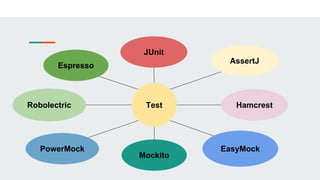
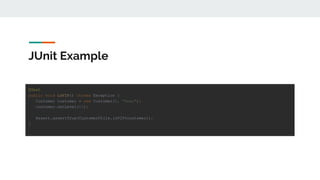
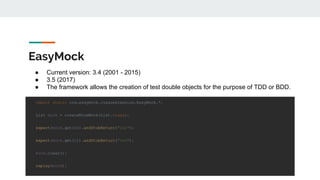
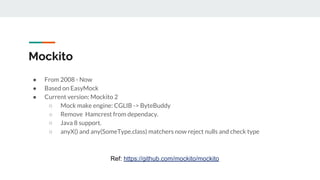
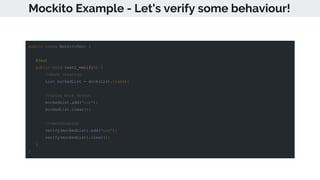
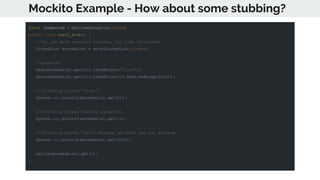
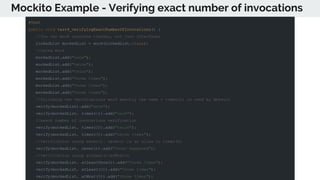
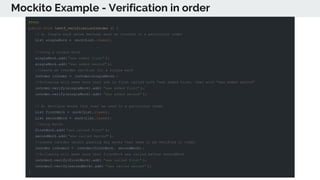
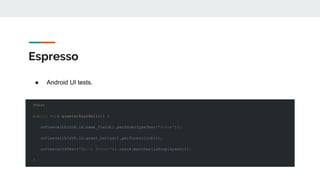
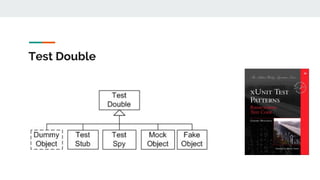
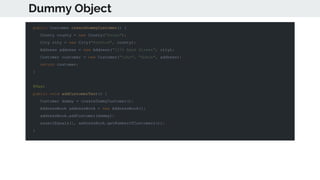
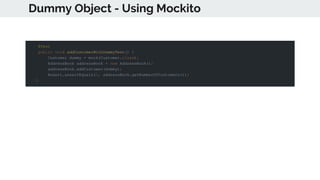
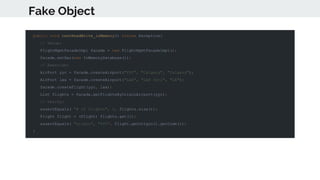
This document provides an overview of various testing frameworks and concepts used for Android testing. It discusses JUnit, Mockito, PowerMock, Robolectric, and Espresso - the most popular tools for unit, integration, and UI testing of Android apps. For each tool, it provides brief descriptions of their purpose and capabilities. It also includes examples demonstrating how to write tests using JUnit, Mockito, and PowerMock. The document aims to explain what these testing tools are and how they can be used for testing Android applications.