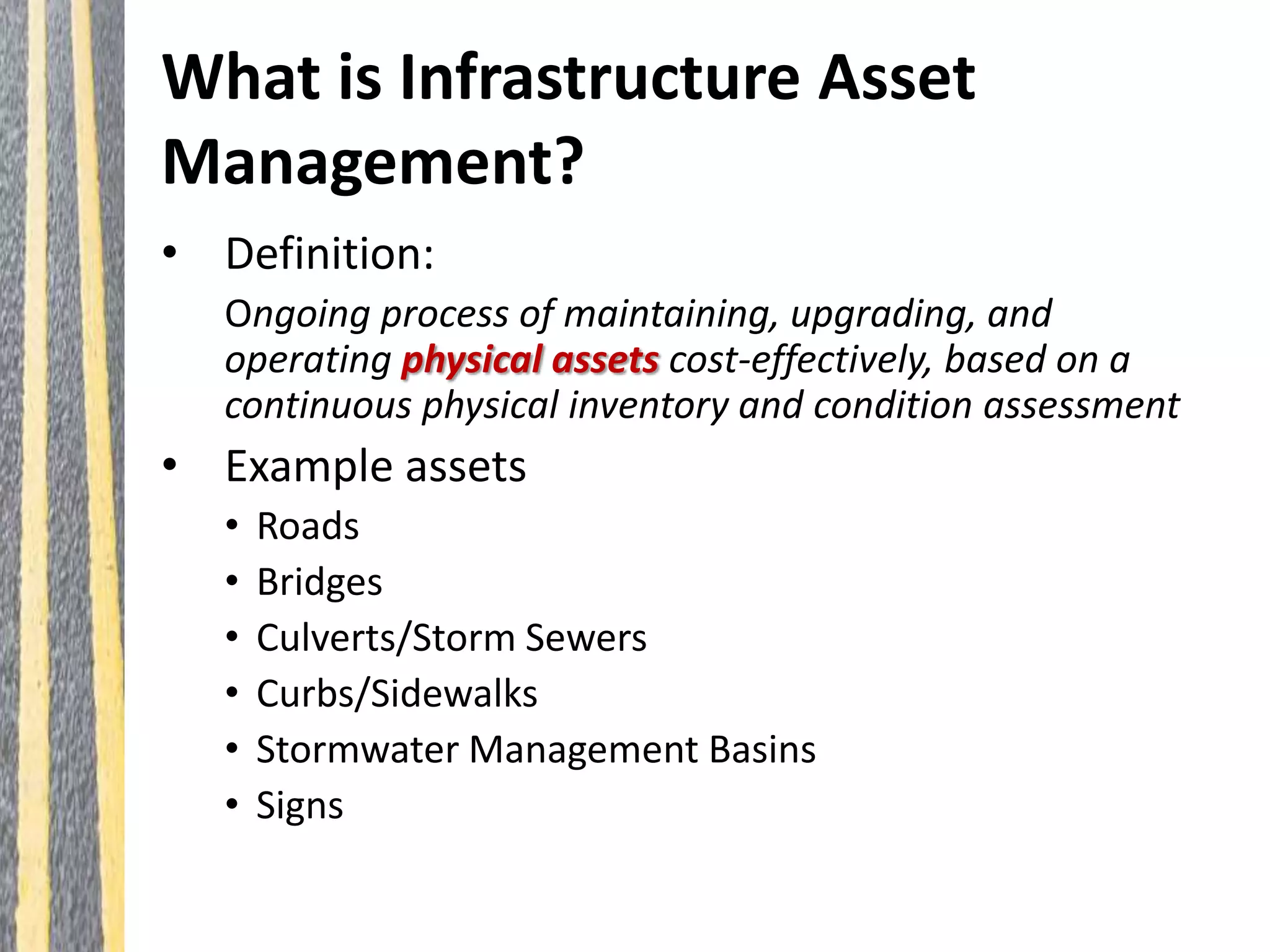
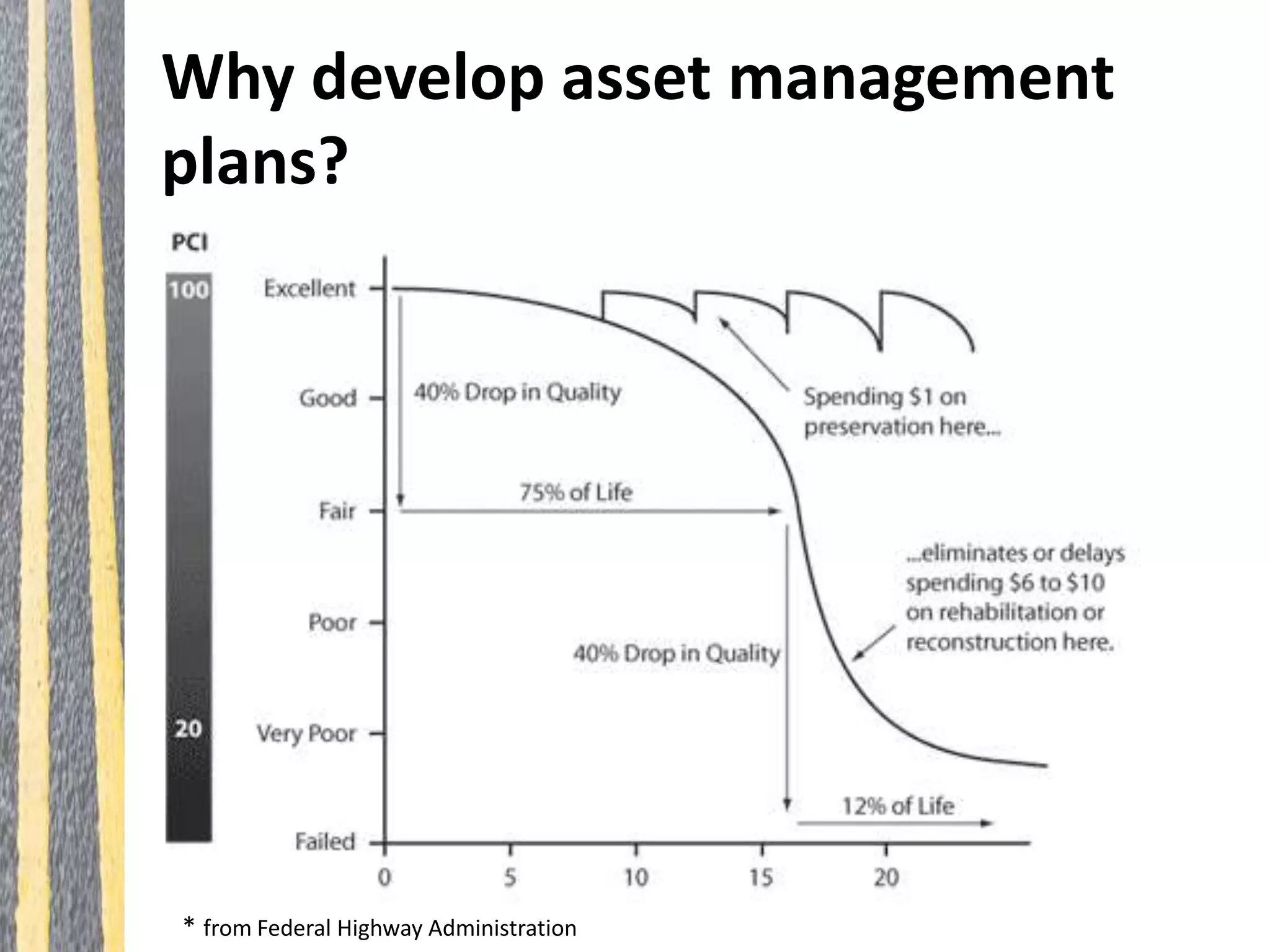
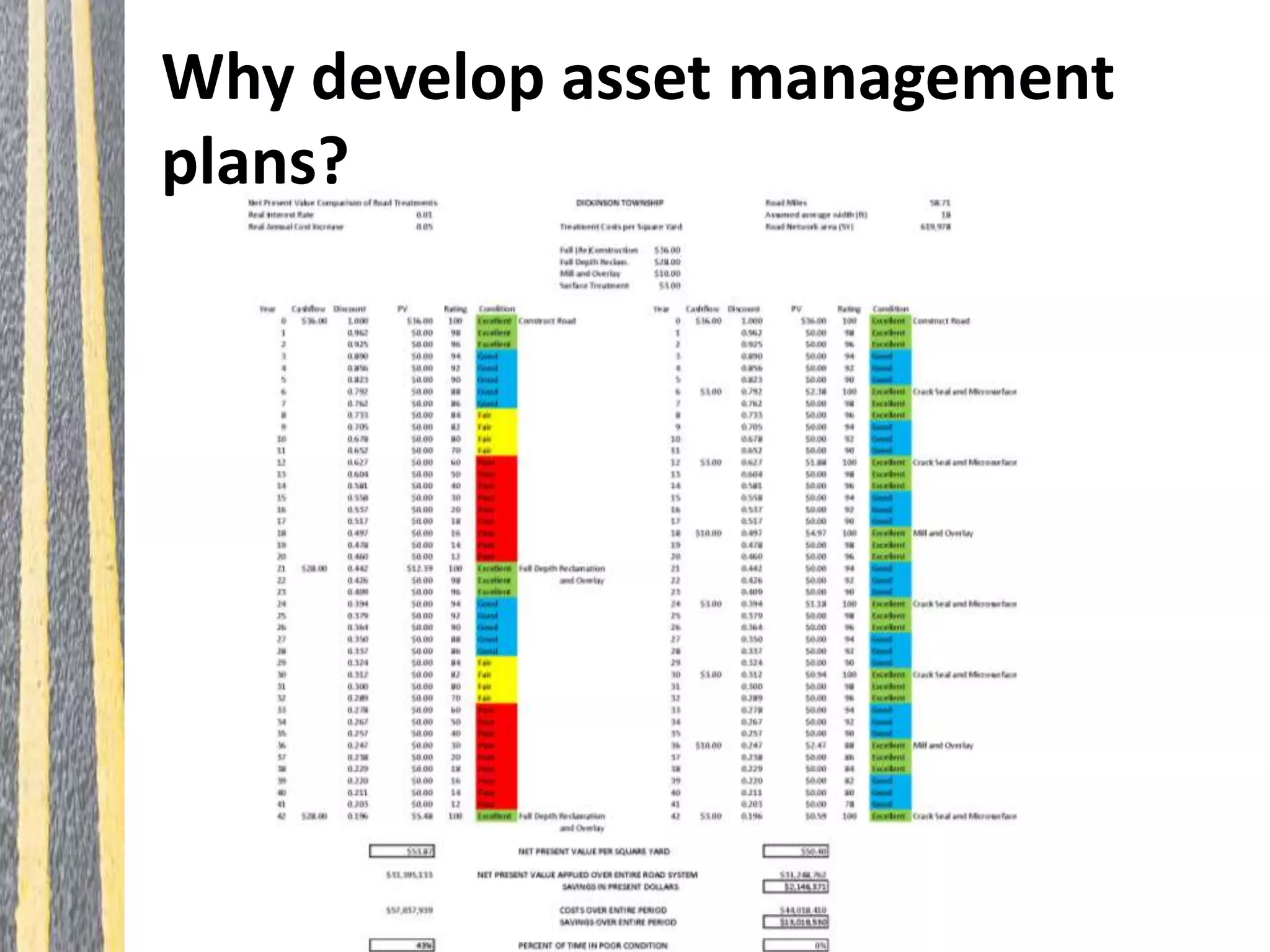
