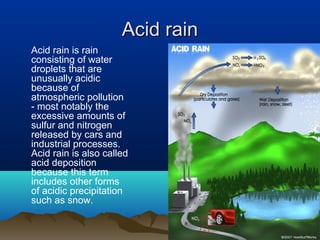
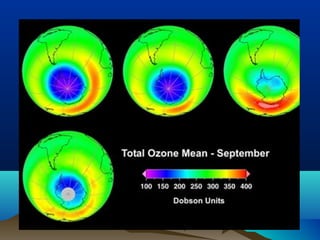
The document discusses several major environmental problems: global deforestation is reducing forests and damaging land, acid rain from pollution is harming forests, soils and buildings, species extinction is occurring due to habitat loss and poaching, and ozone depletion is increasing UV radiation and harming human health, plants and animals. Deforestation has negative effects including reducing habitats and absorbing greenhouse gases. Acid rain damages soils, forests and structures. Species extinction is driven by habitat loss, poaching, wildlife trade and climate change. Ozone depletion causes increased UV radiation which harms humans, plants and animals.