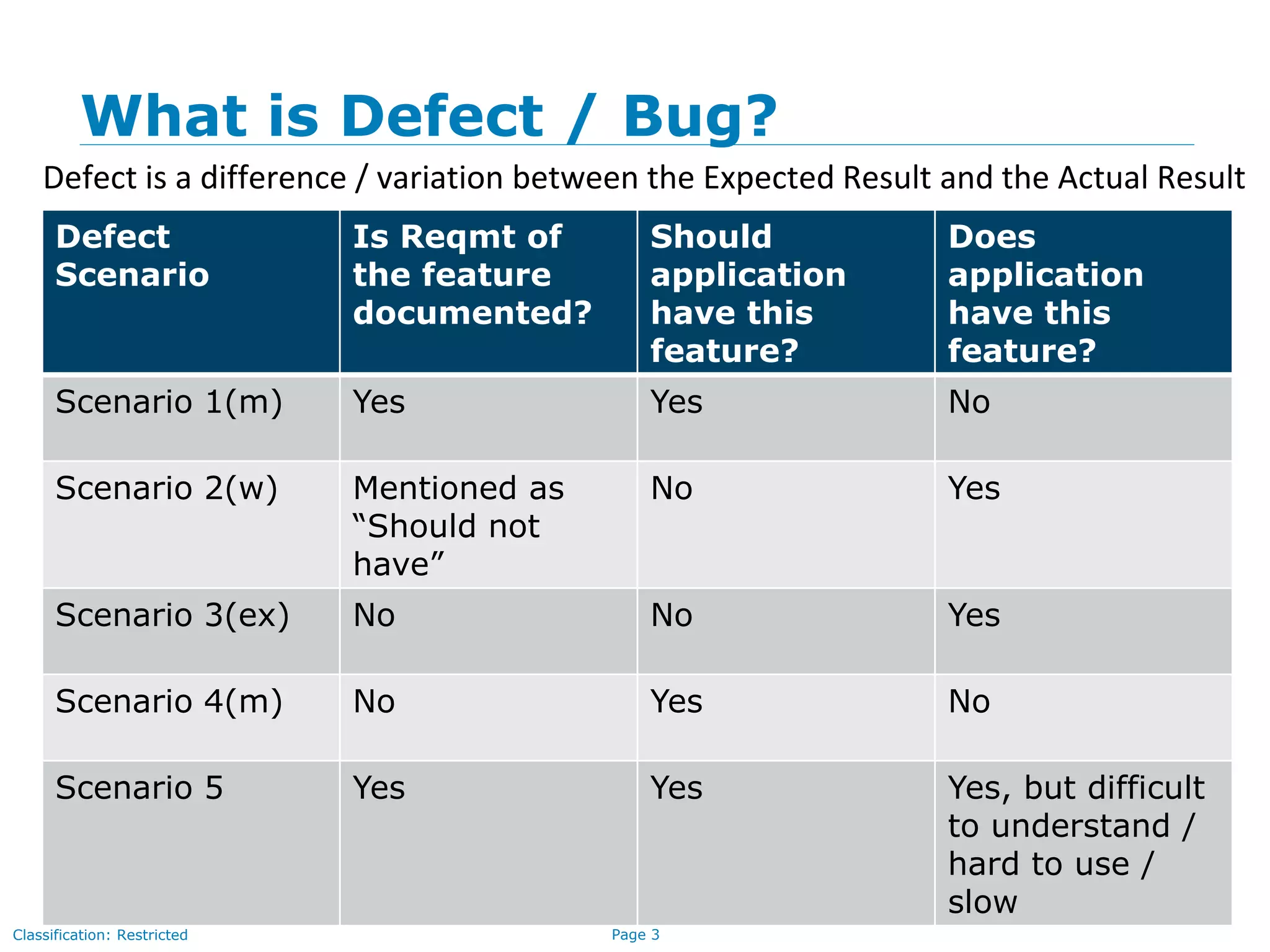
