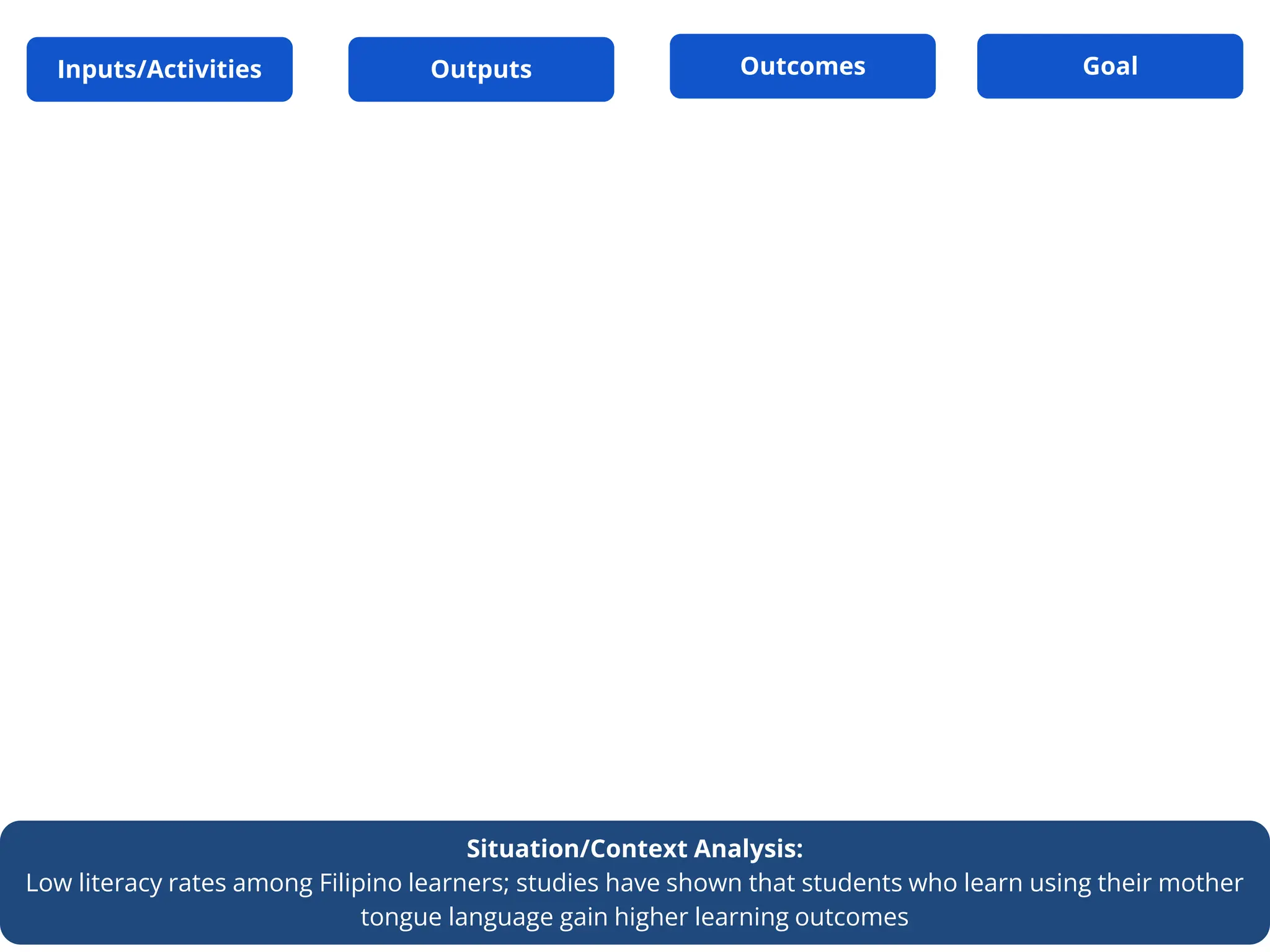
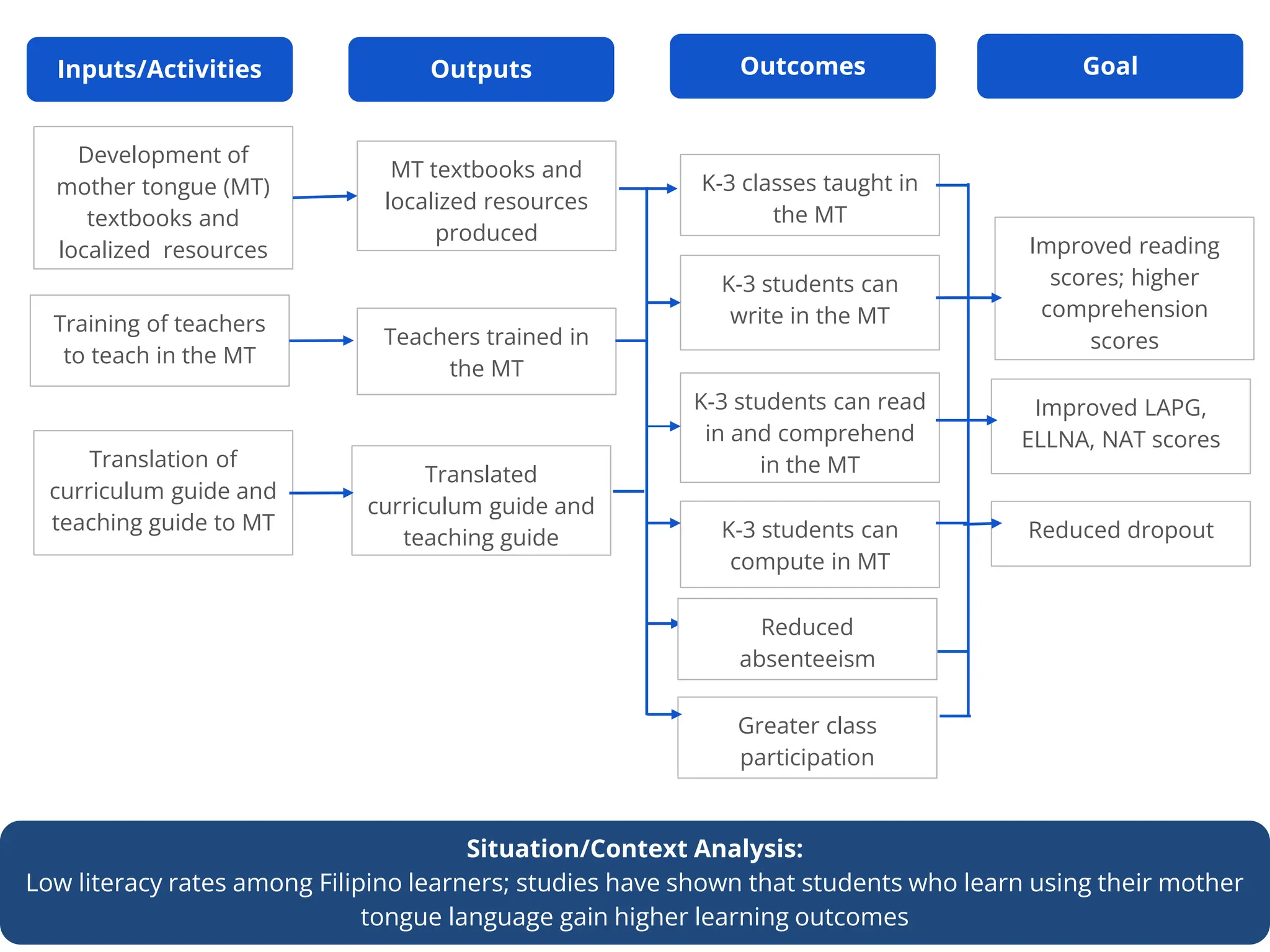
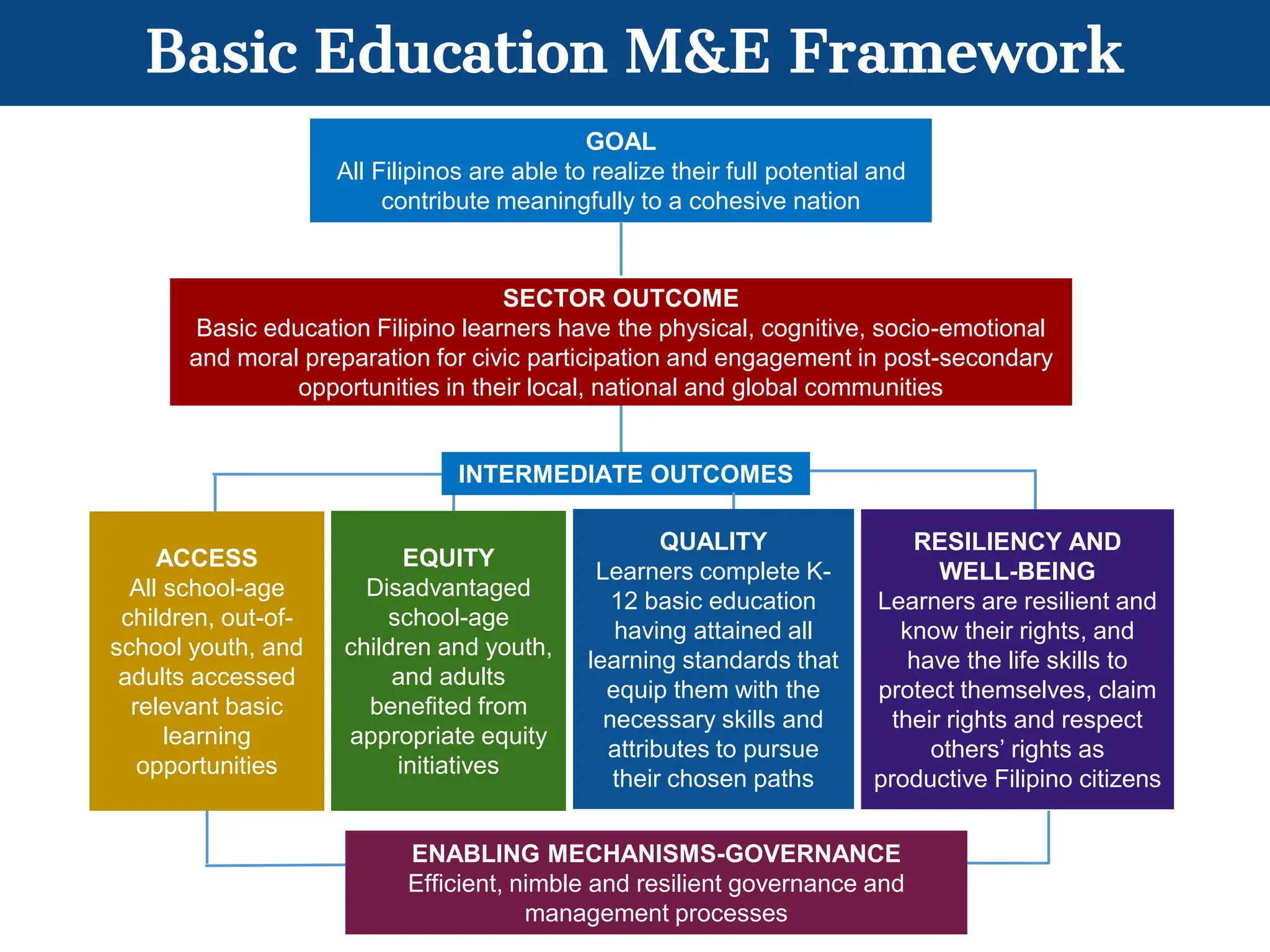
