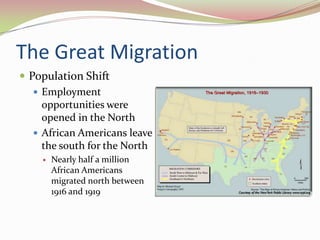
The document summarizes key aspects of progressivism in the United States during the early 20th century. It describes progressivism as a reform movement focused on improving living conditions, education, labor, and gaining women's right to vote. It outlines economic reforms under Presidents Theodore Roosevelt, William Howard Taft, and Woodrow Wilson including trustbusting and the Federal Reserve Act. The document also discusses muckrakers, political reforms like women's suffrage and direct election of senators, and social reforms such as settlement houses.