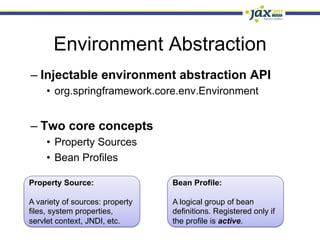
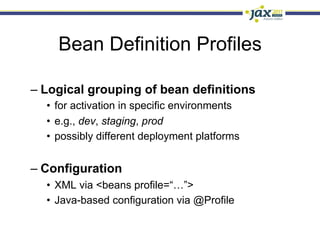
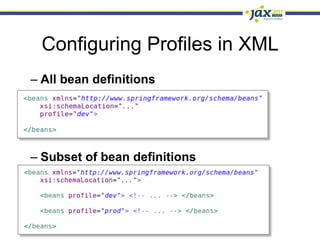
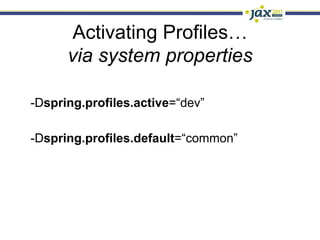
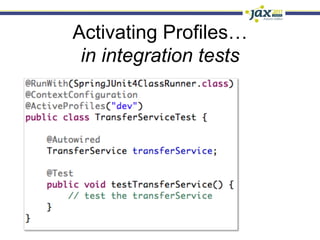
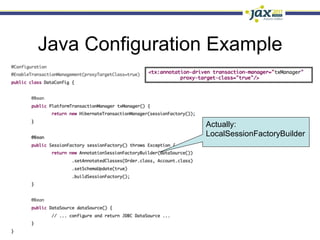
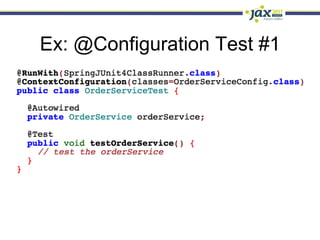
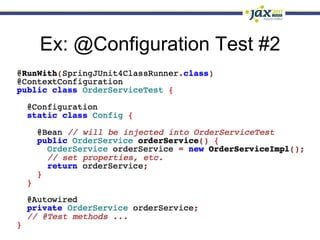
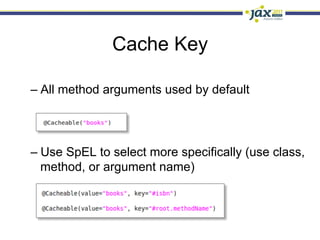
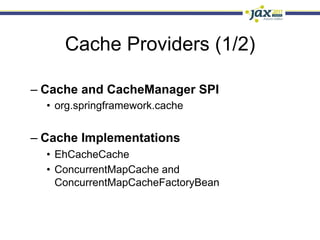
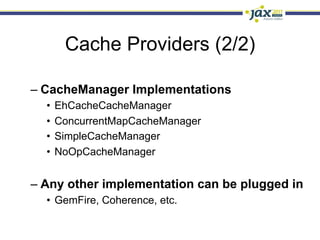
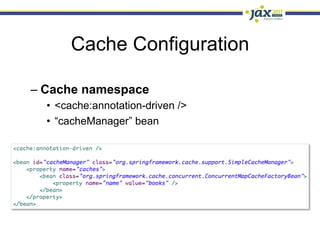
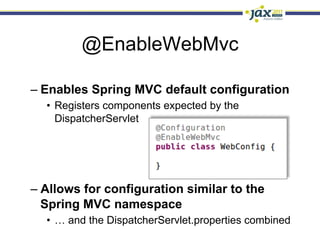
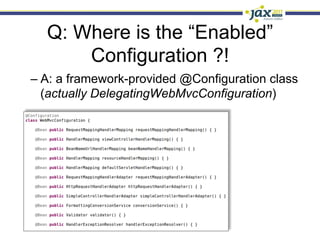
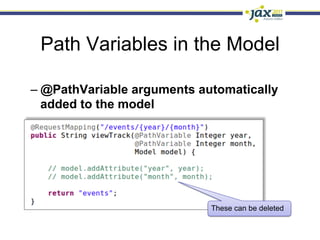
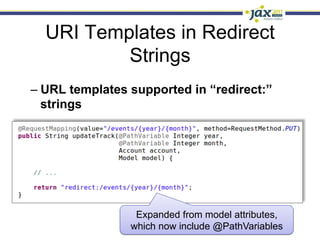
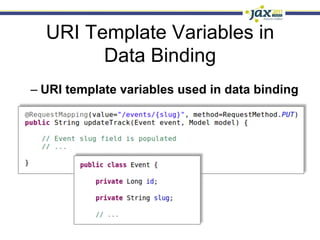
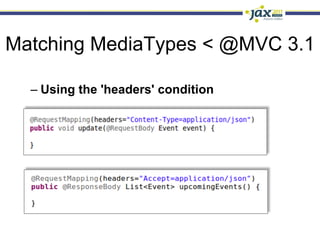
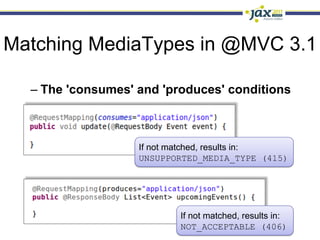
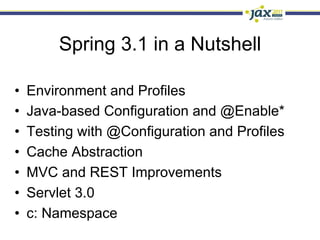
Spring 3.1 in a Nutshell focused on major new features including the environment and profile abstraction, Java-based configuration with @Enable annotations, improved testing support using @Configuration classes and profiles, a high-level caching API, enhancements to MVC and REST support, explicit Servlet 3.0 integration, and miscellaneous improvements like the "c:" namespace. The presentation provided examples and explanations of how to use these new features in Spring applications.