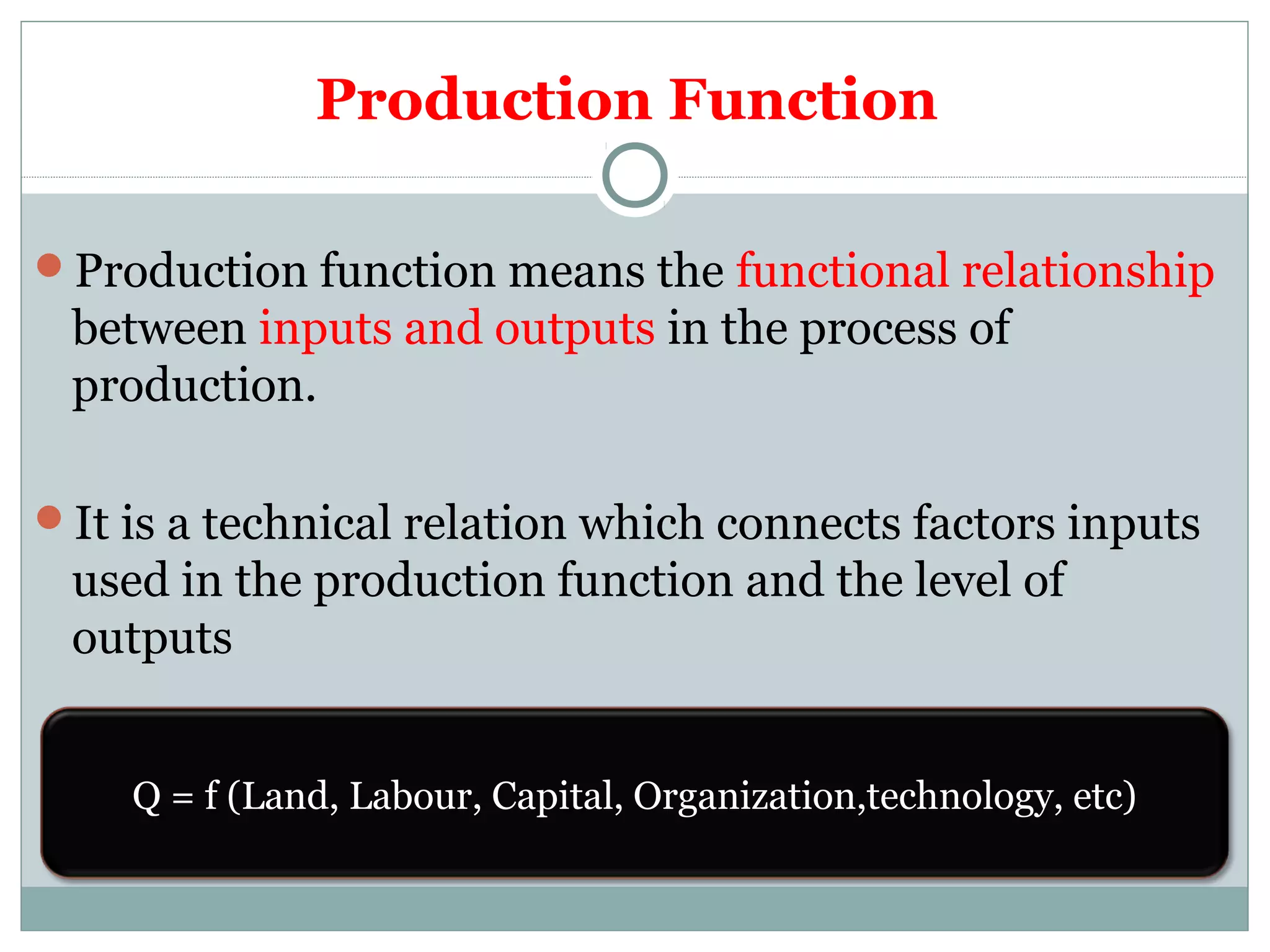
It begins with an introduction to the theory of production, defining it as the process of converting inputs into outputs. It then discusses the production function and how it represents the relationship between inputs and outputs.
