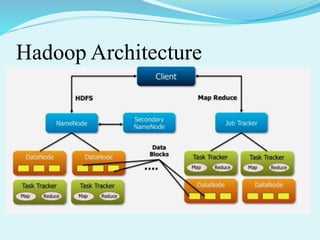
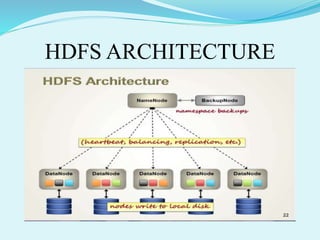
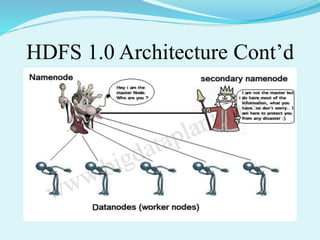
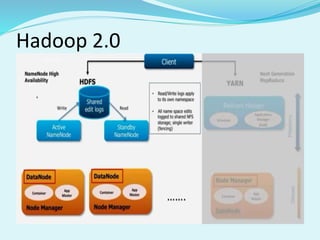
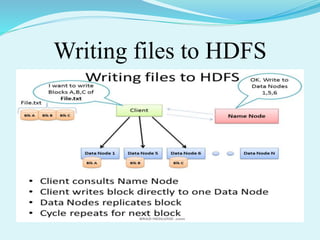
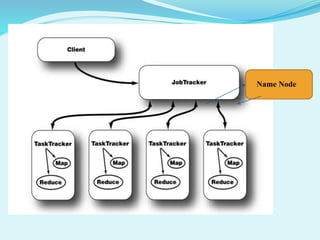
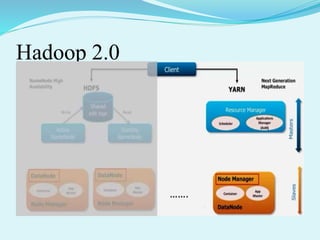
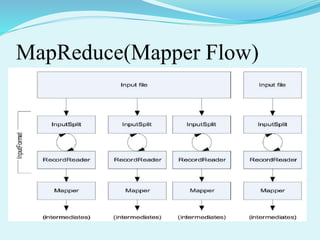
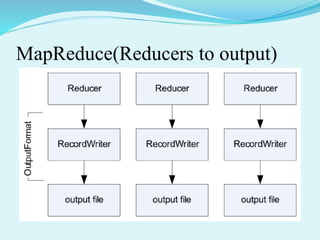
Big data refers to large amounts of data that are beyond the processing capabilities of typical database software. It is characterized by its volume, velocity, and variety. Hadoop is an open-source software framework that can distribute data and processing across clusters of computers to solve big data problems. Hadoop uses HDFS for storage and MapReduce as a programming model to process large datasets in parallel across clusters.