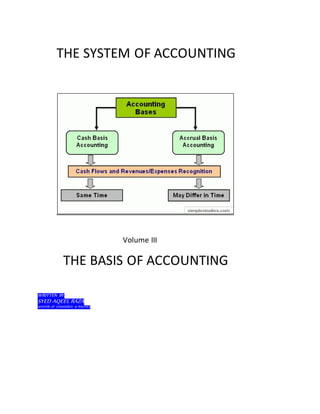
The document outlines the basis of accounting, focusing on cash and accrual methods, detailing their operations, advantages, and drawbacks. It emphasizes the importance of recognizing transactions accurately to present a clear financial picture and discusses methods for bank reconciliation. Additionally, it describes various bank account types, bank transactions, and common discrepancies that occur during reconciliation.