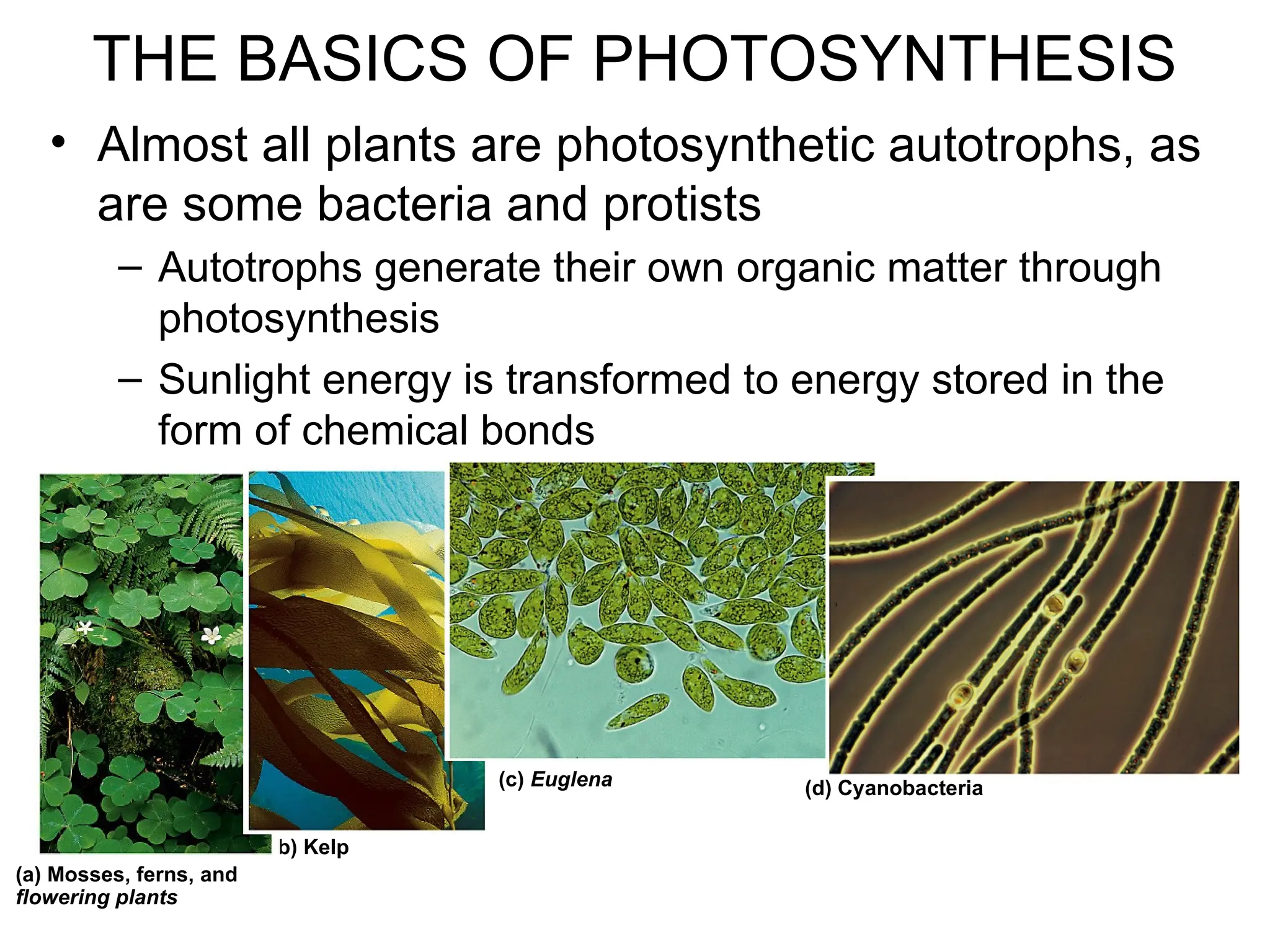
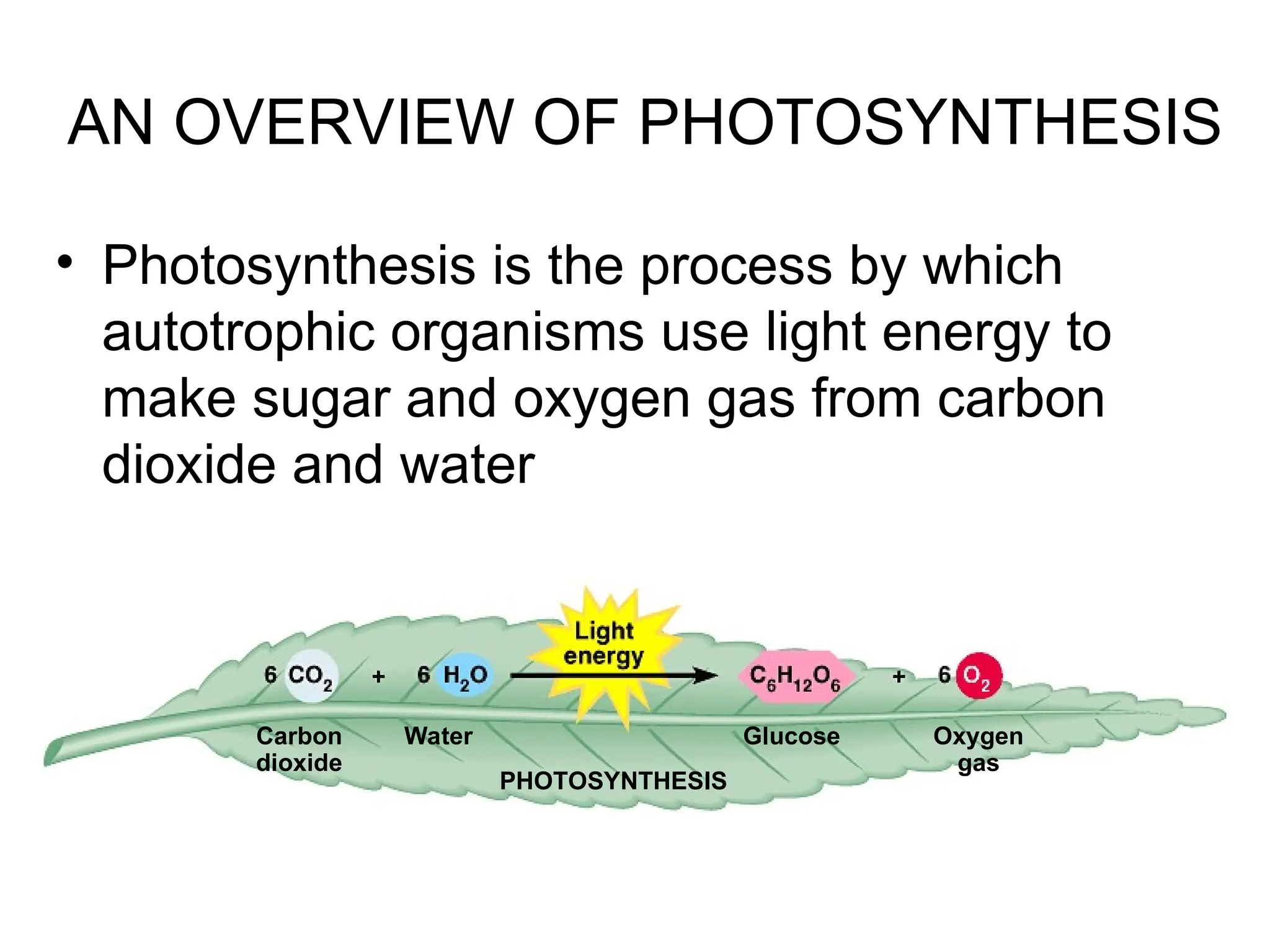
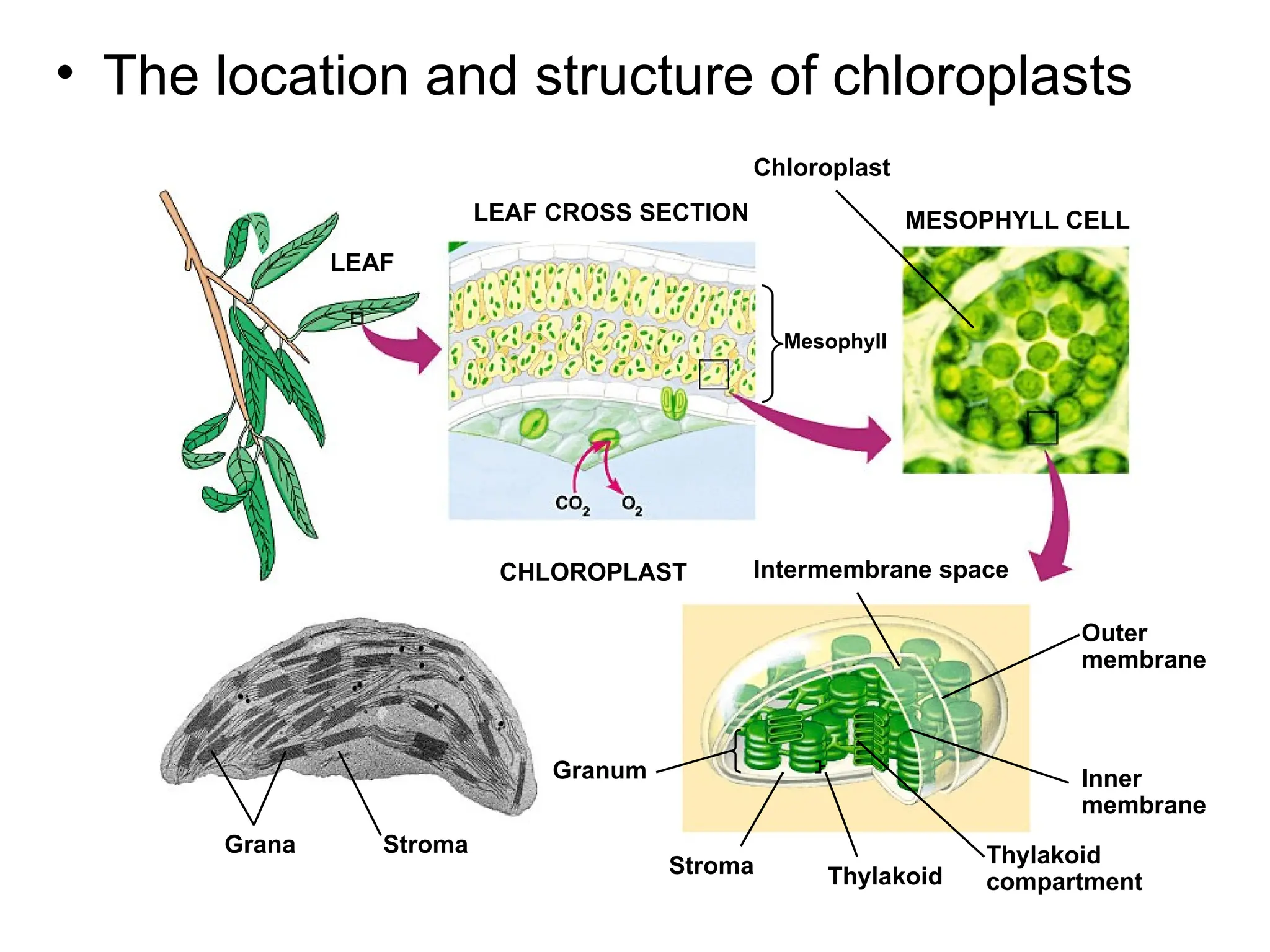
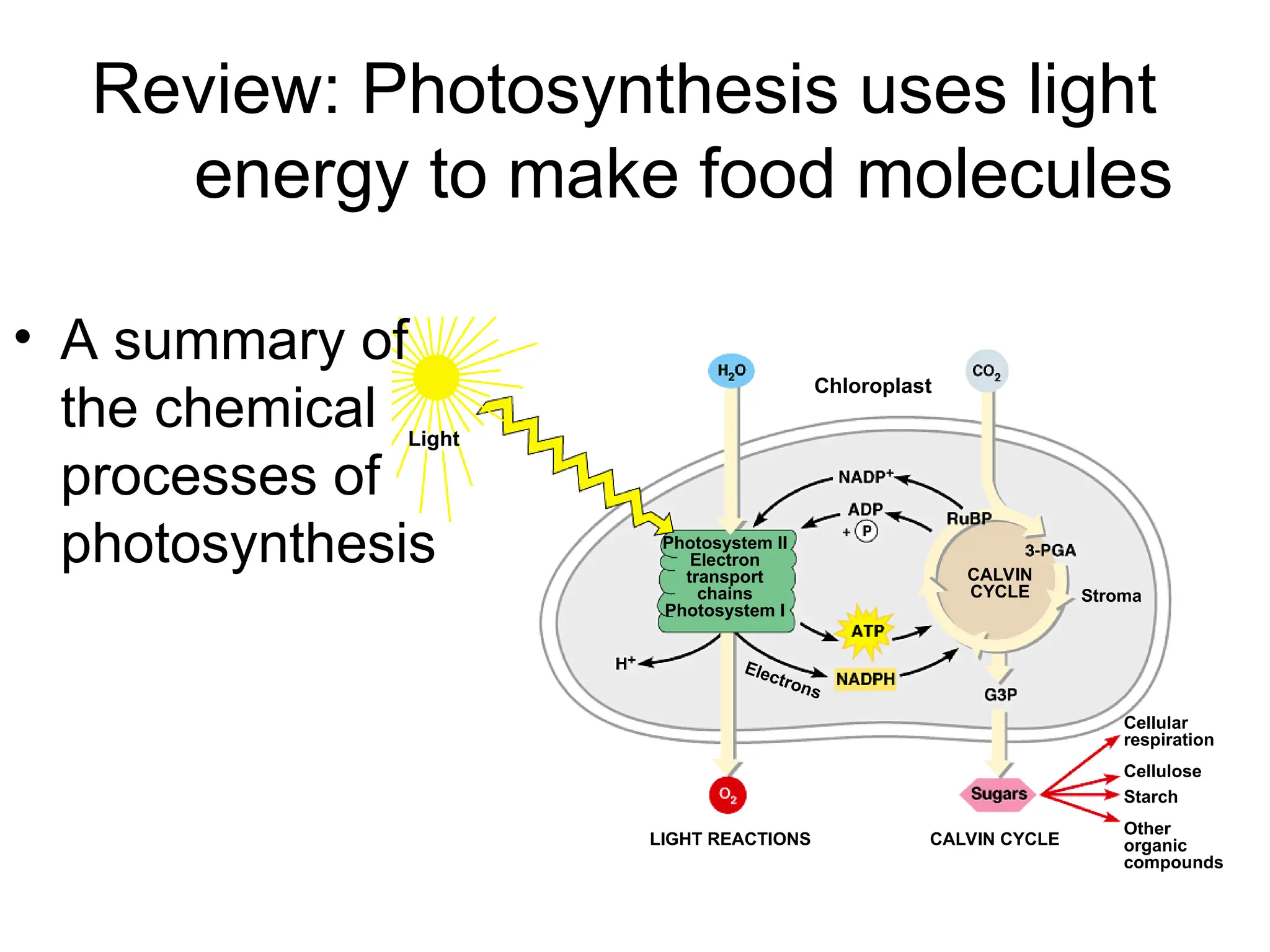
Photosynthesis is the process by which autotrophic organisms, such as plants and certain bacteria, convert light energy into chemical energy, producing glucose and oxygen from carbon dioxide and water. The process consists of light-dependent reactions that generate ATP and NADPH, and the Calvin cycle which synthesizes sugar. Chloroplasts, containing chlorophyll and other pigments, play a crucial role in capturing sunlight for this conversion.