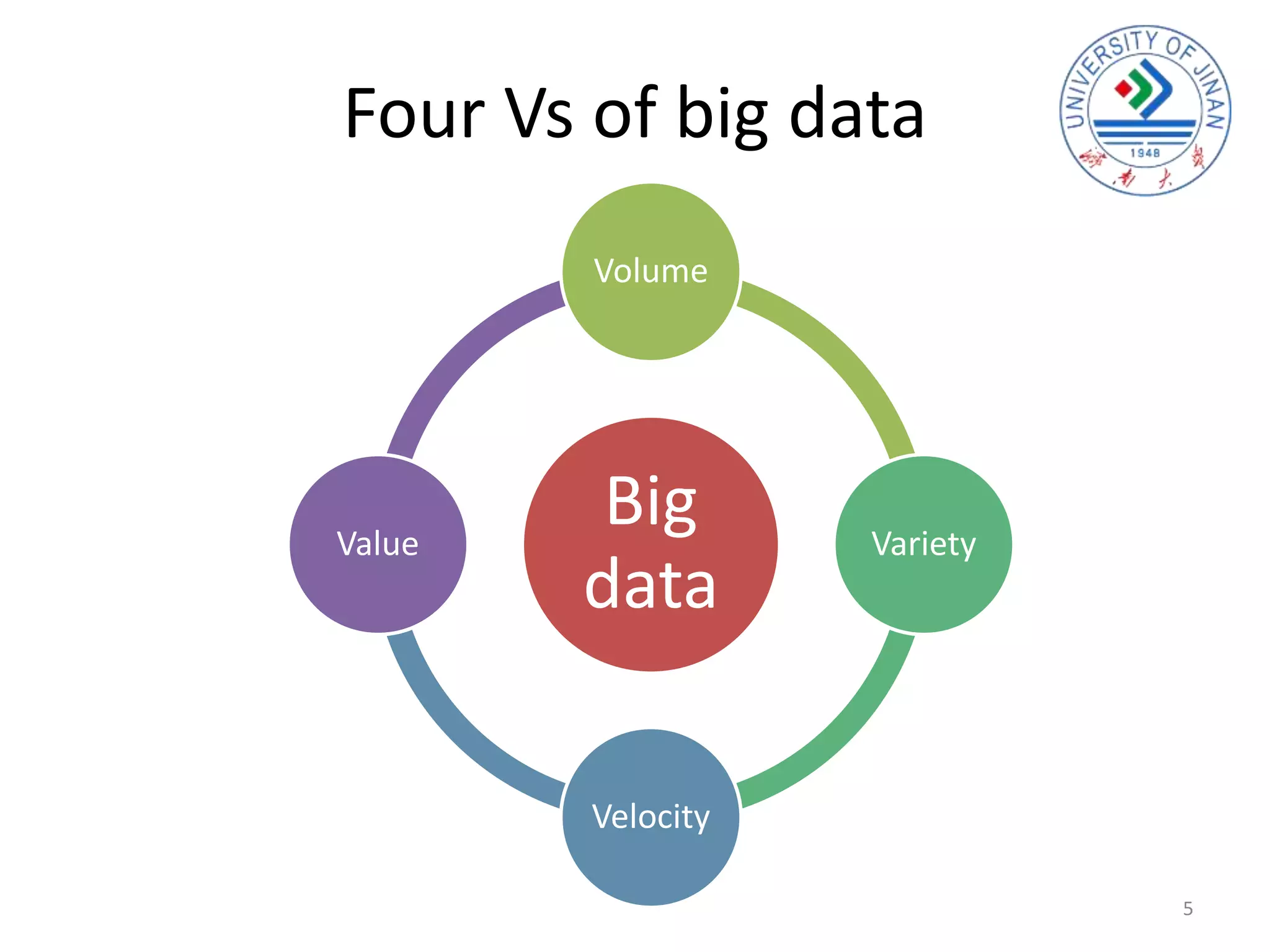
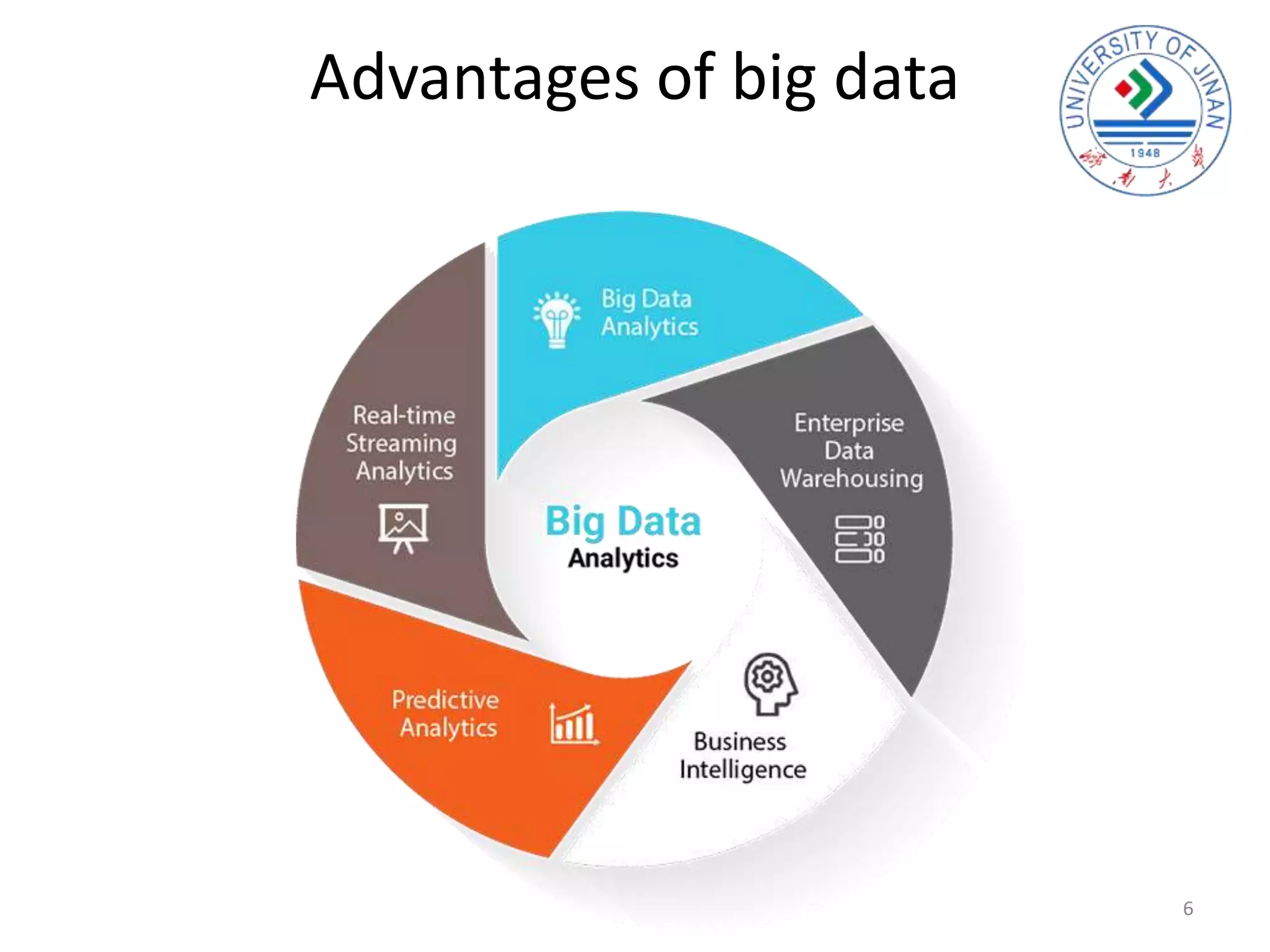
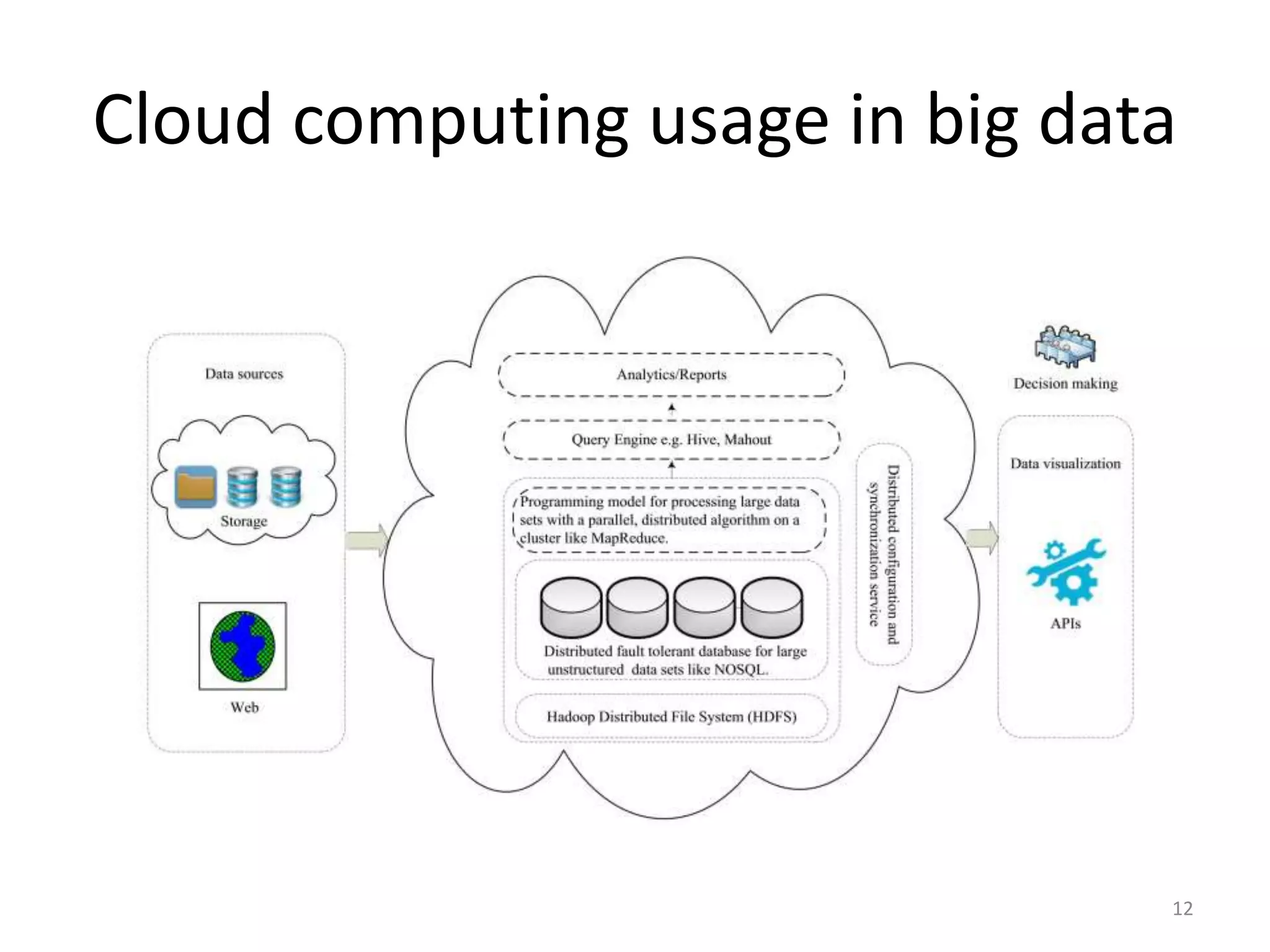
The document discusses the interplay between big data and cloud computing, highlighting the challenges, characteristics, and advantages of both technologies. It details how cloud computing supports big data by enabling scalable storage and processing frameworks like Hadoop. The document concludes that while big data presents significant challenges, cloud technologies offer solutions for efficient data management and analytics.