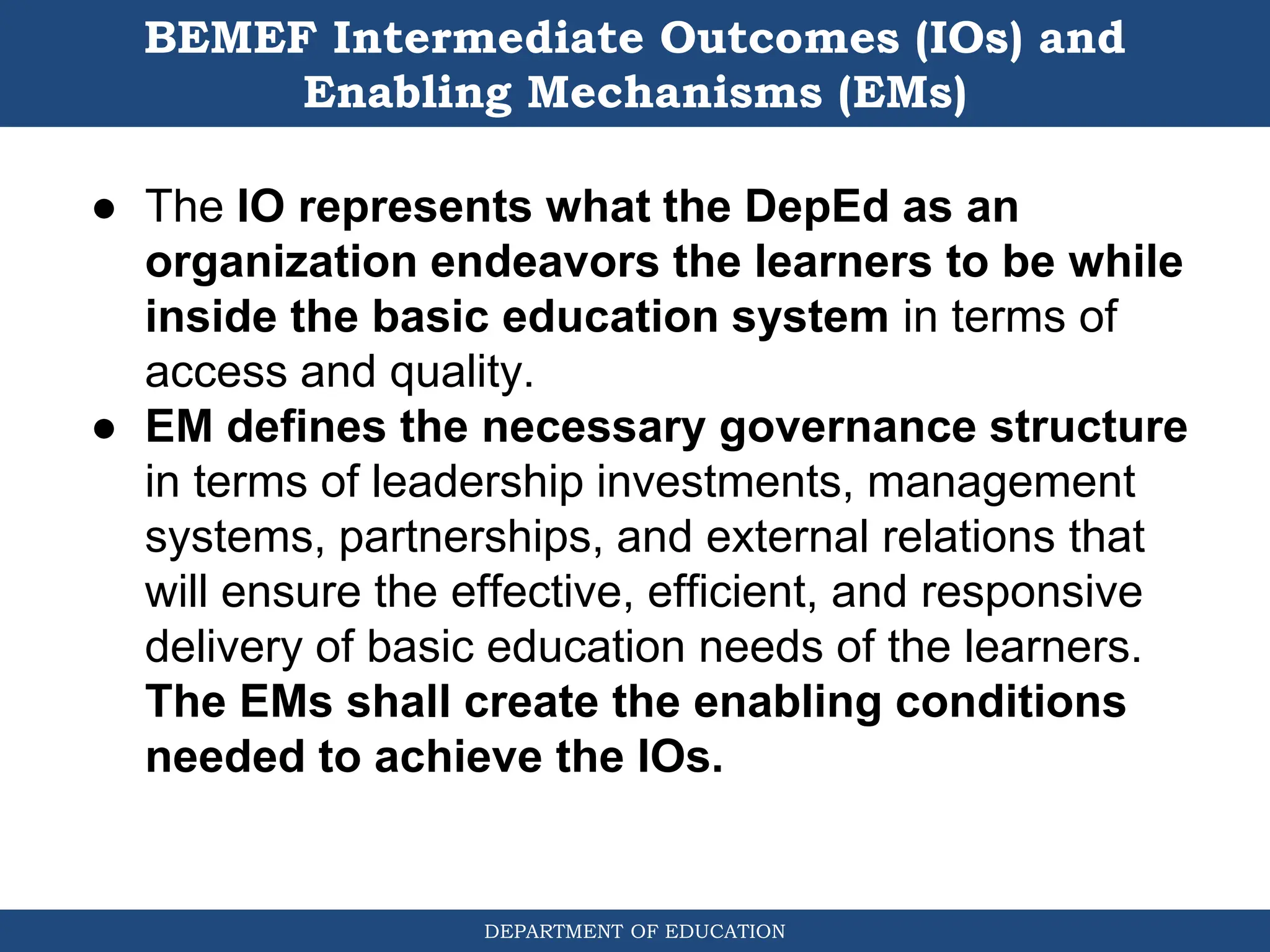
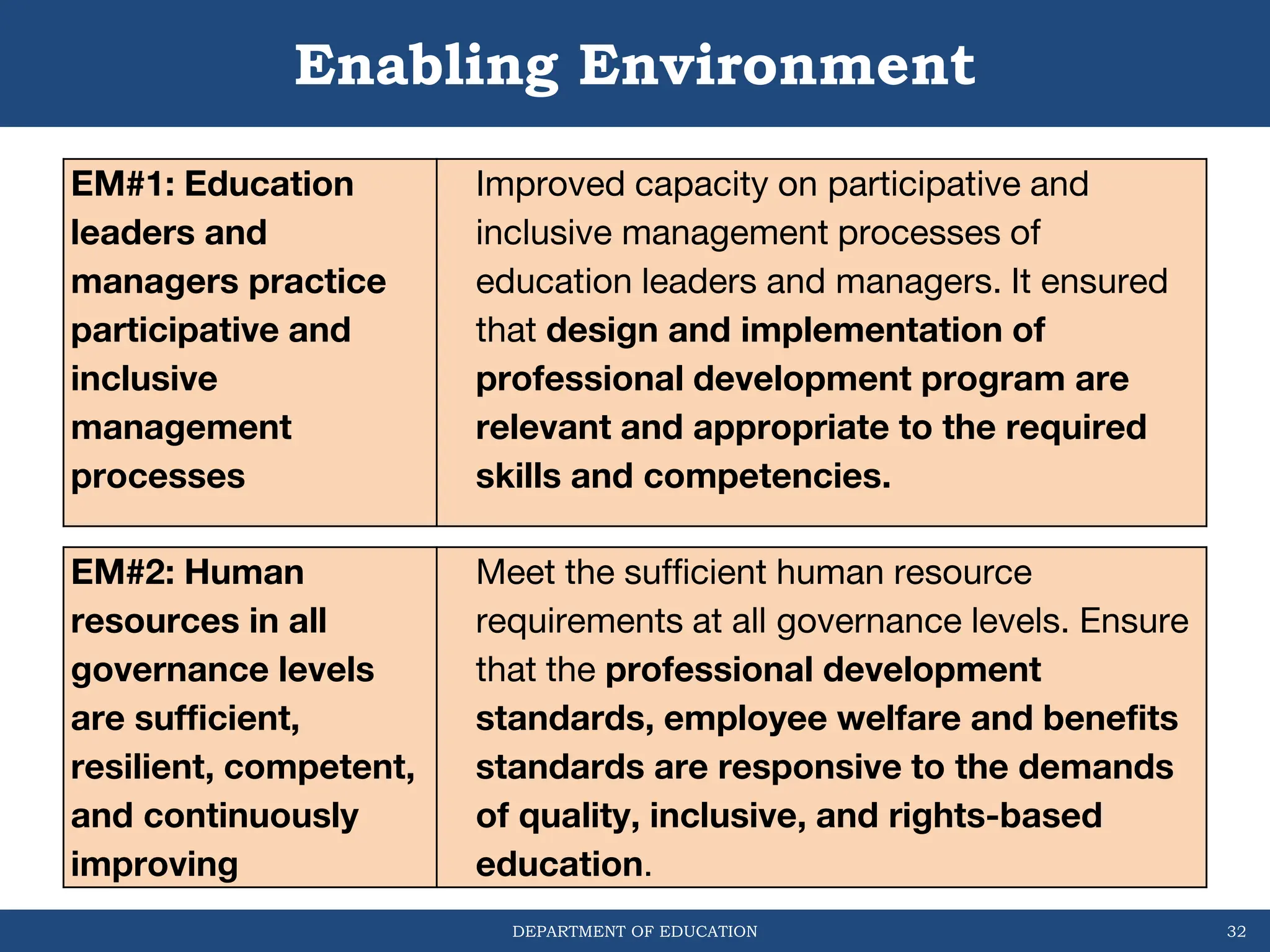
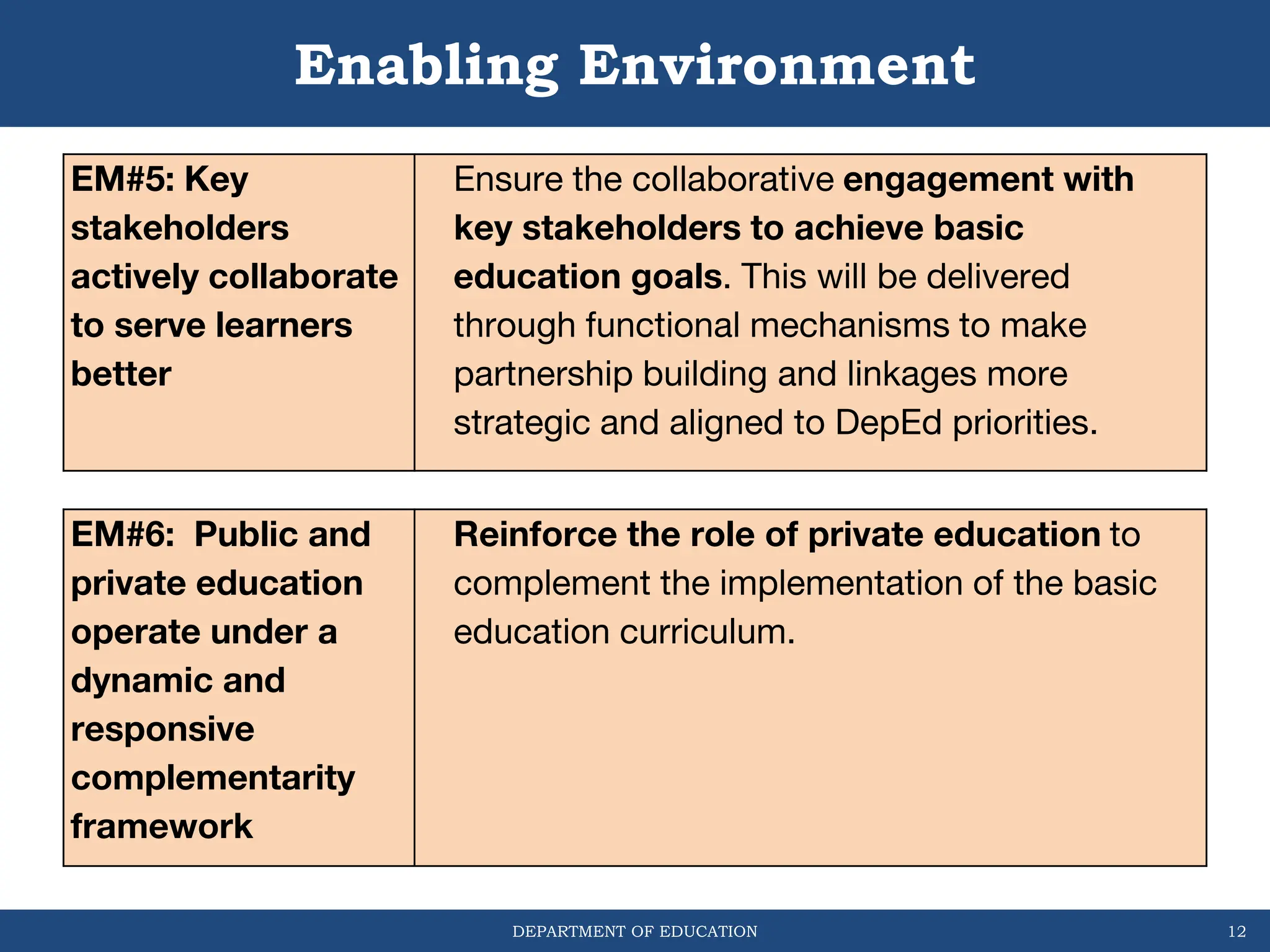
This document outlines the Basic Education Monitoring and Evaluation Framework (BEMEF) established by the Department of Education in the Philippines. It defines the scope, objectives, guiding principles, and key concepts of the BEMEF such as theories of change. The BEMEF identifies intermediate outcomes and enabling mechanisms for basic education and provides examples of performance indicators to track progress. It is intended to guide M&E practices across DepEd units to ensure plans, policies, and processes contribute to organizational goals.