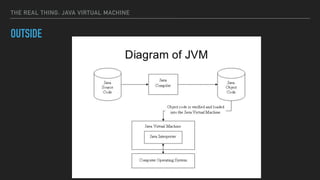
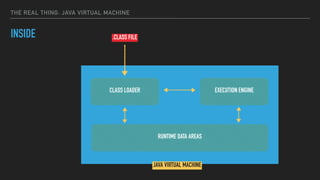
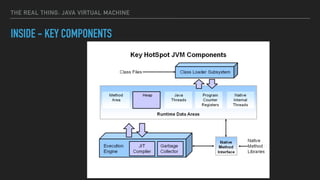
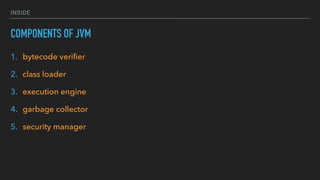
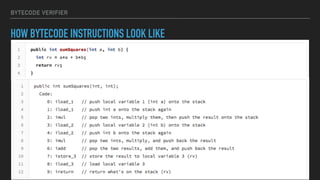
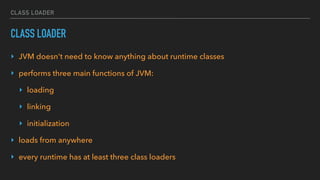
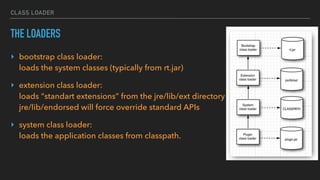
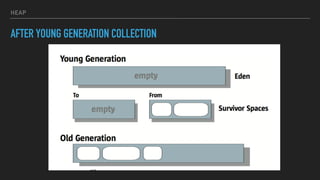
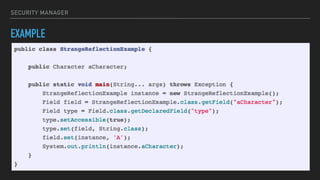
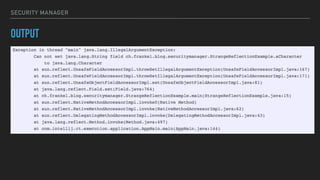
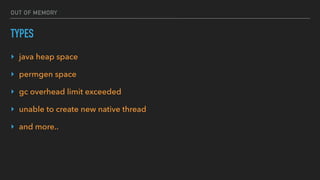
The document provides an overview of the Java Virtual Machine (JVM), detailing its architecture and key components, such as the bytecode verifier, class loader, execution engine, garbage collector, and security manager. It explains how the JVM handles bytecode, optimizes execution with Just-In-Time (JIT) compilation, and manages memory through various types of garbage collectors. Additionally, it discusses common out-of-memory errors and their potential causes, as well as the importance of security policies within the JVM.