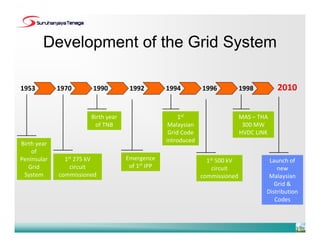
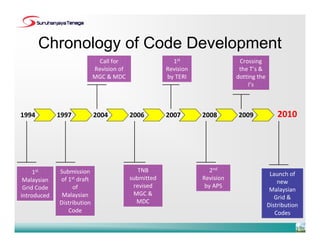
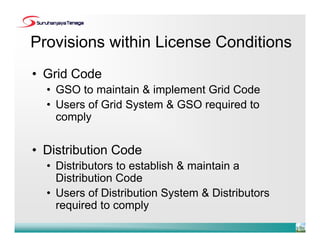
The document provides an overview of the new Malaysian Grid Code and Distribution Code. It summarizes the development of the grid system in Malaysia and the chronology of code development. The key points are:
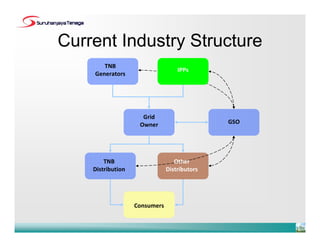
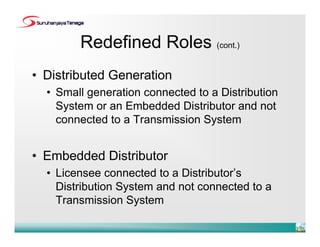
- The new codes have been developed to align with the current industry structure and practices, with clearer separation of roles and more participation from independent power producers and distributed generators.
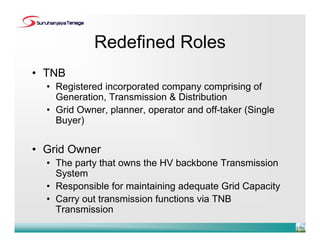
- The roles of the Grid Owner, Grid System Operator and Single Buyer have been redefined under the new TNB corporate structure.
- An independent Grid Code Committee and Distribution Code Committee have been established to oversee the implementation of the codes.
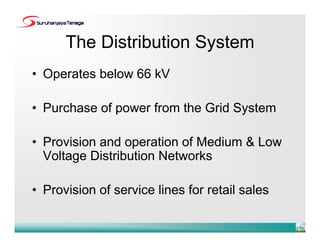
- The Distribution Code sets principles for relationships between parties involved in distribution systems for the first