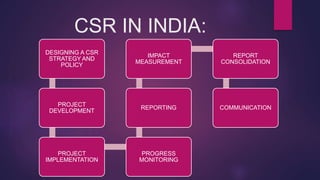
This group assignment presents a case study on integrating social responsibility with corporate strategy at the Tata Group. It discusses the Tata Group's vision and core principles of benefiting economic development and providing equal opportunities. The document outlines the Tata Business Excellence Model (TBEM) for improving organizational performance and managing CSR activities. It provides examples of the Tata Group's long history of CSR activities since 1912 across areas like the environment, community services, health, education, and culture. The assignment compares four models of CSR and concludes with a quote from J.R.D. Tata on serving the needs of the country and people.