The document presents an introduction to testing with Spring, highlighting its capabilities for unit and integration testing in Java applications. It discusses various testing strategies, tools, and Spring's TestContext framework, emphasizing its annotation-driven approach and support for dependency injection, transaction management, and SQL script execution. Additionally, it covers the Spring MVC testing features, providing examples and best practices for effective test management.
































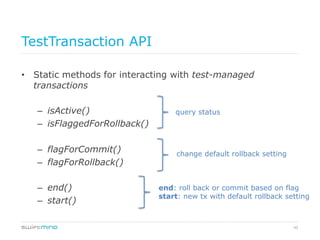









![57
Details
• Included in spring-test module of Spring Framework
3.2
• Builds on
– TestContext framework for loading Spring MVC
configuration
– MockHttpServlet[Request|Response] and other
mock types
• Server-side tests involve DispatcherServlet
• Client-side REST testing for code using RestTemplate](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/testingwithspring-anintroduction-sbrannen-150108124806-conversion-gate02/85/Testing-with-Spring-An-Introduction-57-320.jpg)