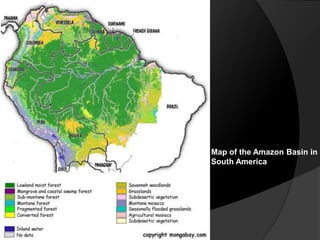
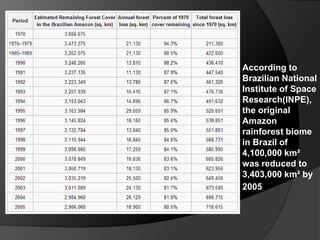
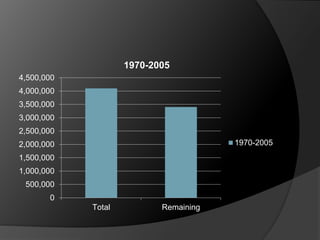
The document summarizes information about the Amazon rainforest, including its location across 9 countries in South America, size, and that it contains over half the world's remaining rainforests. It then discusses some causes of deforestation in the Amazon including cattle ranching, mining, logging, and agriculture. Deforestation has led to over 600,000 square kilometers of forest being lost between 1991-2000. The consequences of deforestation mentioned include the potential for increased hurricane activity in the Caribbean due to rising sea temperatures from less forest transpiration in the Amazon.