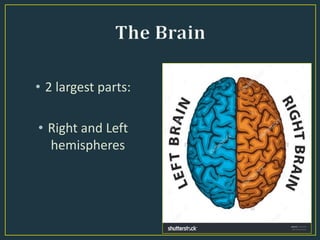
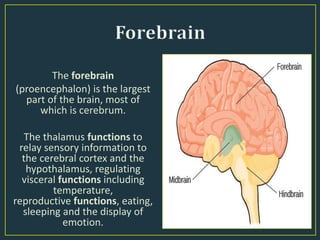
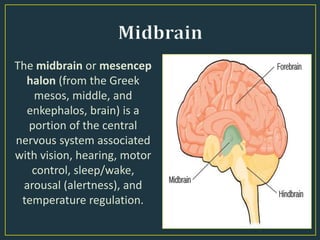
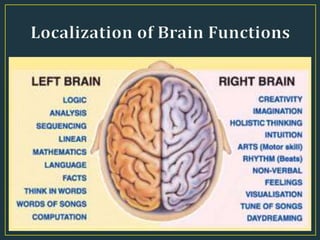
The document summarizes key aspects of the human brain. It discusses the basic structure and functions of the brain, including its size relative to body size, weight, and composition. It describes the major parts of the brain - the cerebrum, right and left hemispheres, and three principal sections: hindbrain, midbrain, and forebrain. It also discusses different types of thinking, including abstract, analytical, creative, concrete, critical, convergent, and divergent thinking.