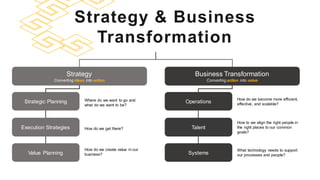
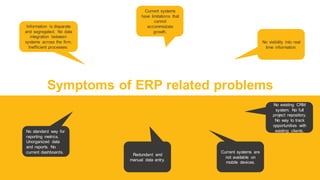
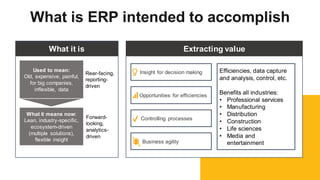
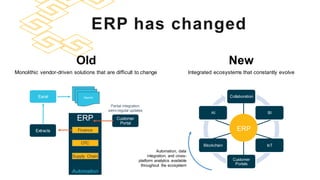
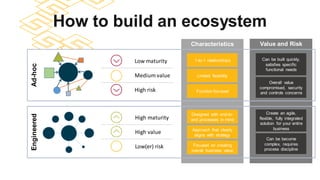
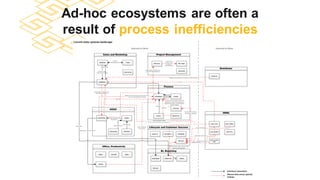
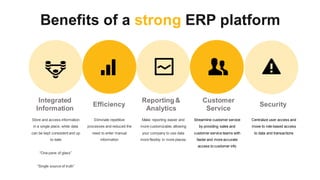
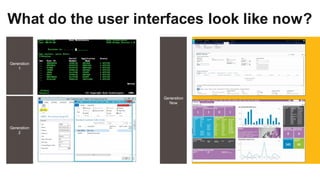
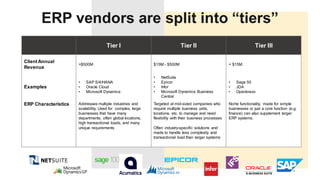
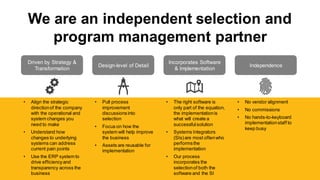
The document discusses the modern ERP landscape, highlighting the importance of identifying ERP-related problems, the value of ERP systems, and strategies for successful implementation. It outlines symptoms of ERP issues, the evolving nature of ERP solutions towards flexible ecosystems, and key characteristics to consider in ERP systems, including user interface and reporting capabilities. Additionally, it emphasizes the critical role of change management, user experience, and independent program management in achieving effective ERP solutions.