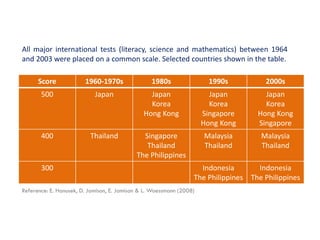
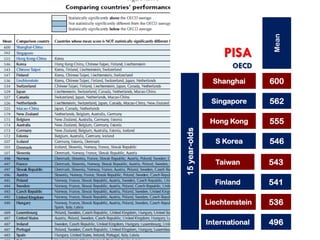
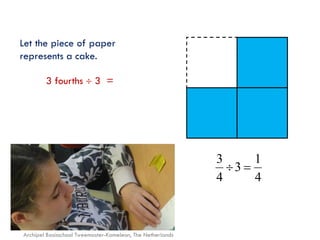
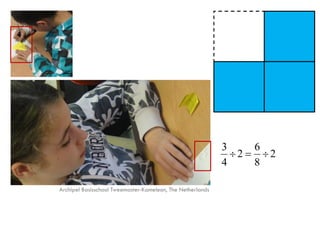
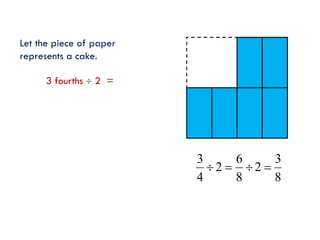
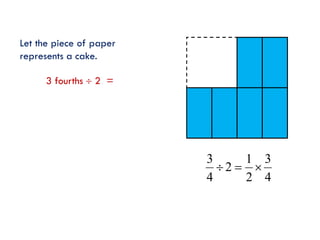
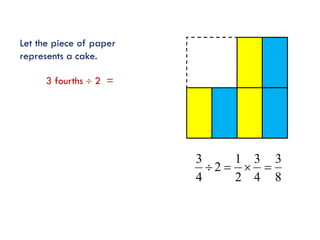
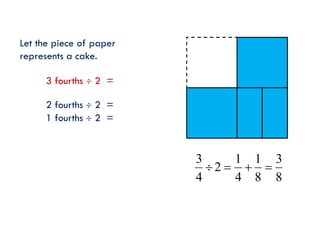
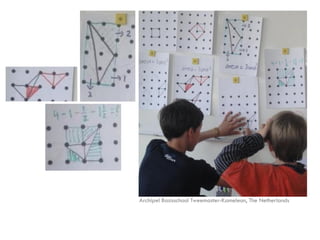
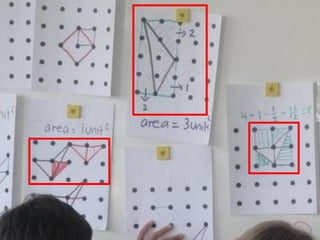
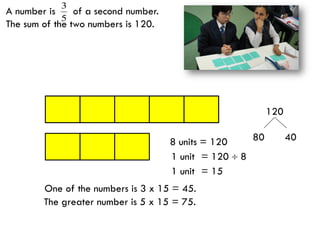
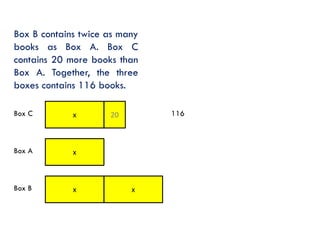
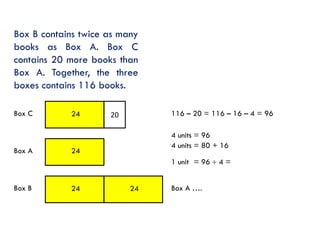
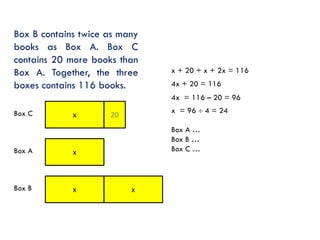
The document is a slide presentation on mathematics learning in Singapore given by Yeap Ban Har from the Marshall Cavendish Institute in Singapore. It discusses Singapore's history of improving mathematics education over time, from achieving low passing rates on early exams to consistently high performance on international tests. It also describes Singapore's focus on visual and concrete learning approaches, as well as the country's emphasis on developing intellectual competence through mathematics.