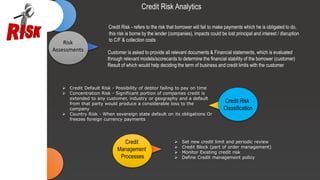
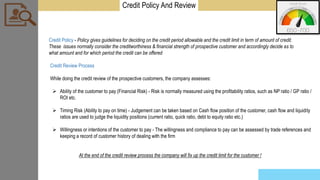
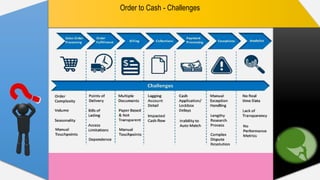
The document provides a comprehensive overview of the Order to Cash (O2C) cycle, detailing key processes such as accounts receivable management, credit risk assessment, sales order processing, and cash application. It outlines the roles and responsibilities of the accounts receivable department, emphasizing the importance of efficient credit management, invoicing, and collections to optimize cash flow and reduce operational costs. Additionally, it discusses various challenges faced in the O2C process and metrics to monitor performance effectively.