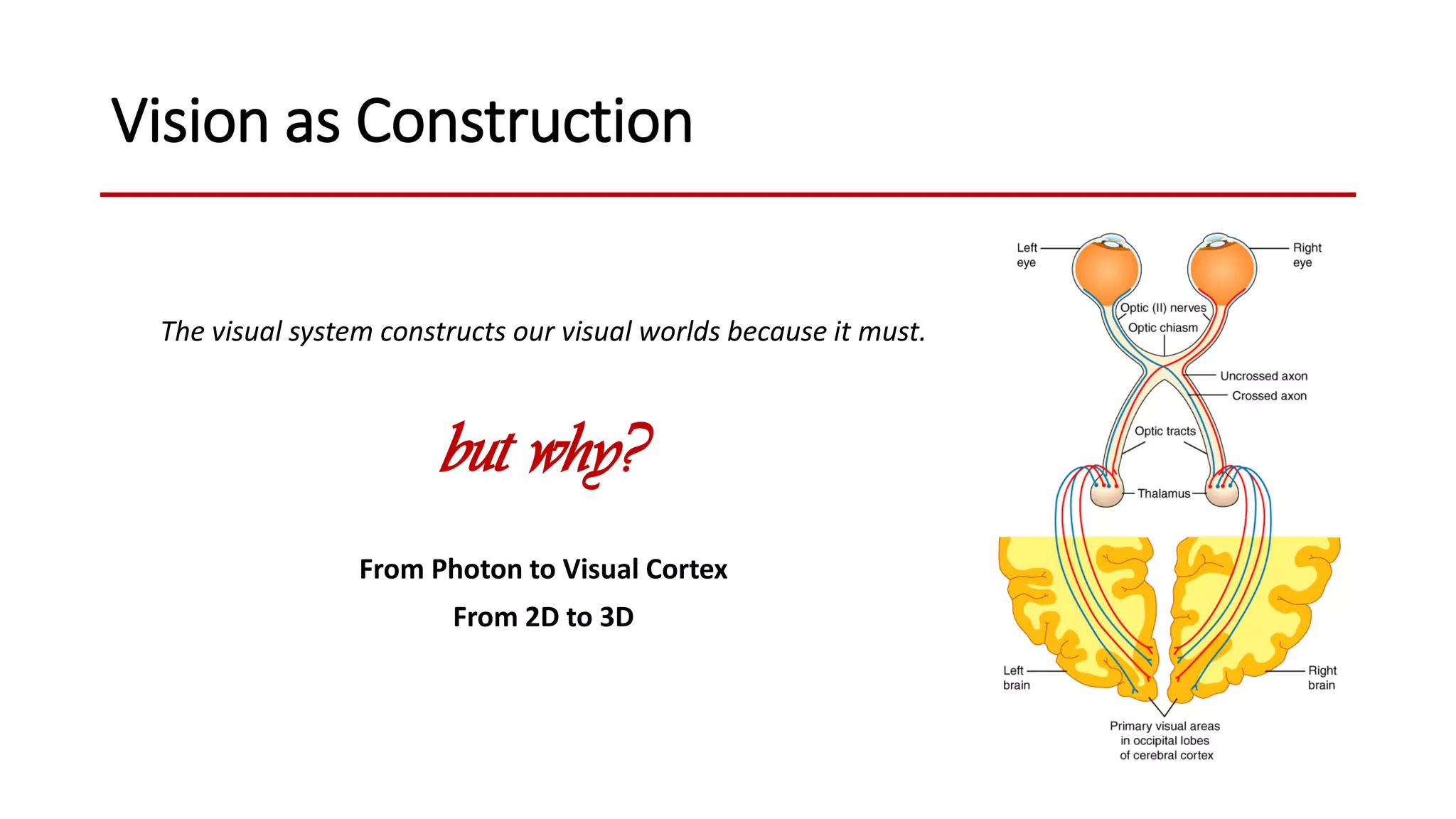
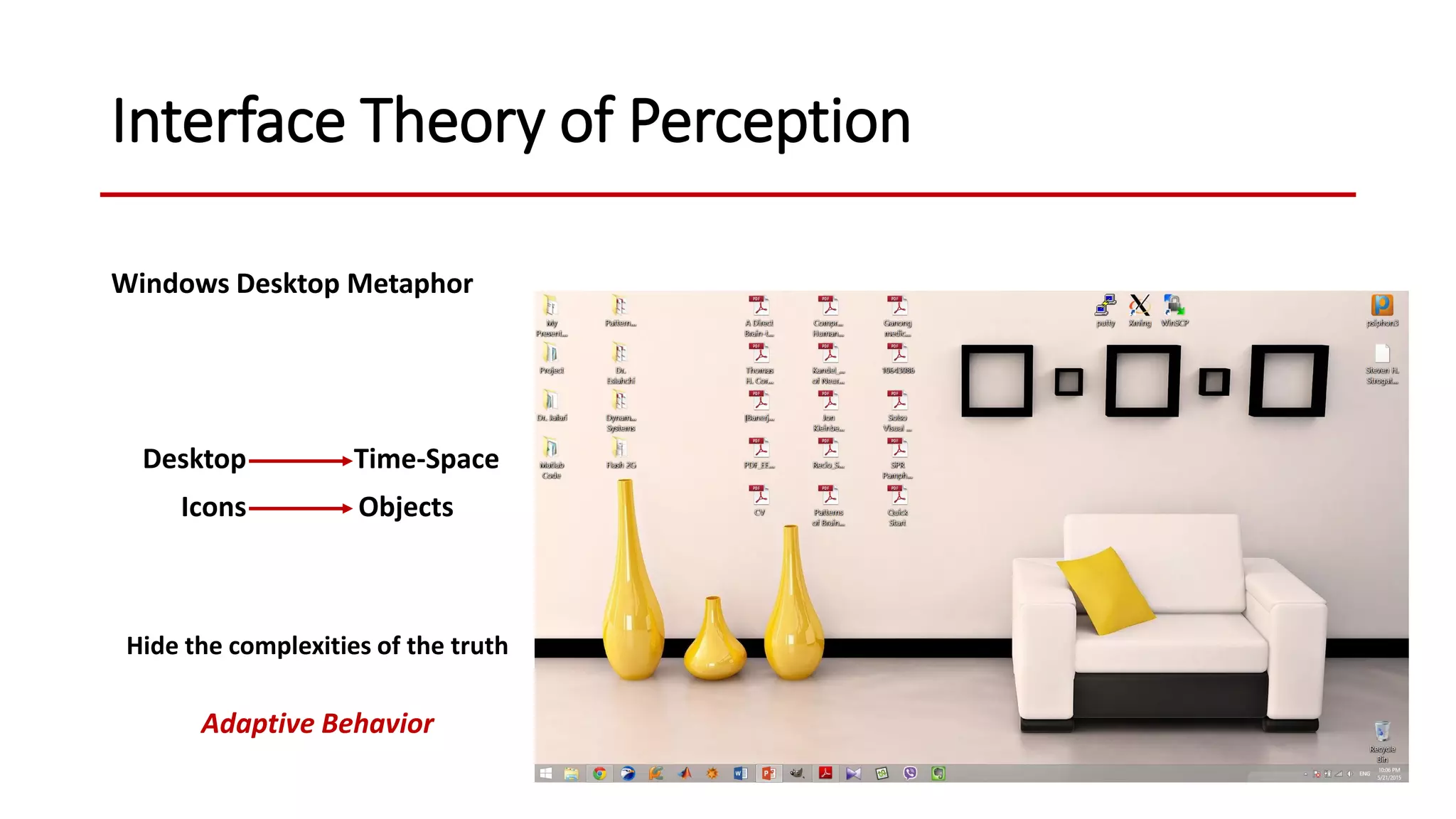
The document discusses the construction of visual reality from several perspectives. It begins with a brief review of the contents of a book on hallucinations. It then discusses visual illusions, explaining that they are incorrect perceptions experienced by most people in specific contexts. The document proposes that vision involves construction rather than passively receiving information, and evolution favors perceptions that guide adaptive behavior over strictly veridical perceptions. It provides examples of biological visual systems that construct reality for utility rather than truth. Finally, it proposes a new theory defining illusions as common non-adaptive perceptions and hallucinations as rare context-less non-adaptive perceptions.