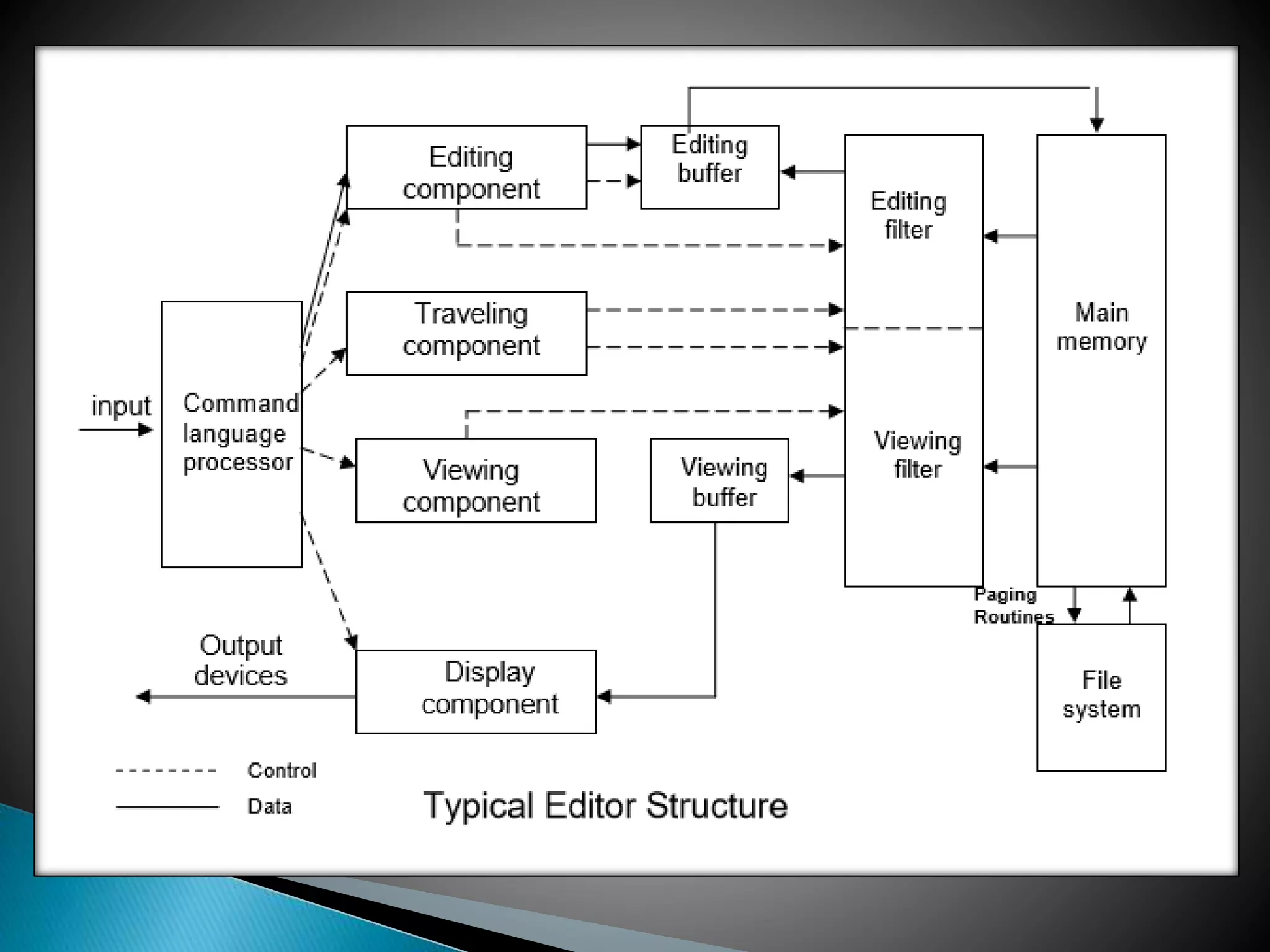
Text editors are an important interface that allow knowledge workers to compose, organize, and manipulate computer-based information. The document discusses the key components and functions of text editors, including input/output devices, user interfaces, editor structure, editing processes, and types of editors based on computing environments like time-sharing, stand-alone, and distributed. Text editors allow users to create and edit text files through functions like moving the cursor, deleting text, searching, and saving files.