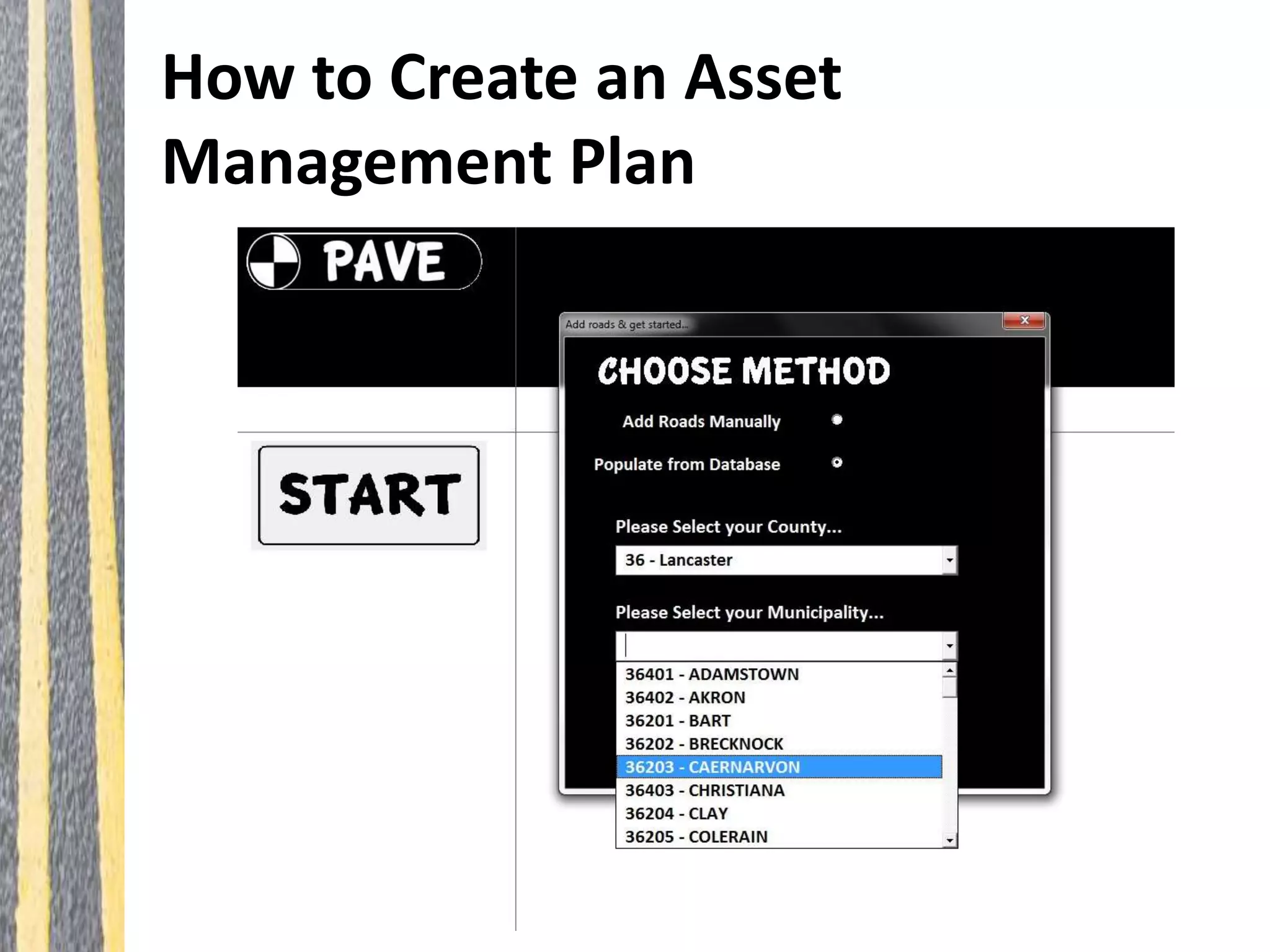
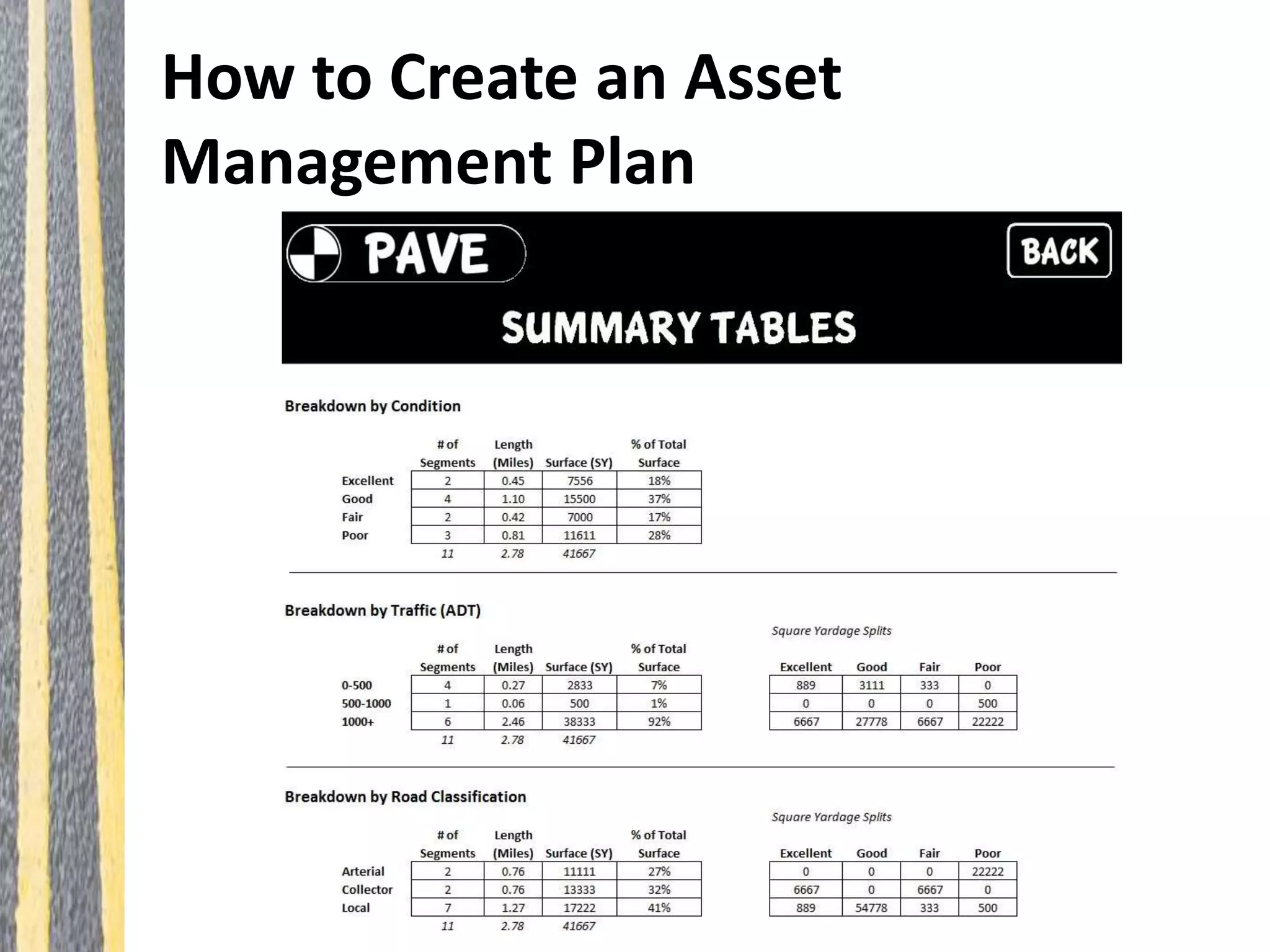
