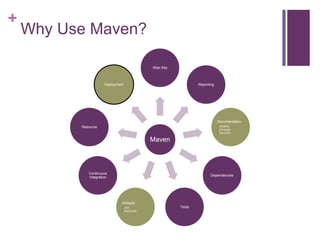
The document provides an overview of Apache Maven, a tool for software project management and comprehension, emphasizing its project object model, dependency management, and lifecycle phases. It compares Maven with Ant and Gradle, highlighting its standardization, built-in reporting, and community support. Key concepts discussed include the Project Object Model (POM), artifact management, versioning, and repository types for deployment.