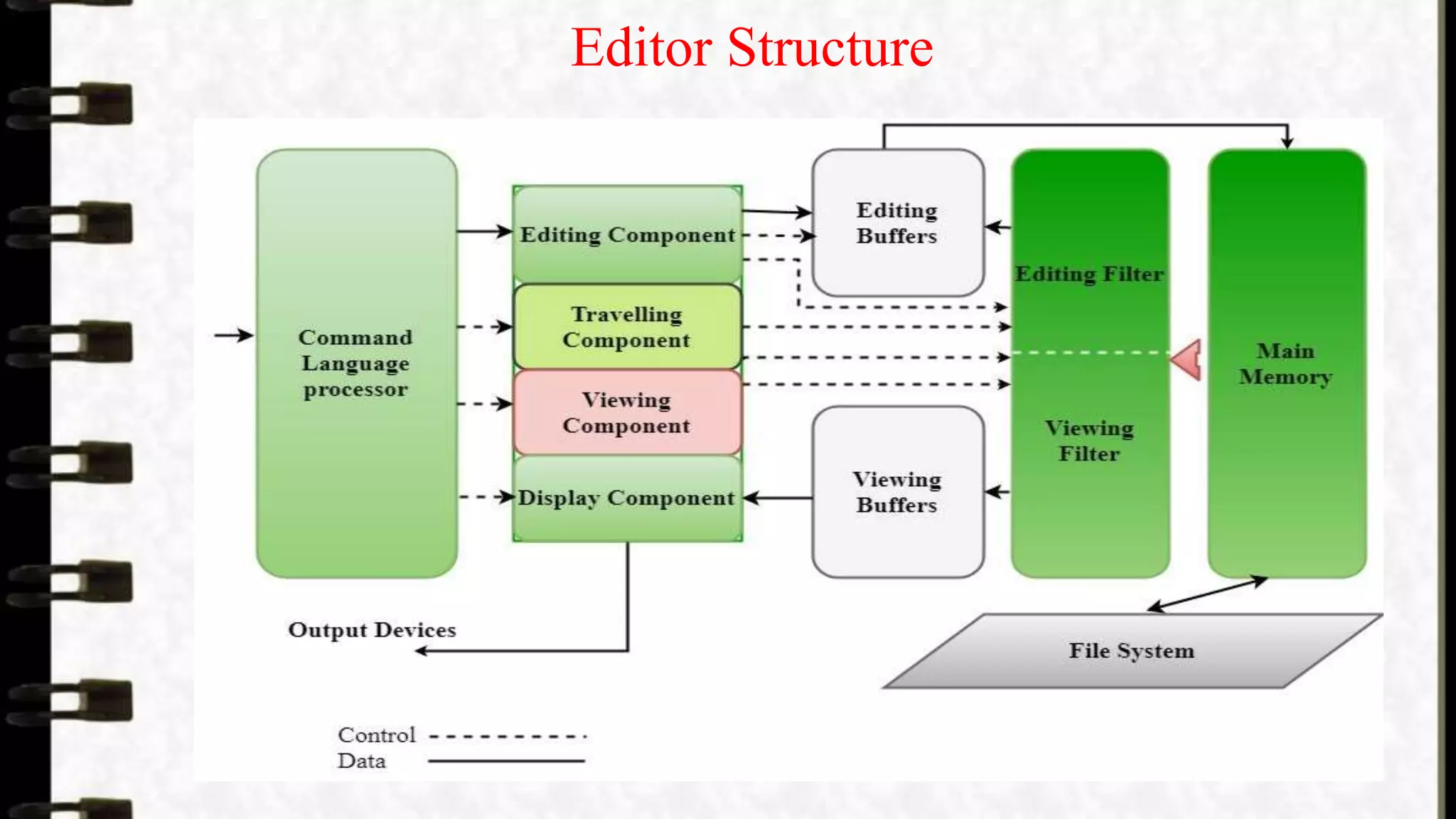
Editors or text editors are software applications designed for creating and modifying text files, categorized into line editors, stream editors, screen editors, word processors, and structure editors. Each type serves different purposes, from simple line-based editing to complex formatting with multimedia. The editing process involves selecting text, formatting, executing modification commands, and updating the display.