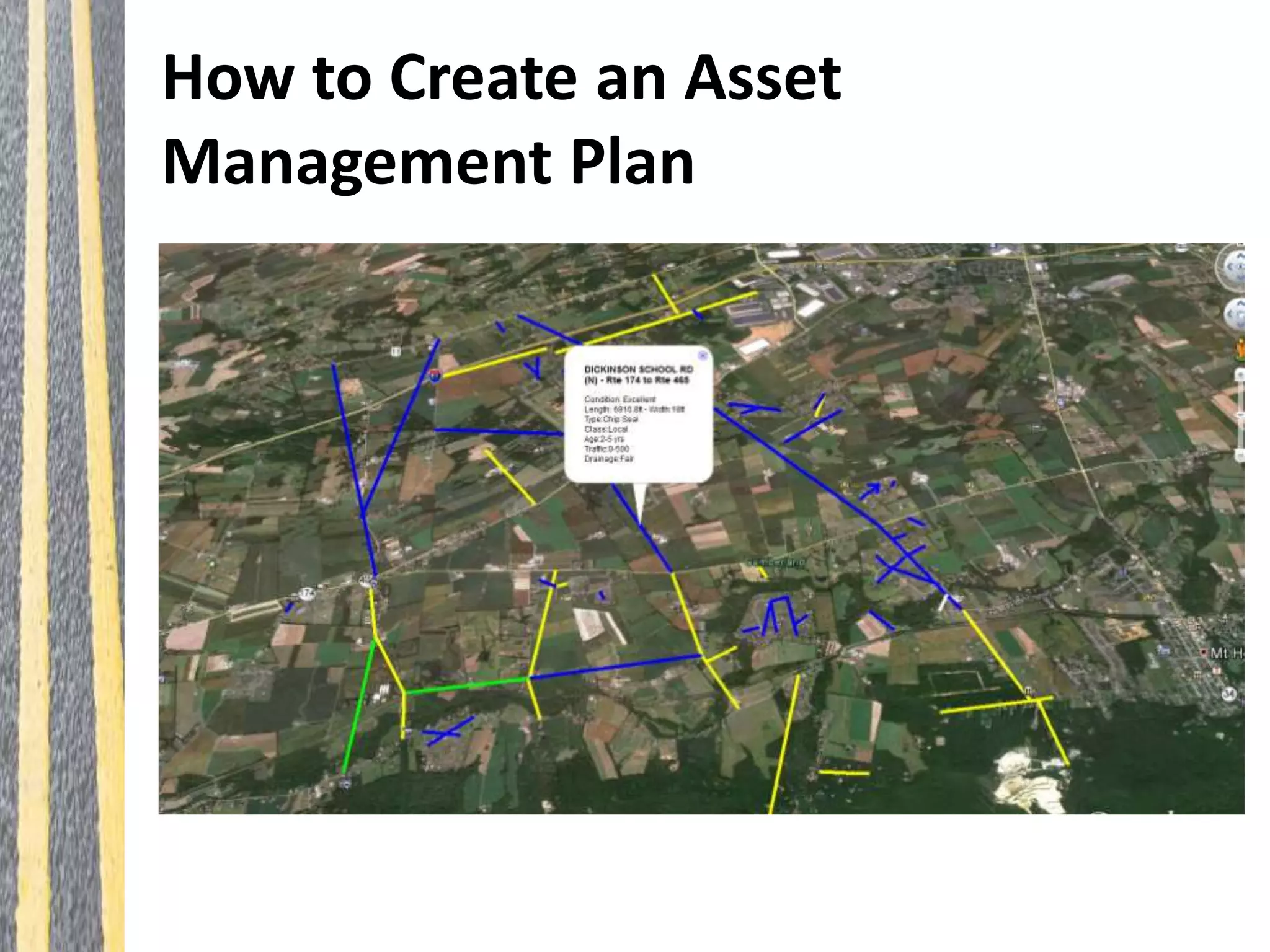
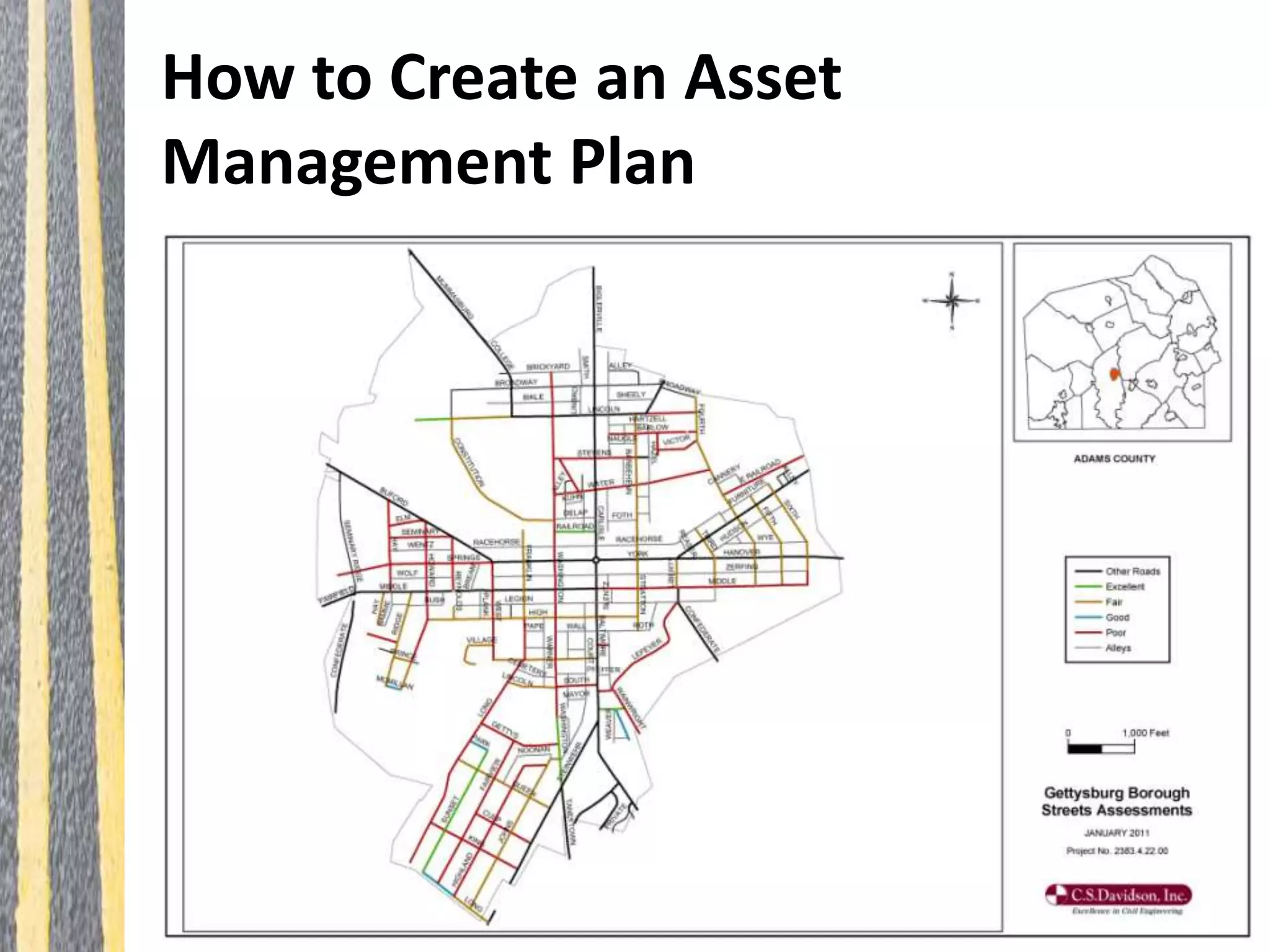
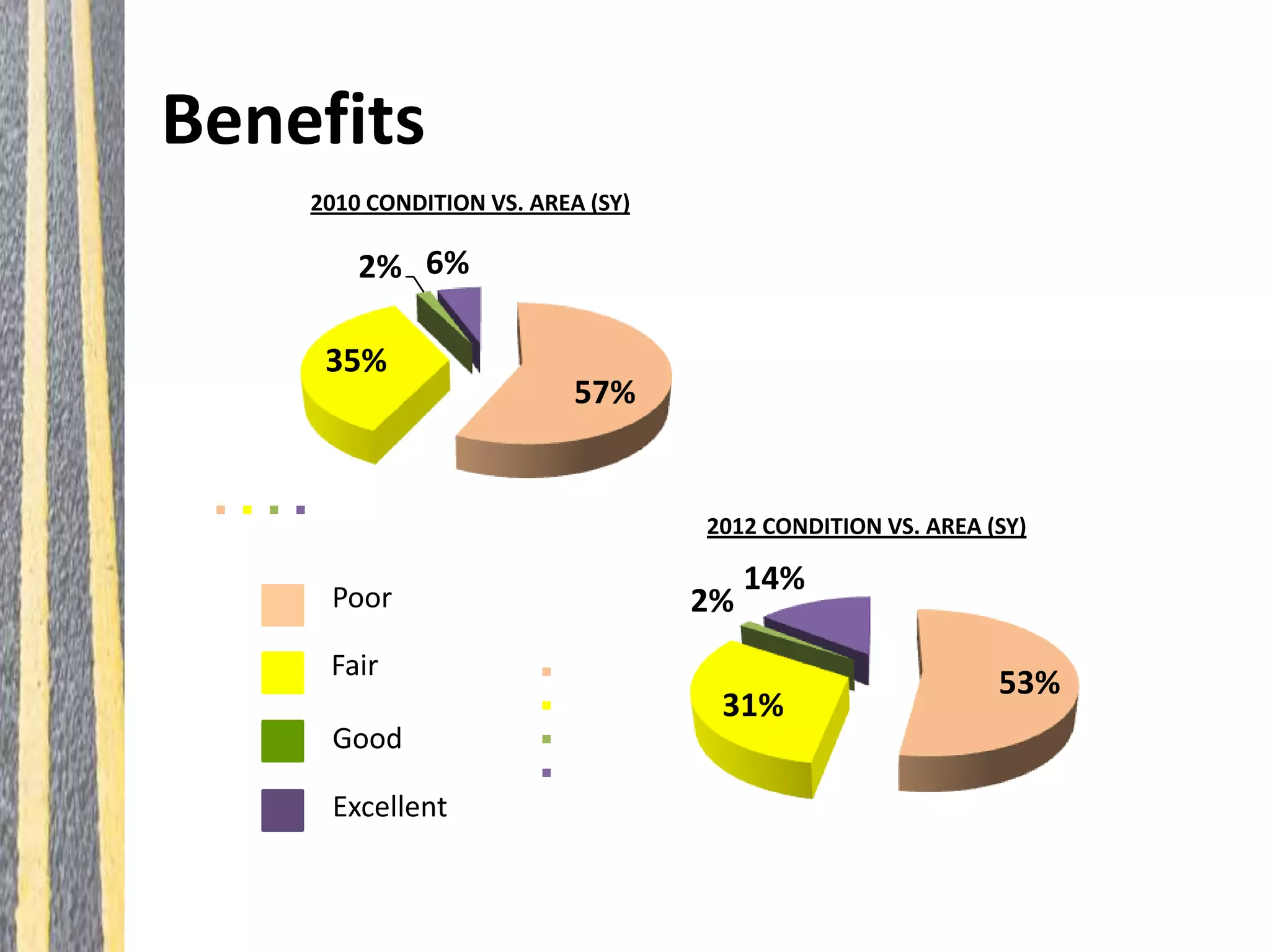
Infrastructure asset management is the ongoing process of maintaining, upgrading, and operating physical assets cost-effectively, ensuring communities can sustain their infrastructure despite increasing operational costs. Effective asset management plans are essential for addressing deteriorating infrastructure, aligning funding with needs, and maintaining service levels. The document outlines steps for creating these plans, including inventorying assets, assessing conditions, and developing budgeted multi-year strategies.