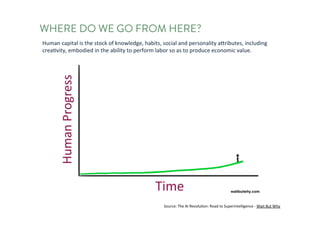
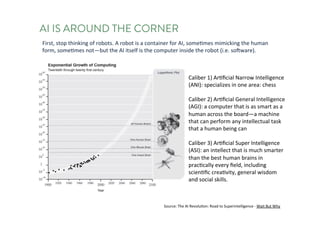
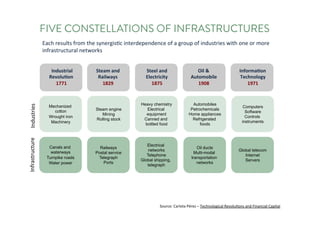
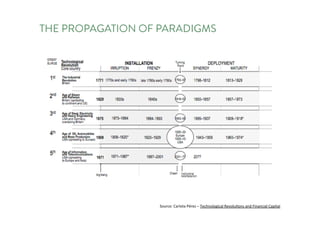
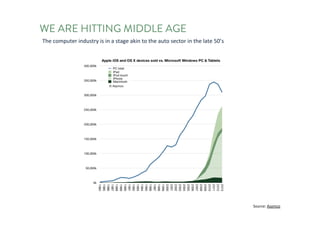
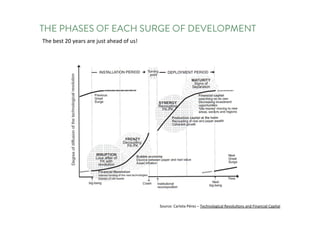
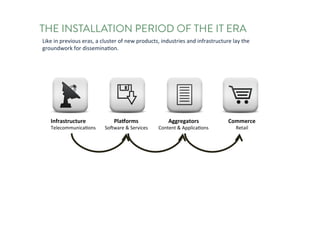
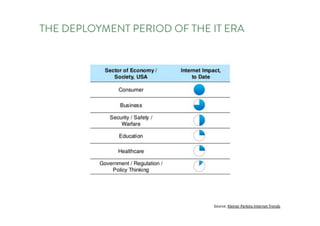
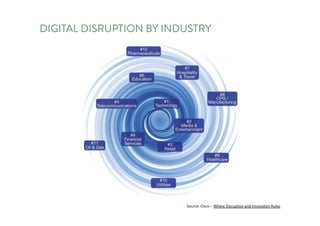
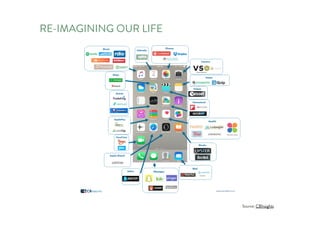
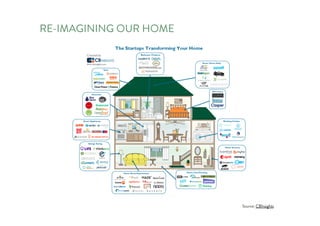
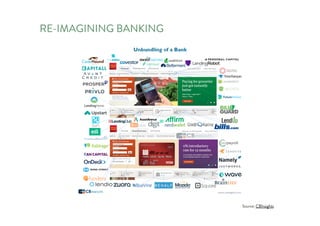
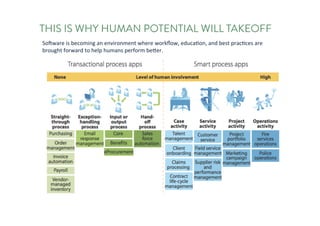
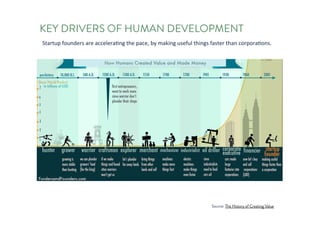
The document discusses the future of human potential, highlighting significant economic opportunities over the next two decades driven by technology and entrepreneurship. It outlines the evolution of artificial intelligence and its implications for human productivity and organizational management. The author asserts that all companies will become technology-driven, emphasizing the critical role of startup founders in accelerating innovation and human capability.