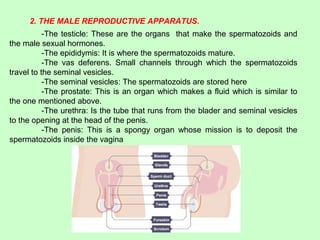
The reproductive function in humans begins with the formation of gametes - sperm in males and eggs in females - in specialized organs. Males and females develop both primary and secondary sexual characteristics through puberty due to the action of sex hormones like estrogen and androgens. These changes allow the reproductive systems and organs to mature and function properly.