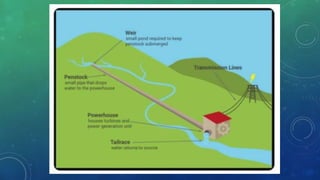
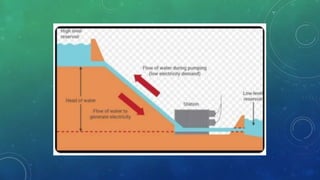
There are three main types of hydroelectric power plants: impoundment, diversion, and pumped storage. Impoundment plants require reservoirs and control water release through dams and turbines. Diversion plants divert river portions through pipes to powerhouses, then return water to the river. Pumped storage plants operate like batteries by pumping water between upper and lower reservoirs. Hydroelectric energy provides renewable power but can impact habitats, migration, and livelihoods if not properly managed.