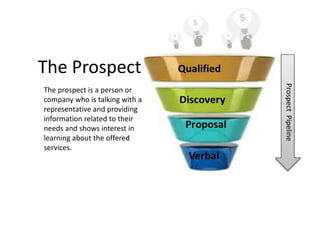
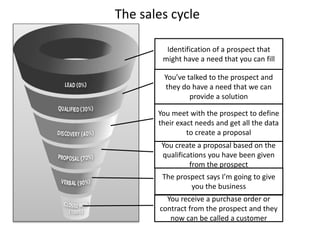
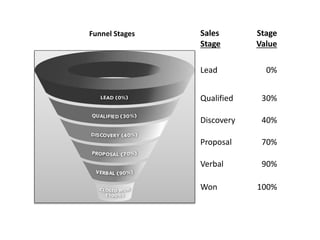
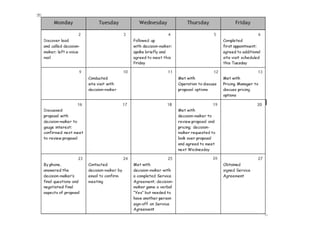
The document discusses the importance of a sales funnel in predicting revenue and managing sales processes effectively. It outlines the stages of a sales funnel, from leads to prospects to customers, and describes the criteria for each stage, as well as the probabilities of closing deals at each step. Additionally, it emphasizes the need for a structured approach to sales funnel management to enhance decision-making and sales forecasting.