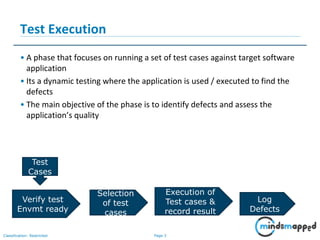
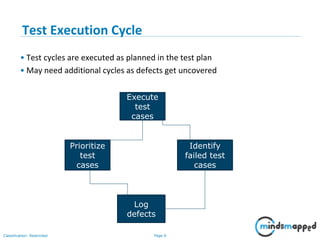
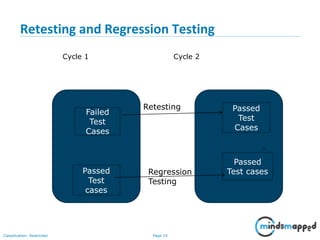
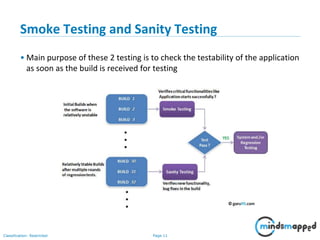
This document provides an overview of test execution, including its purpose, entry and exit criteria, cycles, and methodologies. Test execution involves running test cases against software to find defects and assess quality. Key activities include verifying the test environment, selecting test cases, executing them, and logging any defects found. Test cycles are run as planned, with additional cycles as more defects are uncovered. Retesting and regression testing help ensure defects are closed without impacting previous functionality. Testing ends when criteria like completing test cases, reaching an acceptable defect rate, and schedule constraints are met.