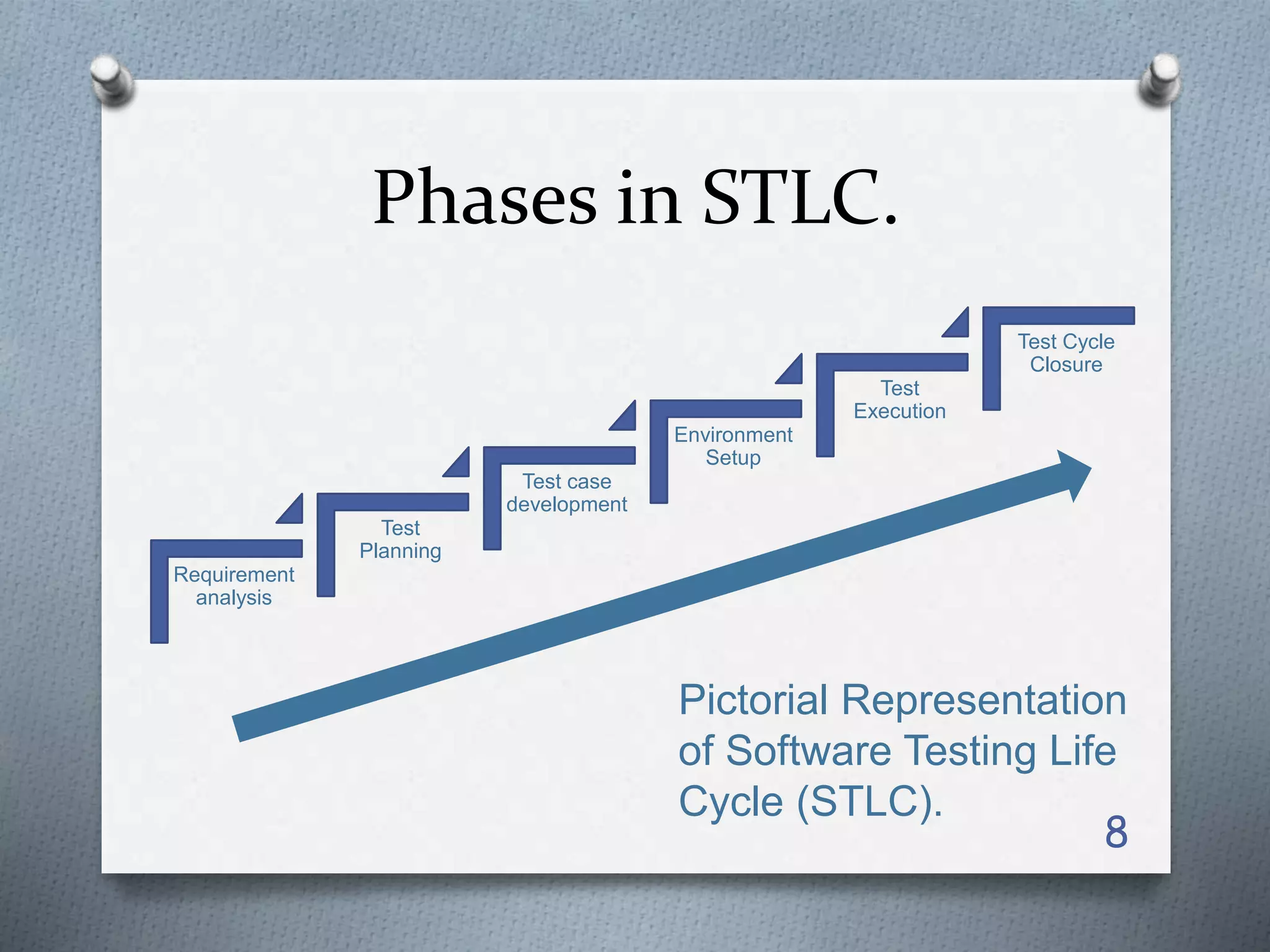
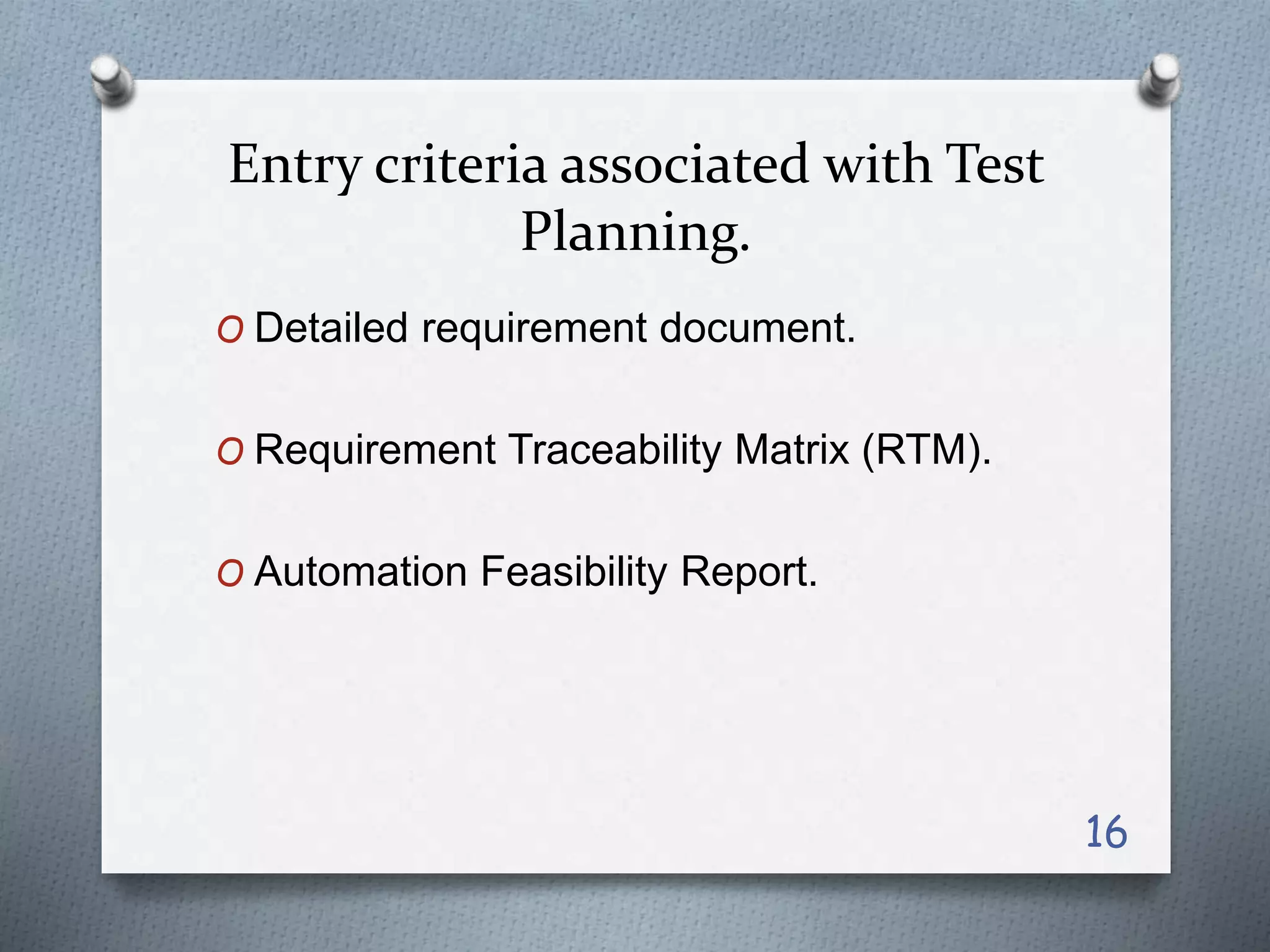
The document describes the phases of the Software Testing Life Cycle (STLC). It discusses the 6 main phases: 1) Requirement Analysis, 2) Test Planning, 3) Test Case Development, 4) Environment Setup, 5) Test Execution, and 6) Test Cycle Closure. Each phase has entry and exit criteria, activities, and deliverables. The STLC is a testing process executed in a systematic, planned manner, following the software development life cycle to ensure quality.