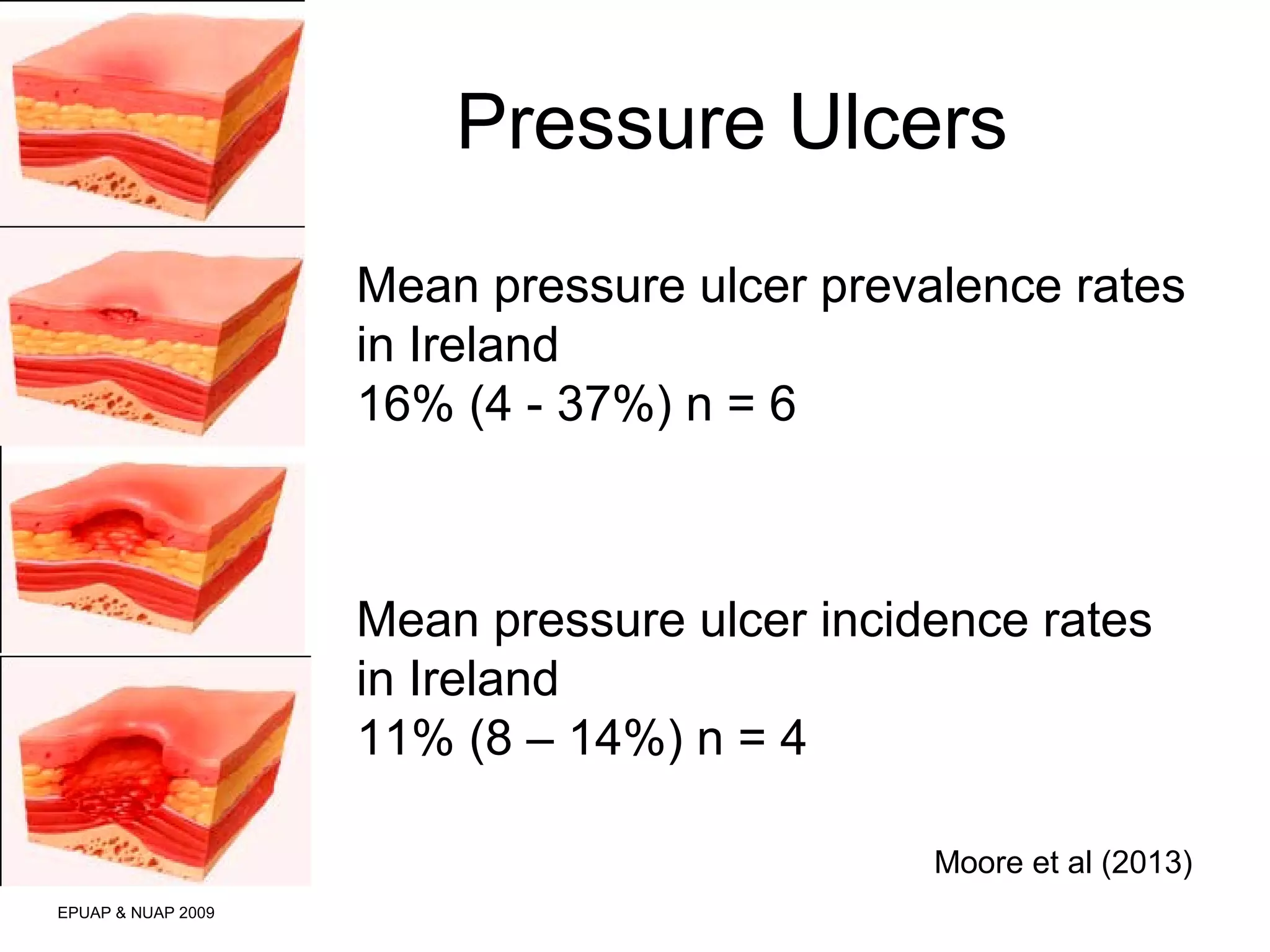
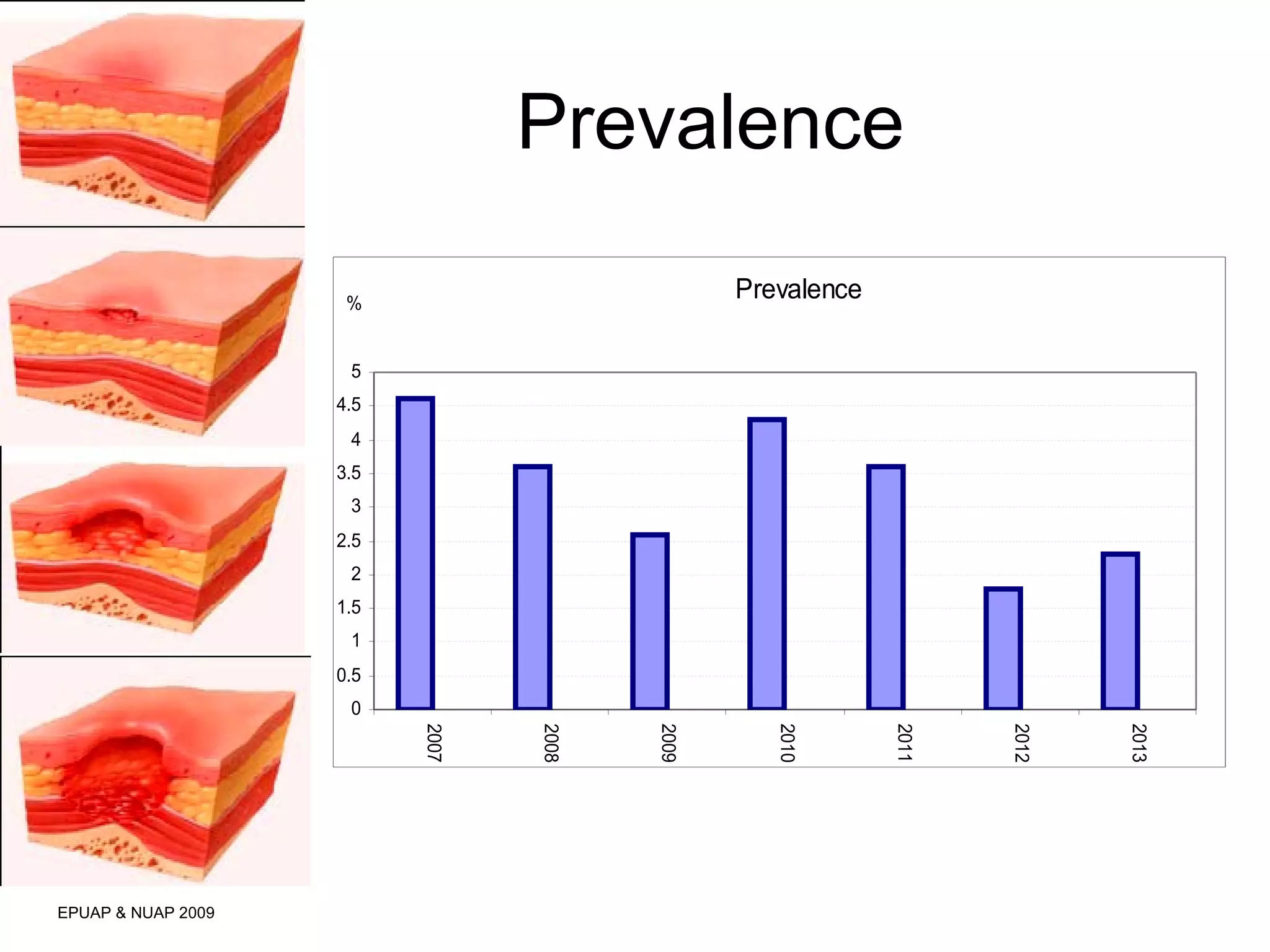
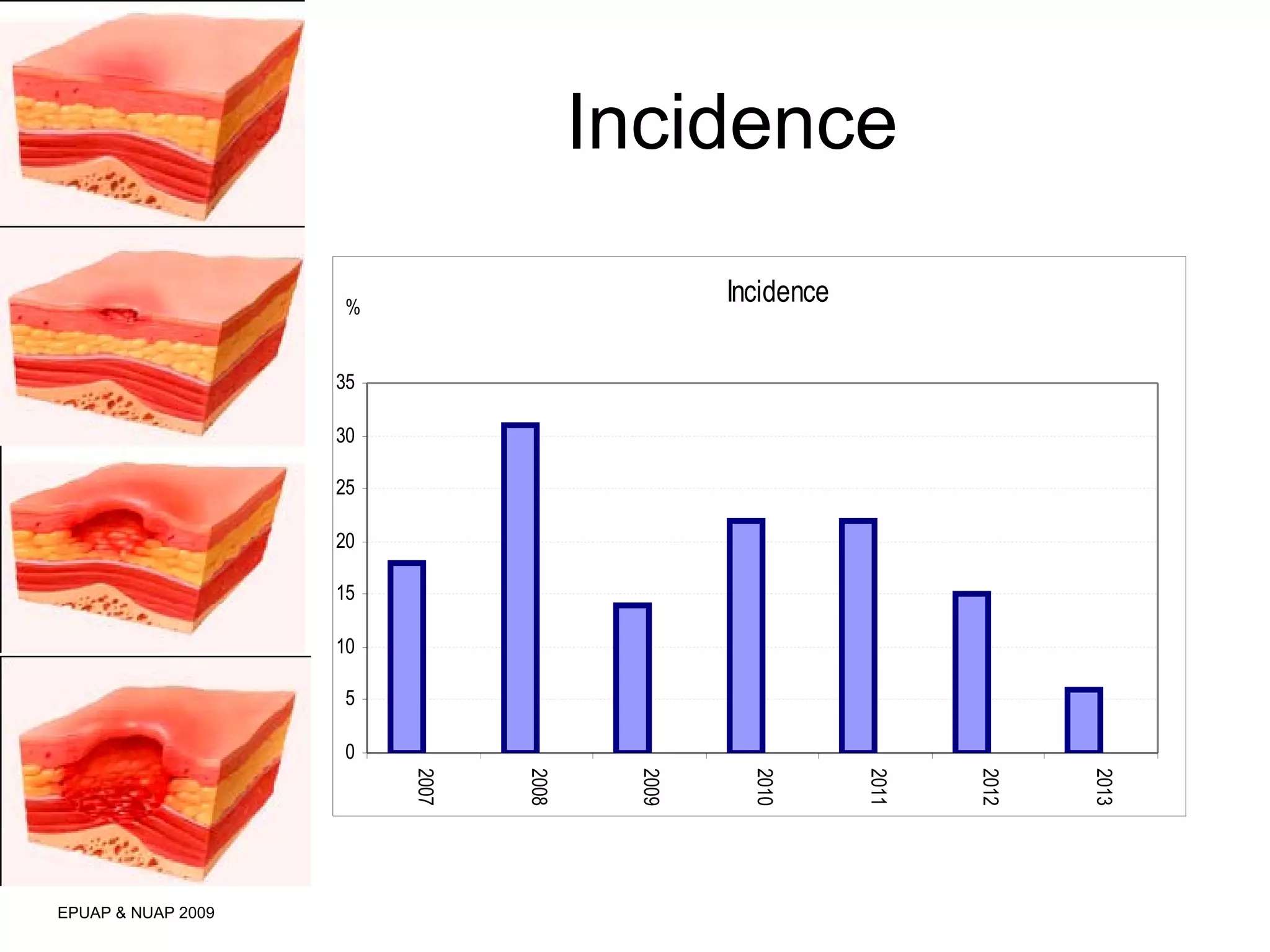
