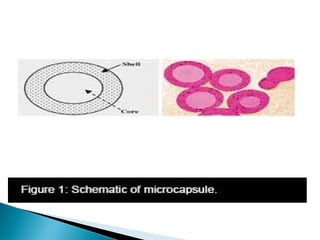
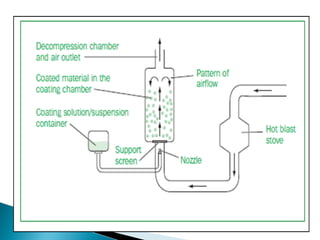
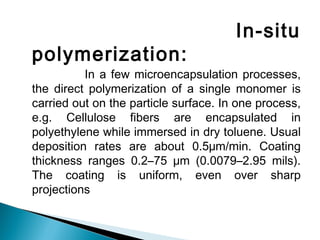
Microencapsulation is a technique used in textile finishing to encapsulate active ingredients like fragrances, antimicrobials, and phase change materials. It involves coating small droplets or particles of a core material with a shell to protect the core and control its release. This allows ingredients like moisturizers and insecticides to be incorporated into fabrics in a long-lasting way. Various techniques like spray drying, air suspension coating, and solvent evaporation can be used to produce microcapsules for textile finishing. Microencapsulation improves properties like wash durability and provides benefits like controlled fragrance release and thermoregulation. It is becoming a popular eco-friendly method in the textile industry.