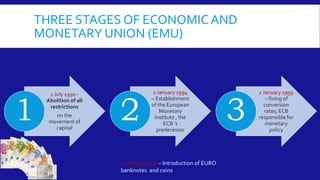
The document summarizes the history and progress of European integration, from the initial European Coal and Steel Community in 1952 to the establishment of the European Union with the Maastricht Treaty in 1993. It describes the enlargement of the EU to include additional countries over time. It also outlines the three stages of establishing the Economic and Monetary Union, including adopting the euro as a common currency, and the criteria for countries to join the eurozone. Finally, it discusses benefits of the euro like price transparency and elimination of exchange rate risk, as well as increased financial integration within the euro area.