This document discusses the role of technology in curriculum delivery. It identifies several key points:
1) Technology can upgrade teaching and learning quality, increase a teacher's ability to teach effectively, and help students master lessons.
2) Technology allows education to be delivered outside of schools through open universities and lifelong learning.
3) Effective technology integration is guided by the TPACK framework, considering technological, pedagogical, and content knowledge.
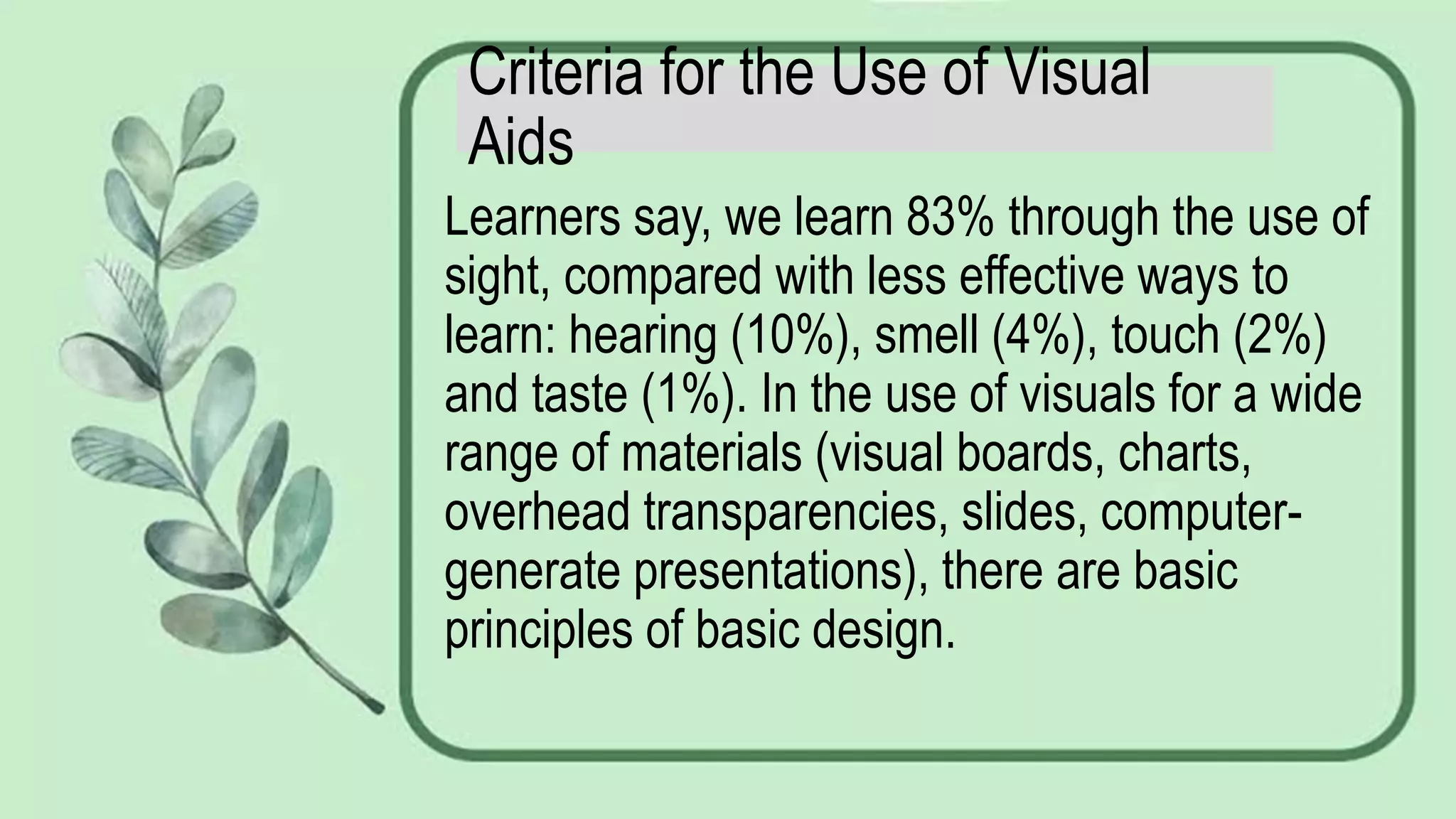
4) Various media like models, printed materials, and computer presentations can be used depending on practicality, appropriateness for learners, activity suitability, and matching learning objectives.