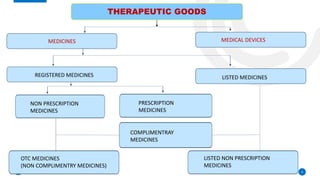
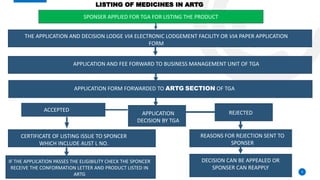
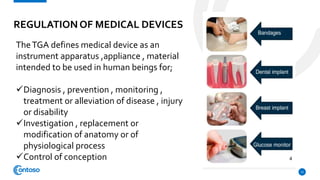
The Therapeutic Goods Administration (TGA) is an Australian government body responsible for regulating therapeutic goods, ensuring their quality, safety, and efficacy. Established under the Therapeutic Goods Act 1989, it maintains the Australian Register of Therapeutic Goods (ARTG), categorizing products into registered and listed medicines and medical devices. The TGA also conducts pre-market evaluation, ongoing monitoring, and compliance activities, positioning itself as a leading global regulator in the field.