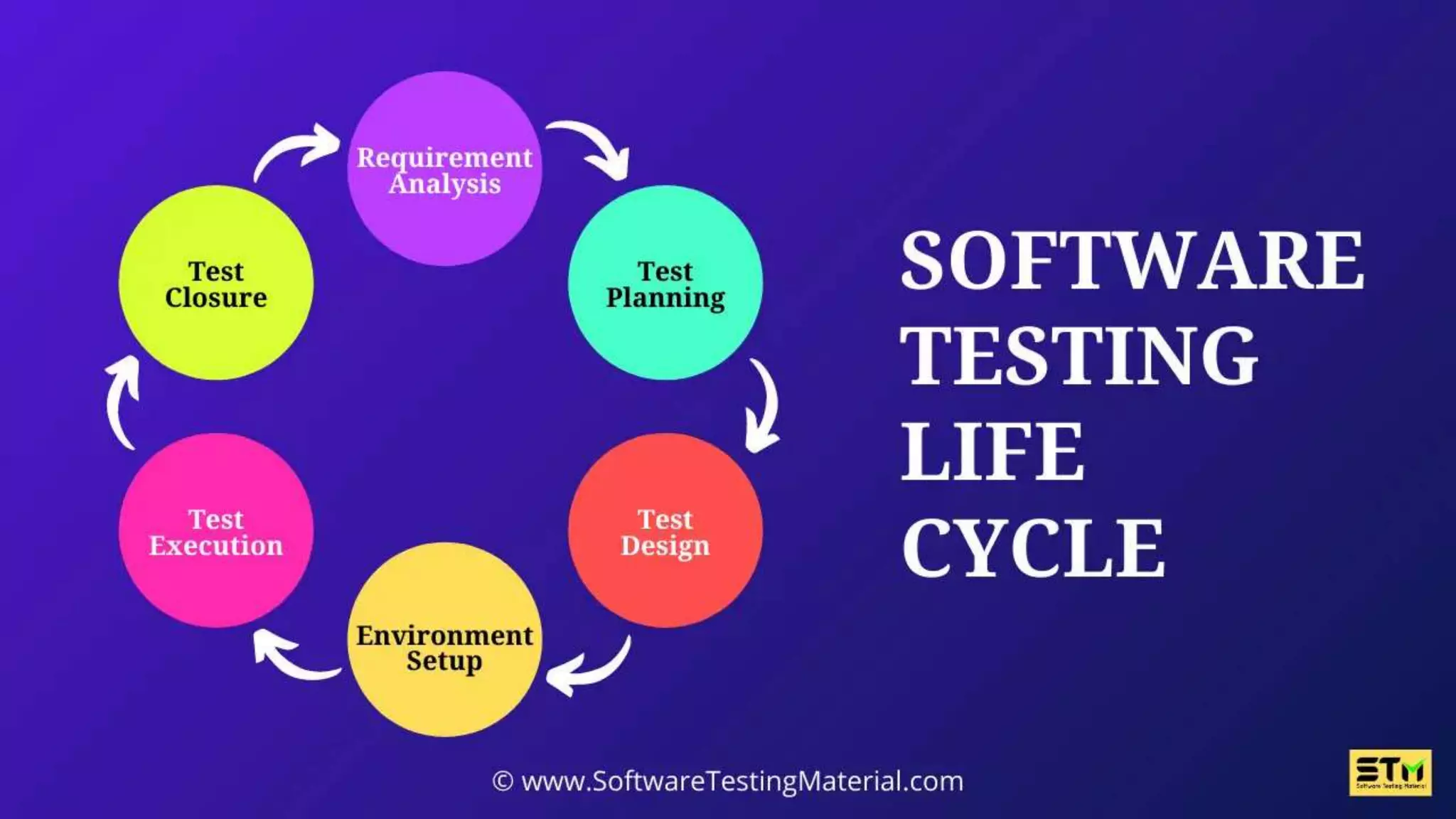
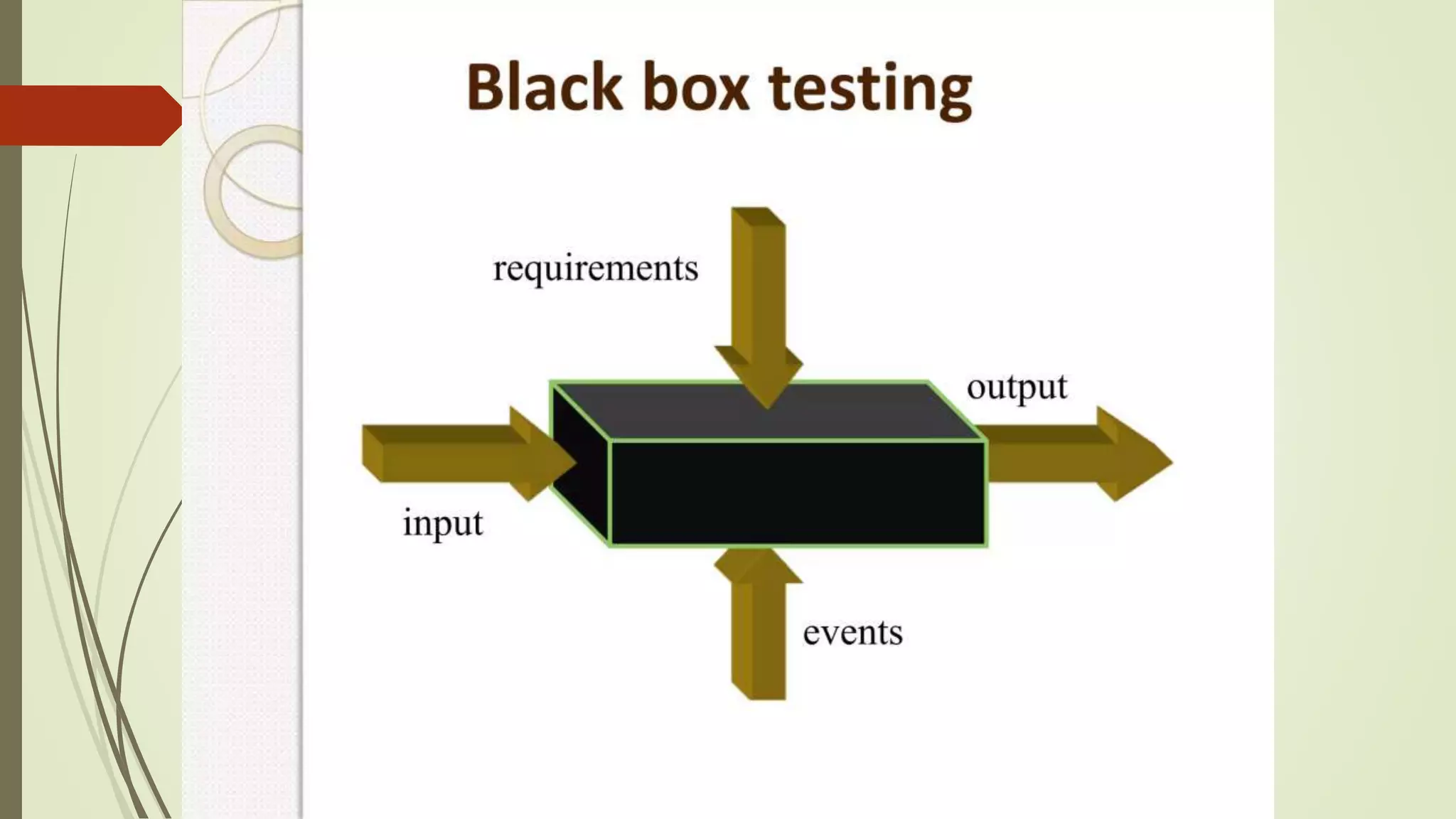
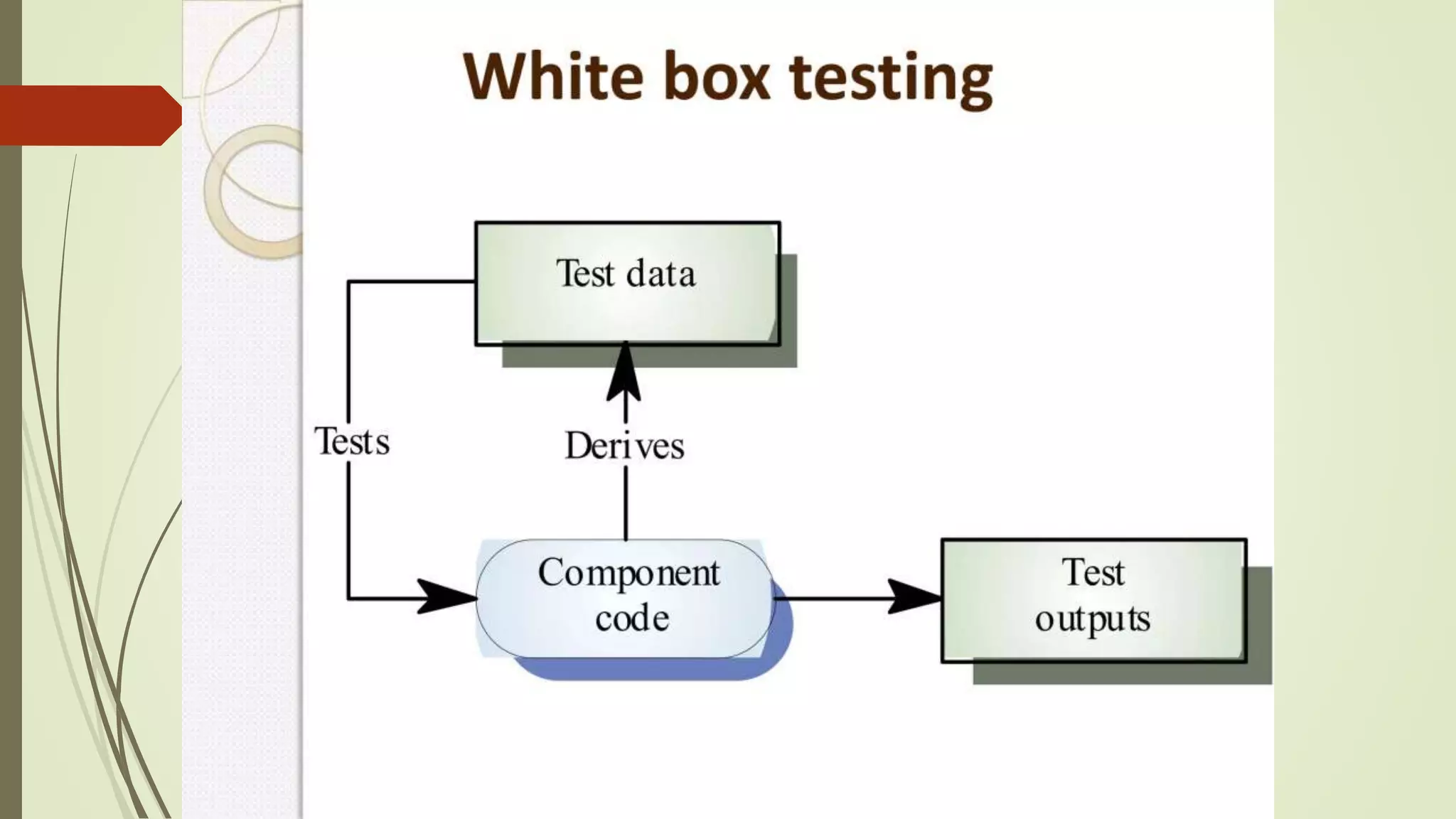
Software testing is the process of evaluating a software application to ensure it functions correctly and meets requirements. There are different types of testing including manual testing, where a tester uses the software without automation, and automation testing, where scripts are used to repeatedly test the software. Testing occurs at various levels such as unit testing of individual code components and system testing of the full application. Effective testing requires clear requirements, collaboration between teams, and addressing challenges like time constraints.