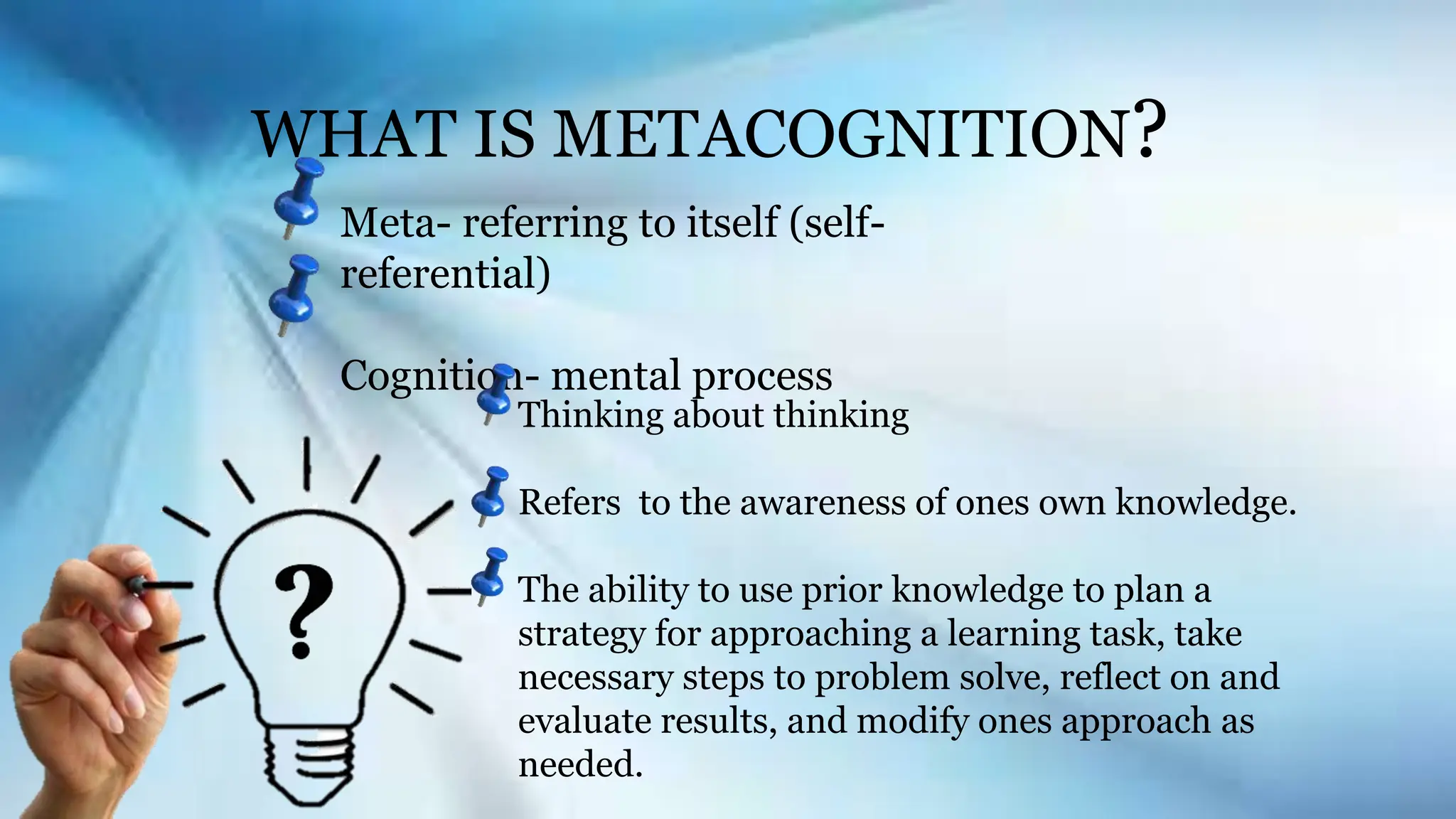
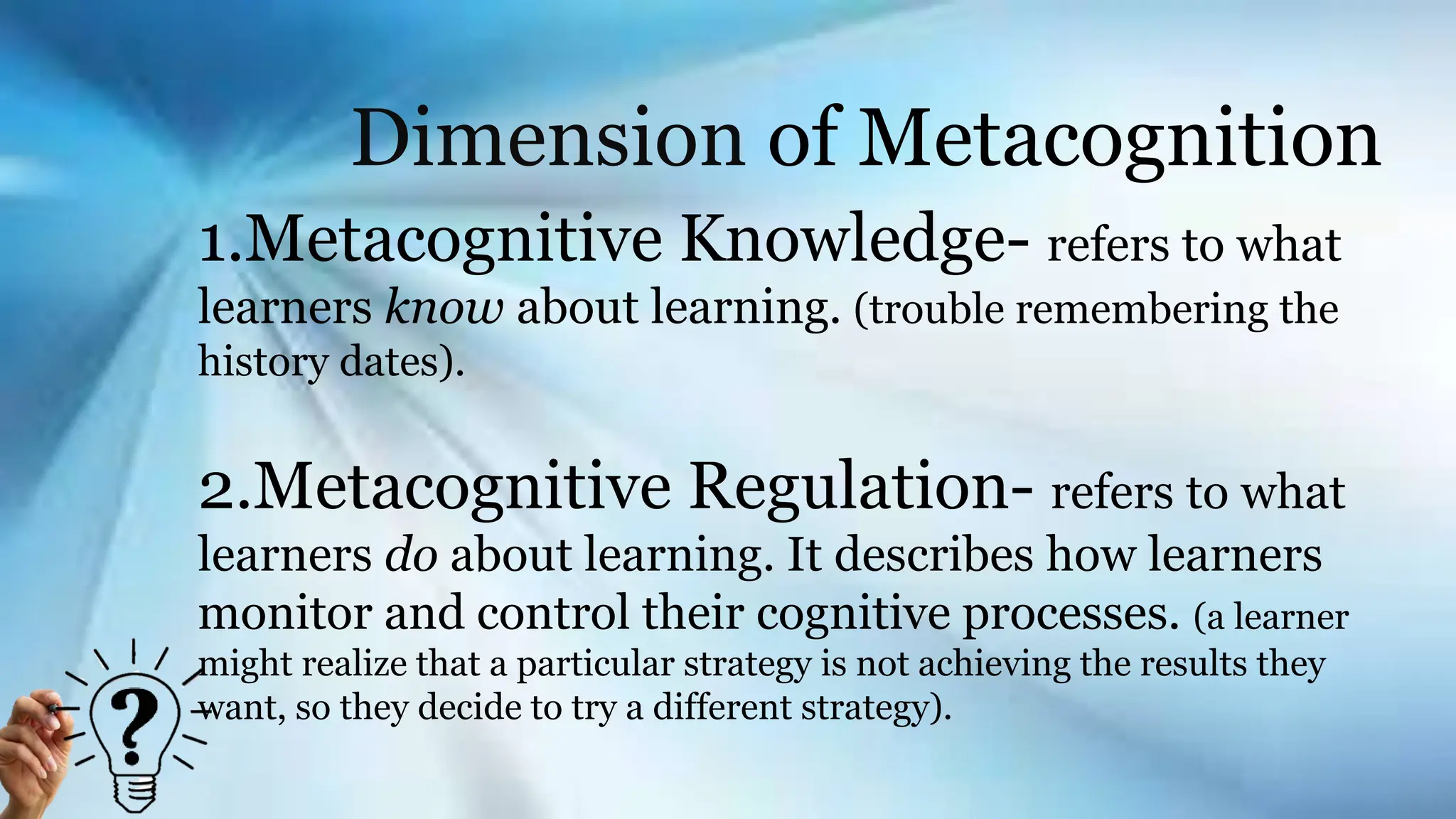
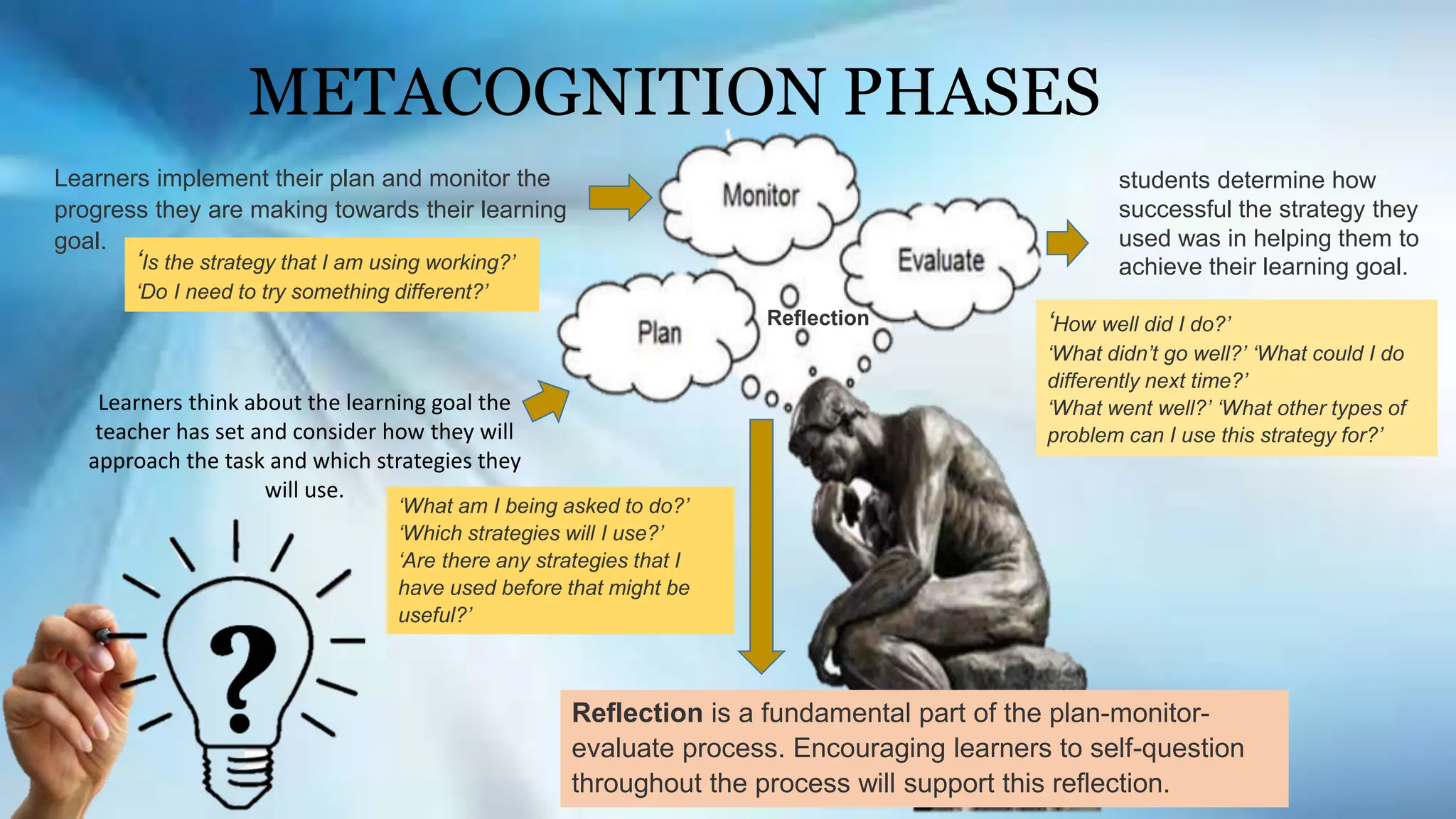
John Flavell, an influential psychologist, coined the term metacognition, which encompasses both metacognitive knowledge and experiences. Metacognition involves learners' awareness of their thought processes and their ability to regulate their learning strategies, encouraging self-reflection and improvement. The practice has significant benefits, aiding students in becoming independent learners and enhancing their overall educational outcomes.