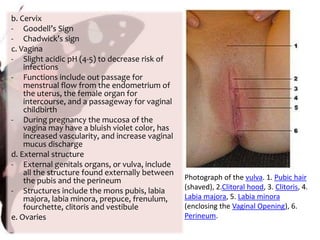
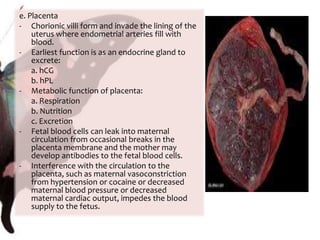
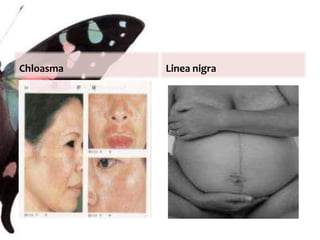
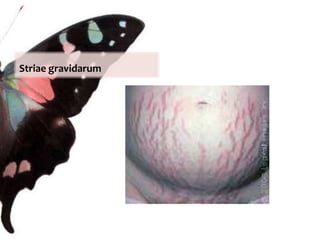
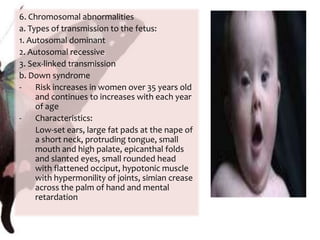
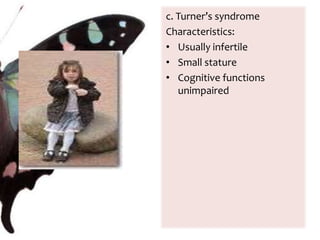
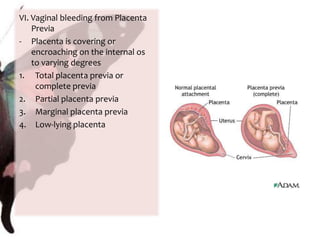
The document provides information on anatomy and physiology changes during pregnancy and assessment of high-risk conditions. It discusses the uterus, cervix, vagina and other organs. It also covers fetal development stages and complications that can arise. Common high-risk conditions addressed include preterm labor, incompetent cervix, premature rupture of membranes, diabetes, and abruptio placenta. Nursing interventions are outlined for monitoring and managing clients with various complications.