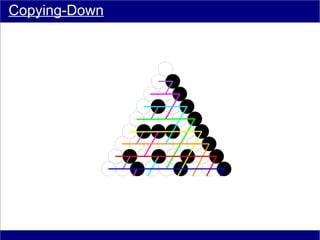
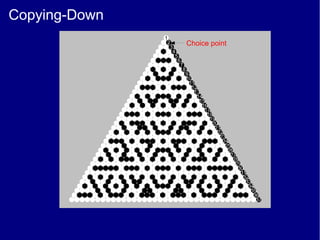
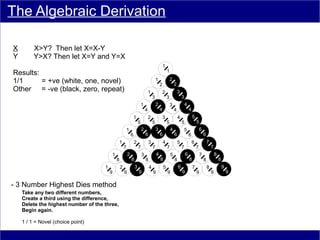
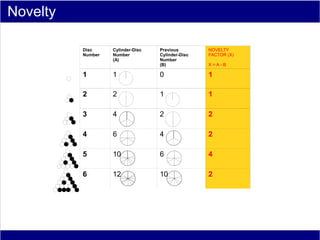
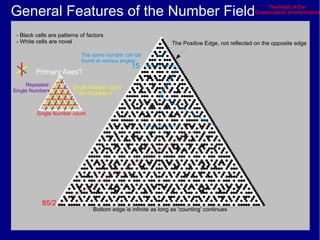
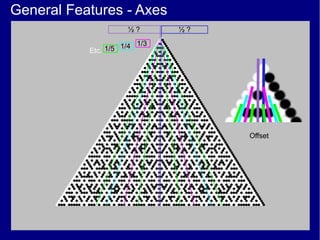
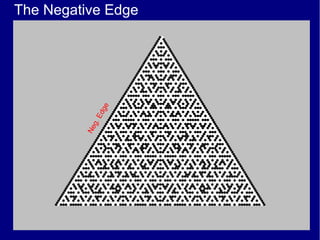
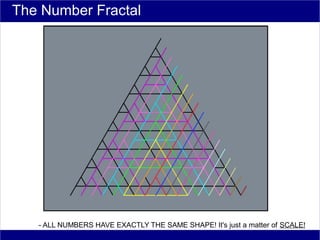
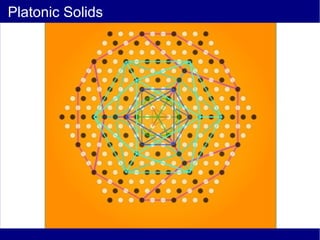
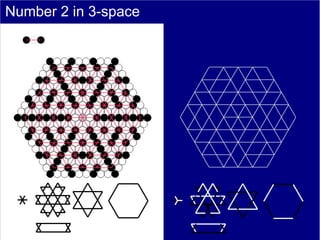
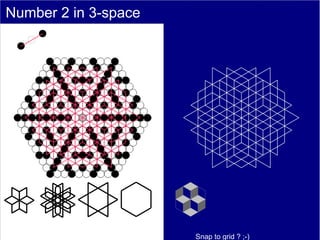
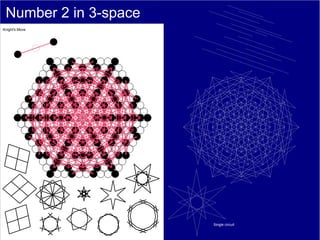
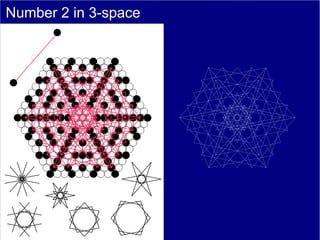
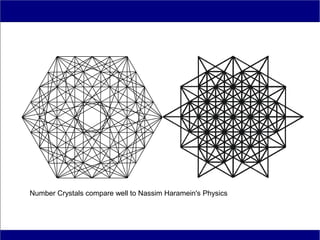
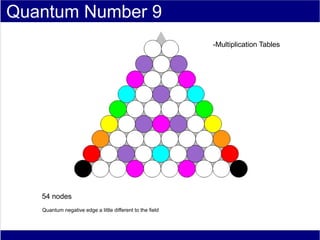
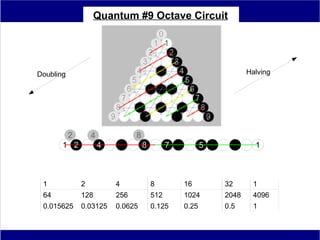
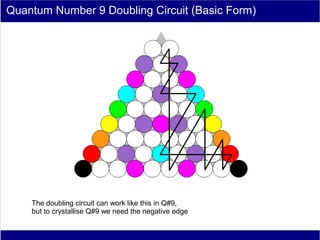
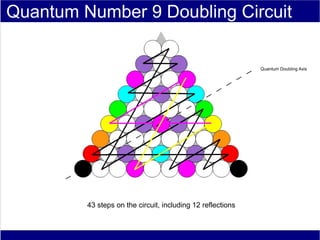
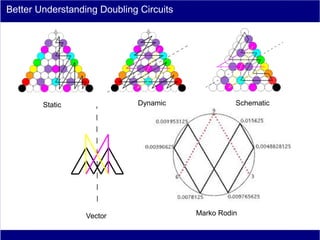
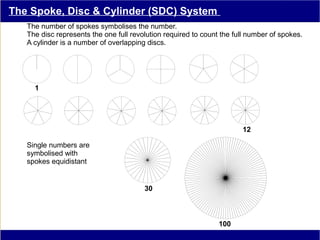
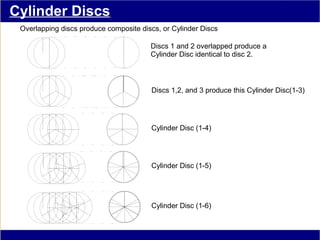
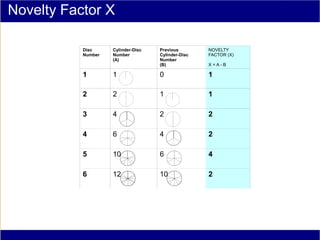
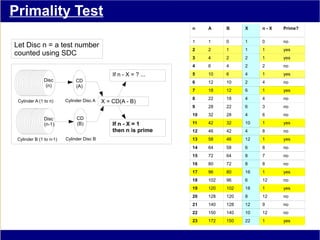
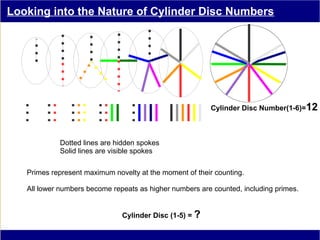
This document discusses various methods of counting and deriving number fields. It begins by describing dot-row counting, pyramid counting, and triangular numbers. It then discusses different methods for deriving the number field, including the copy-down method, coat-hanger method, and algebraic method. The document goes on to describe features of the number field such as conservation of information, negative edges, and applications. It concludes that correct counting involves distinguishing novel from repeated information, and basic exploration of these concepts yields insights into the nature of number fields.