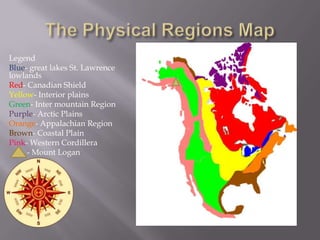
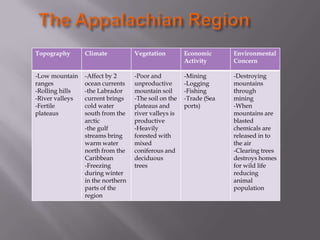
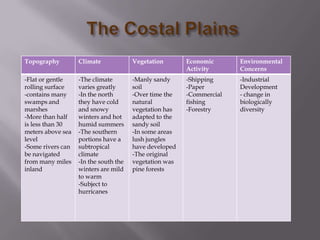
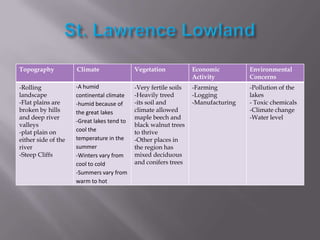
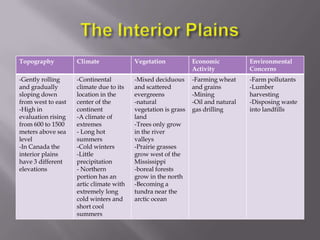
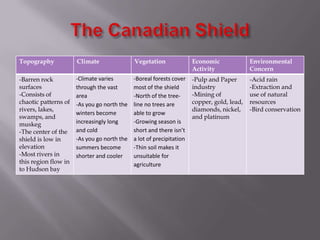
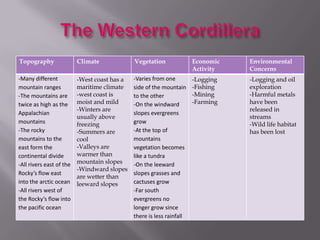
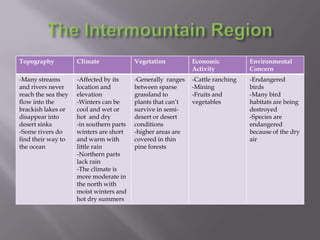
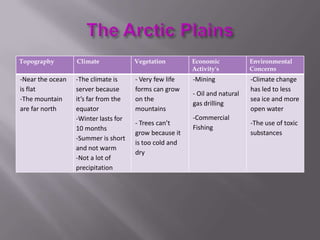
The document describes the major physical regions of Canada based on topography, climate, vegetation, and economic activity. It includes 8 regions: Appalachian Region, Coastal Plains, St. Lawrence Lowland, Interior Plains, Canadian Shield, Western Cordillera, Intermountain Region, and Arctic Region. Each region is summarized in a table outlining its defining geographic features. The largest and most northern region is the Canadian Shield, characterized by barren rock surfaces and boreal forest. The document provides a high-level overview of Canada's major geographic regions through condensed summaries.