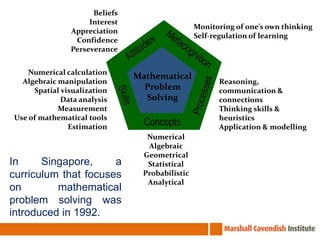
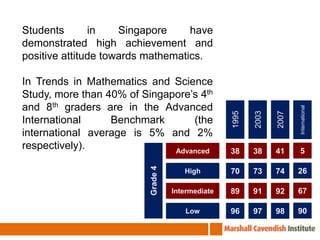
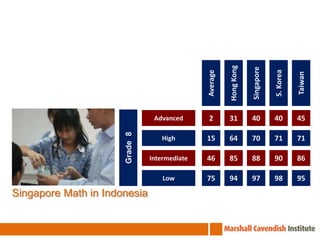
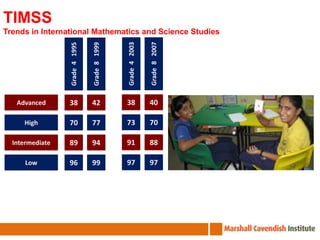
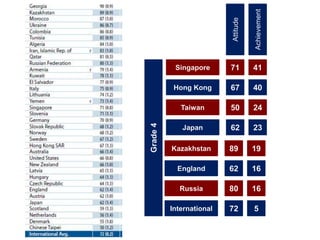
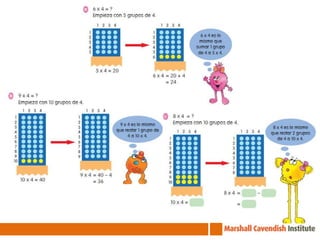
The seminar on Singapore Math in Chile focuses on effective mathematics teaching and learning strategies, especially for average and struggling learners. It emphasizes problem-solving and the development of critical thinking skills within a curriculum introduced in Singapore in 1992, which has led to high student achievement in international assessments. Essential teaching principles include concrete experiences, a spiral approach to revisiting core ideas, and systematic variation of tasks, all aimed at fostering a positive attitude towards mathematics among students.