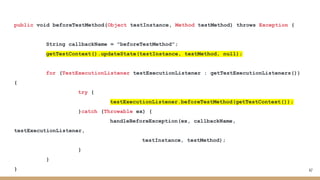
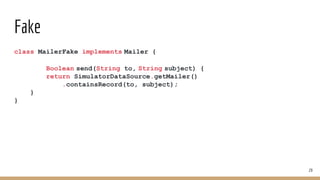
Unit testing involves writing small pieces of code to test specific functionality. Integration testing involves testing components together without full deployment. Spring Boot provides helpful tools for testing Spring applications, including test slices to load only parts of the configuration. The document discusses unit testing, integration testing, test patterns, test doubles, the Spring TestContext framework, and testing Spring Boot applications.




















![@Unroll
def "#testDB : using implicit ResultSet Mapper to map result set"() {
given:
setup(testDB)
when:
customerDao.createCustomer0(“Abdullah”, “Mohammad”)
def list = customerDao.listCustomers(list)
then:
1 == list.size()
with(list.get(0)){
“Abdullah” == firstName()
“Mohammad” == lastName()
}
cleanup:
cleanup(testDB)
where:
testDB << [HSQL, MYSQL, SQLServer, ORACLE]
}
22
https://github.com/mhewedy/spwrap/blob/master/src/test/groovy/spwrap/DAOIntTest.groovy](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/200qj1czqxw1ef9agin7-signature-047740293d2af03cbfac6a69fee3f61112c86b4a1525596839914c29034534f6-poli-190501111310/85/Testing-Spring-Applications-22-320.jpg)















![Meta Annotations
@Target({ElementType.TYPE, ElementType.METHOD})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@DisabledIf( expression =
"#{systemProperties['os.name'].toLowerCase().contains('mac')}",
reason = "Disabled on Mac OS")
public @interface DisabledOnMac {}
40](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/200qj1czqxw1ef9agin7-signature-047740293d2af03cbfac6a69fee3f61112c86b4a1525596839914c29034534f6-poli-190501111310/85/Testing-Spring-Applications-40-320.jpg)