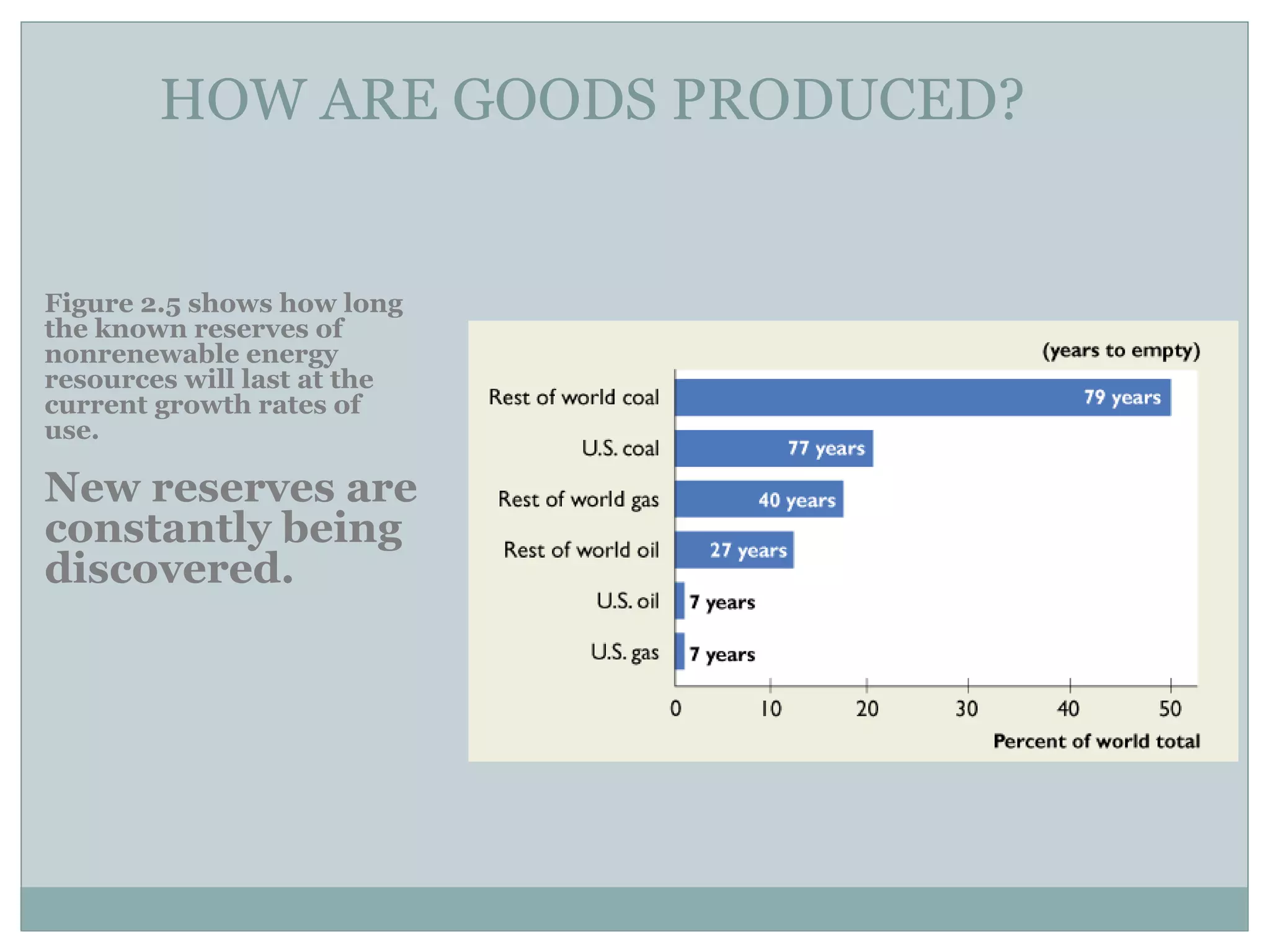
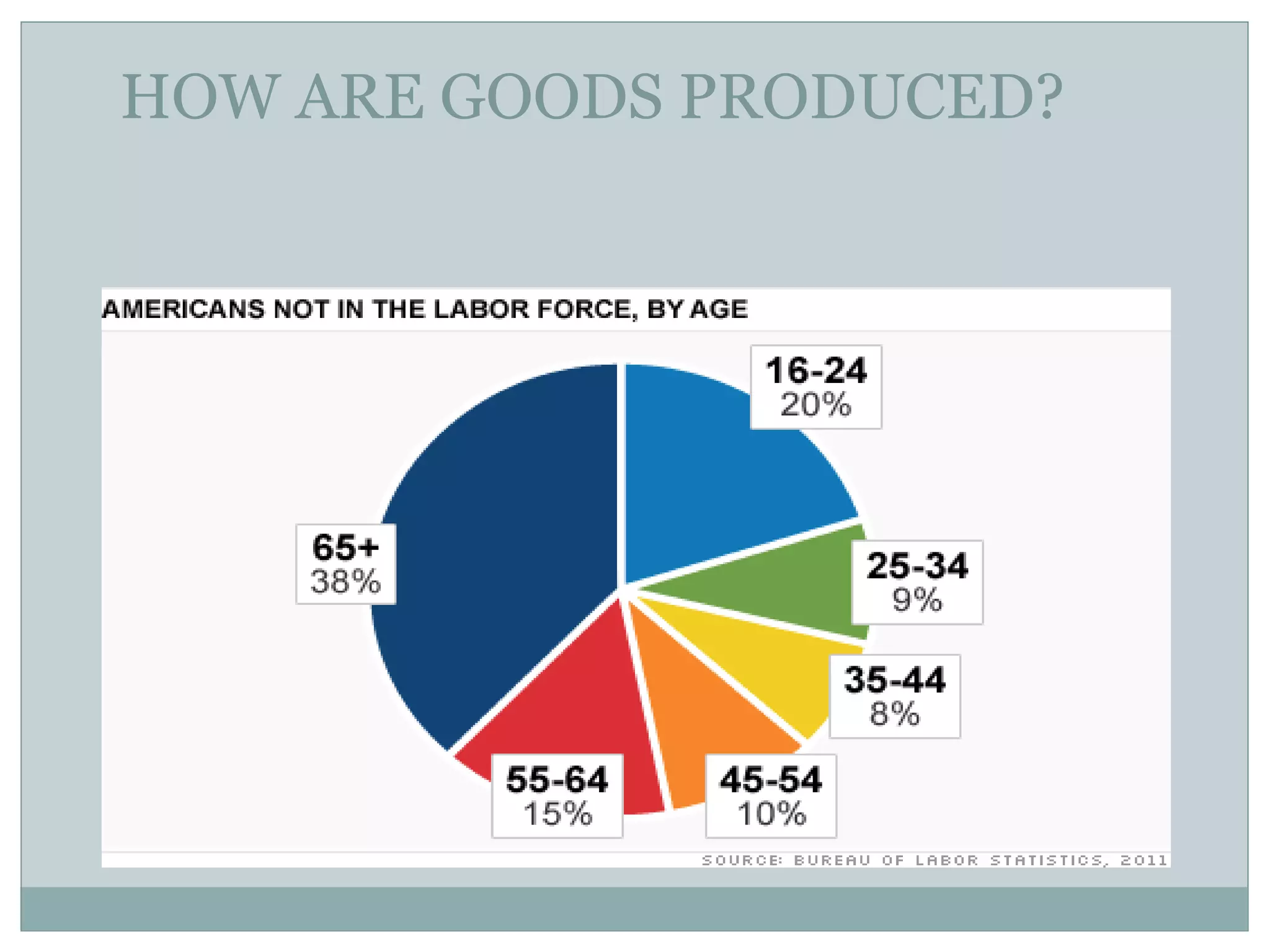
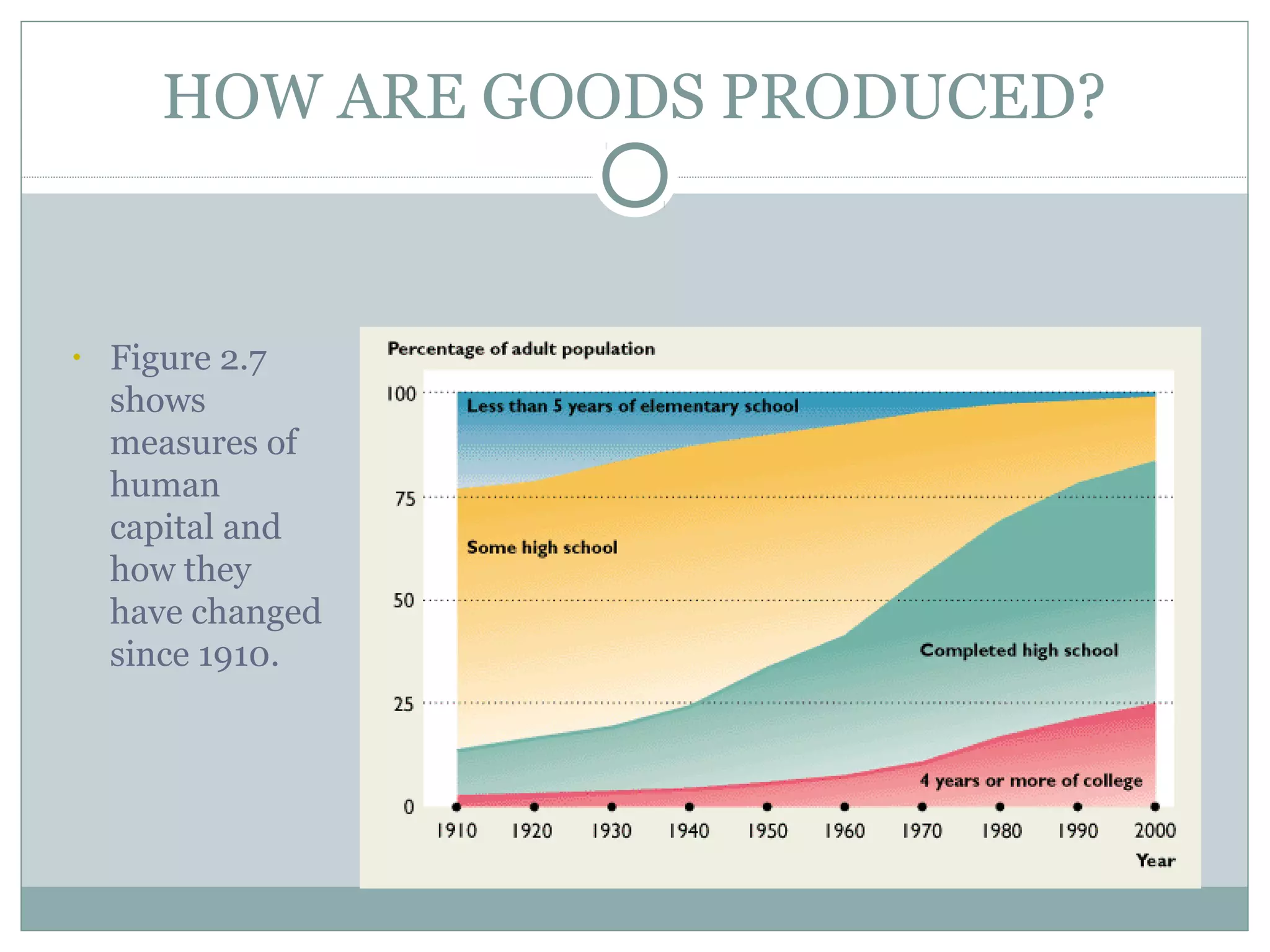
The main body of the document is dedicated to explaining the four factors of production: land, labor, capital, and entrepreneurship. It provides examples and definitions for each factor.
The document concludes by discussing some concepts that influence entrepreneurial decision making, such as scarcity, opportunity cost, and productivity. It emphasizes how entrepreneurs must use resources efficiently to maximize profits.