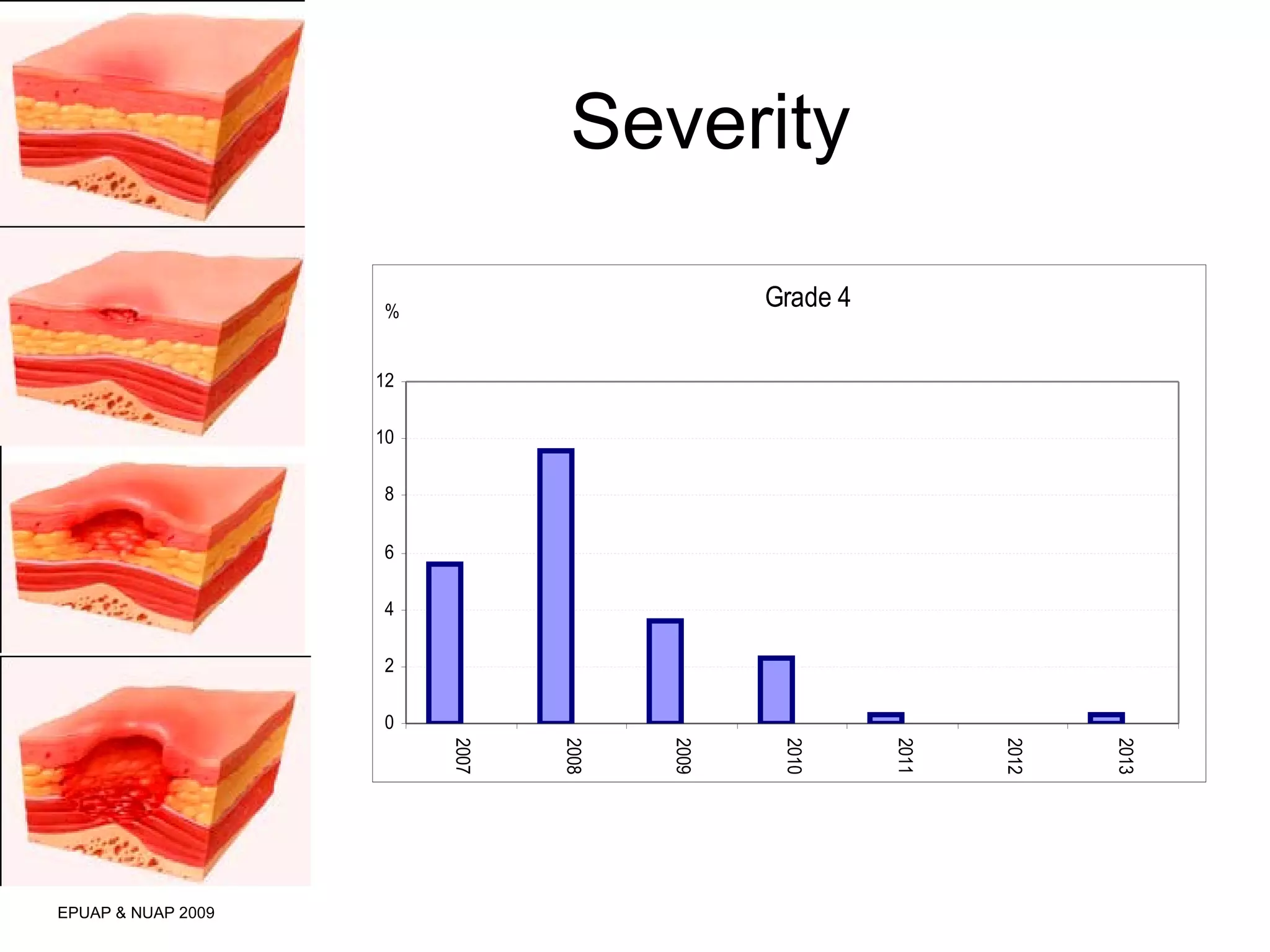
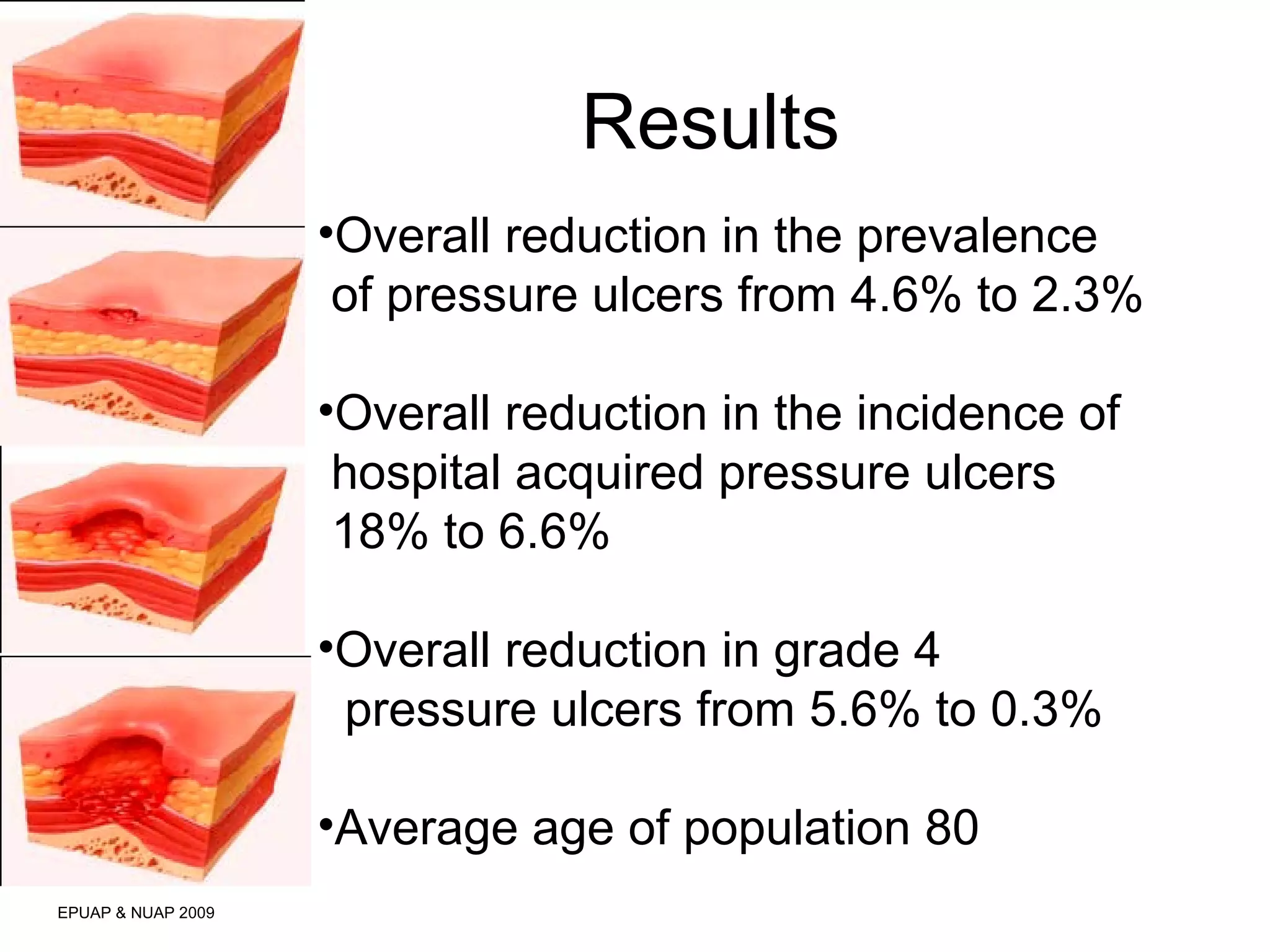
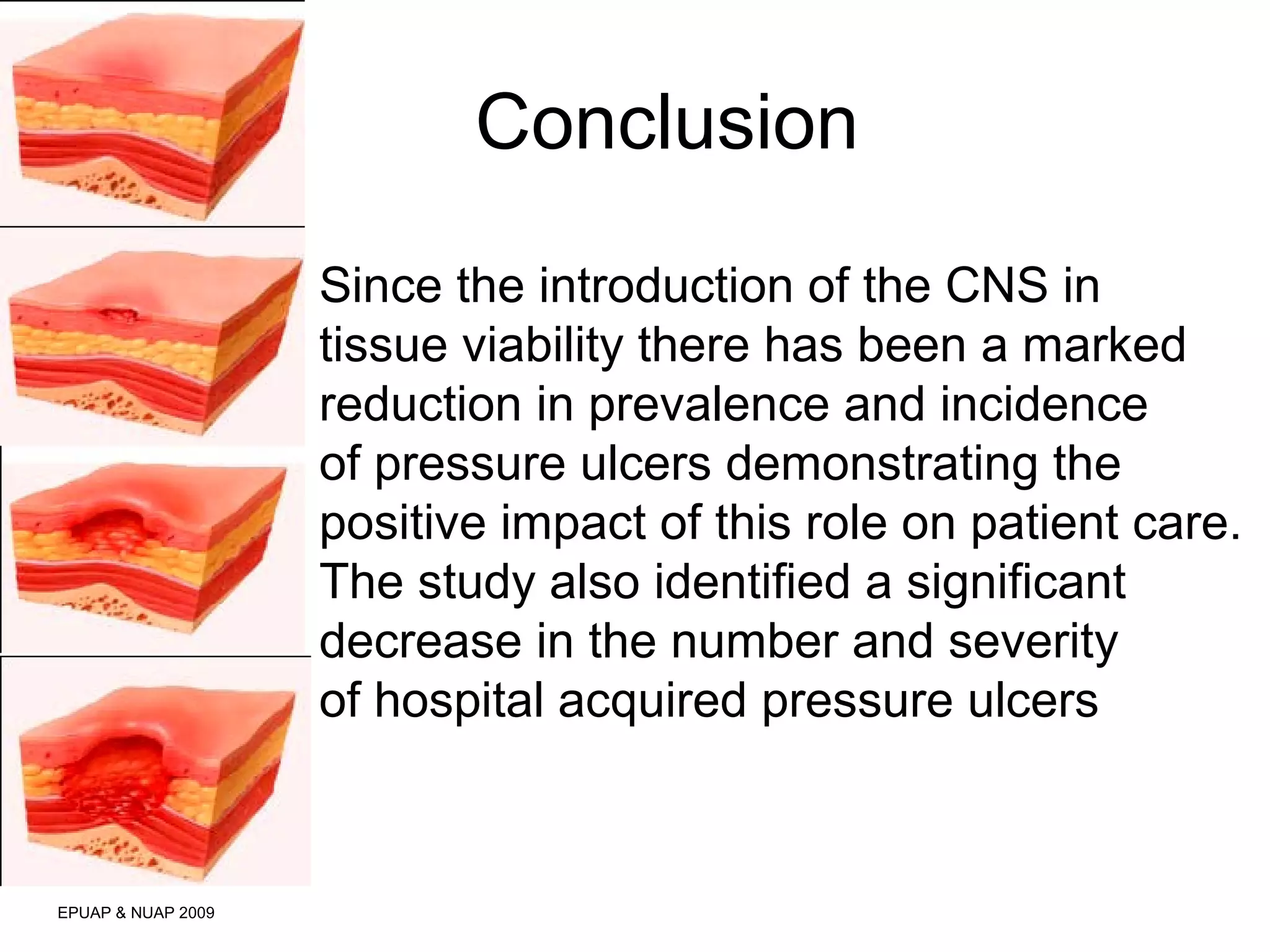
The document discusses the impact of a clinical nurse specialist (CNS) in tissue viability on reducing pressure ulcers in older adult care settings. It finds that since introducing the CNS role, there has been a marked reduction in pressure ulcer prevalence from 4.6% to 2.3%, incidence from 18% to 6.6%, and grade 4 ulcers from 5.6% to 0.3%. The CNS role focuses on education, motivation, monitoring prevalence and incidence, collaboration, risk assessment, empowering staff, and has led to improved patient outcomes in pressure ulcer prevention.