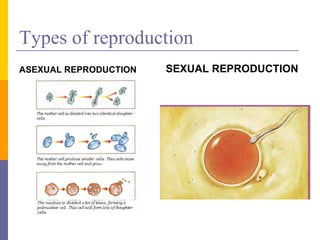
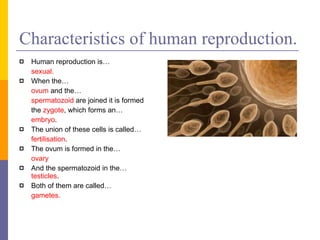
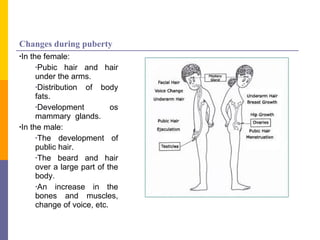
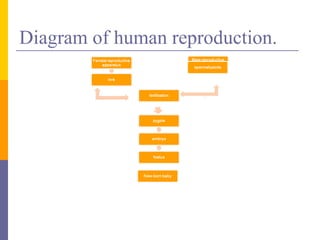
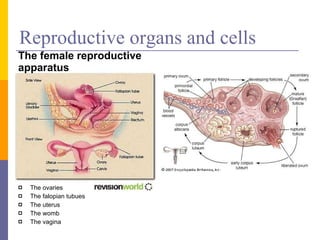
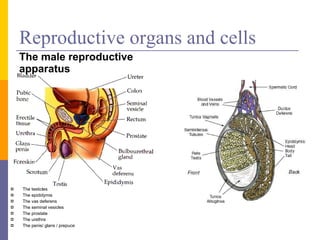
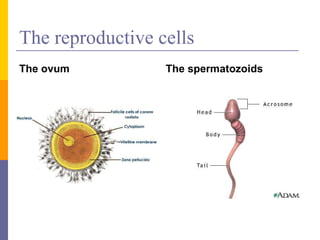
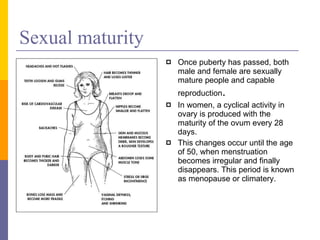
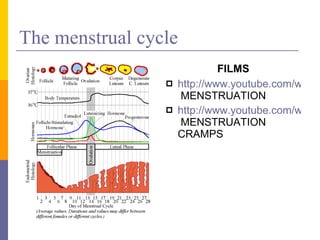
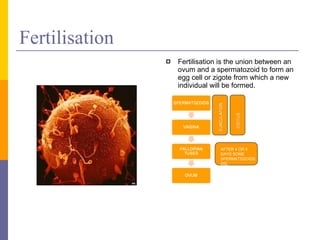
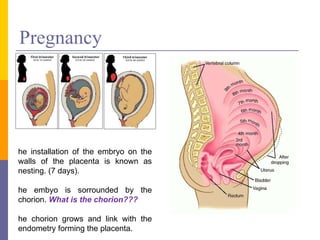
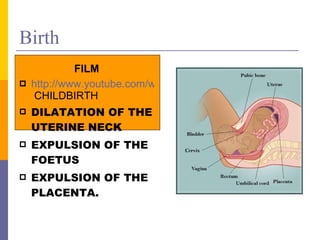
Human reproduction involves the union of male and female reproductive cells. In humans, sexual reproduction occurs through the fertilization of an ovum by a spermatozoon within the female's reproductive tract. At puberty, females develop breasts and pubic hair and begin menstruating due to increased estrogen production, while males experience voice changes and increased hair and muscle growth due to rising androgen levels. Pregnancy is established when a fertilized ovum implants in the uterus and develops into an embryo and later a fetus, receiving nourishment from the mother via the placenta. Childbirth involves dilation of the cervix and birth of the infant followed by the placenta.