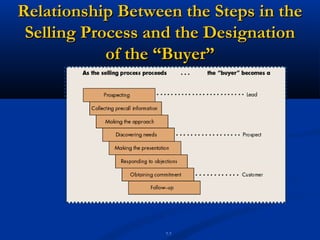
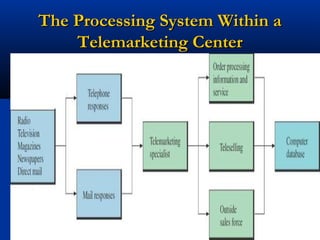
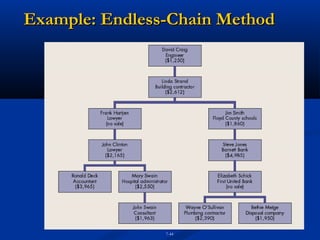
The document discusses various prospecting methods that salespeople can use to identify and qualify potential customers, including obtaining referrals from satisfied customers, using centers of influence, telemarketing, seminars, and spotters. It provides details on how to implement these different prospecting strategies and defines what characteristics make a lead a qualified prospect, such as having a need, ability to pay, and authority to purchase.