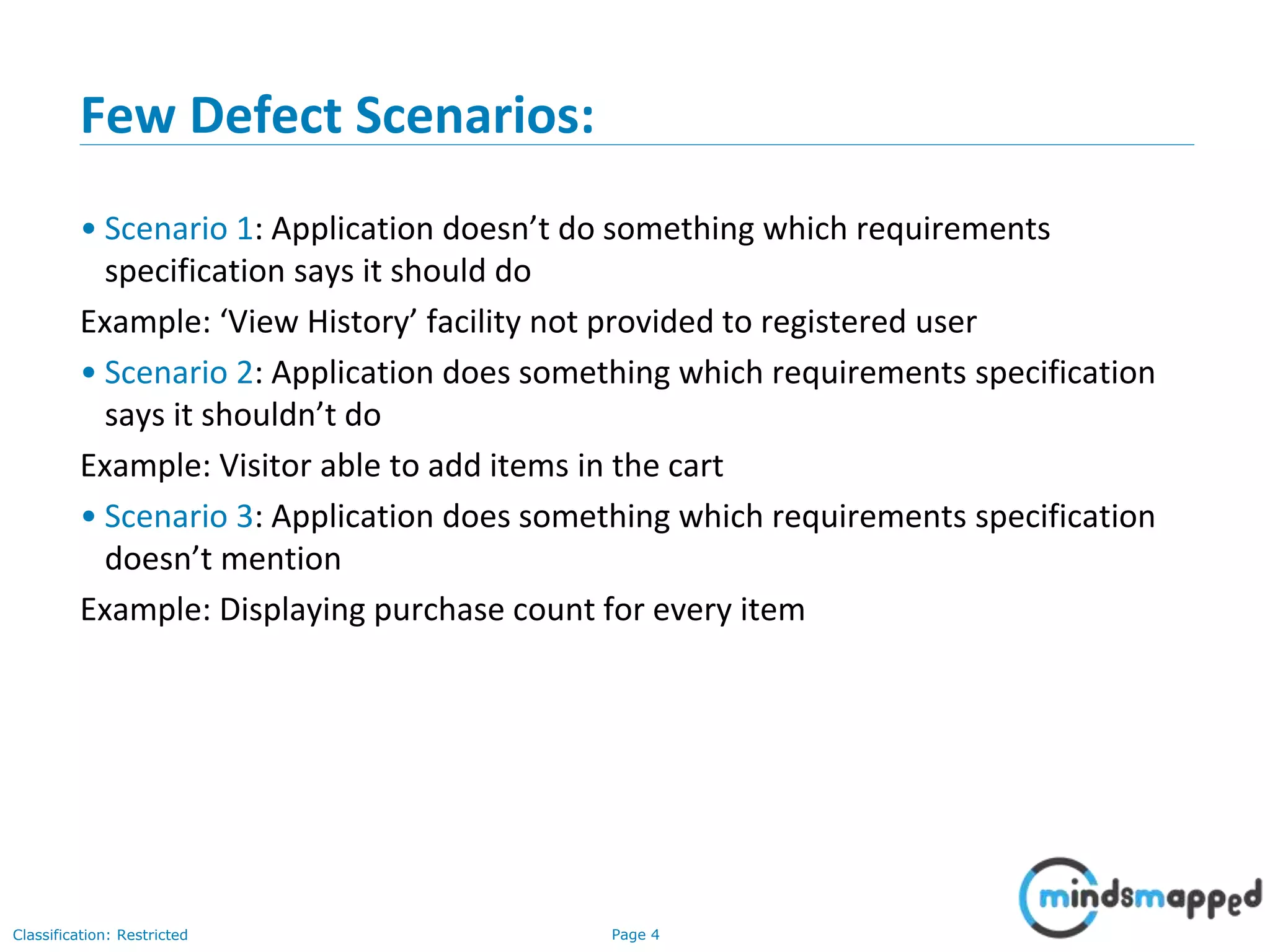
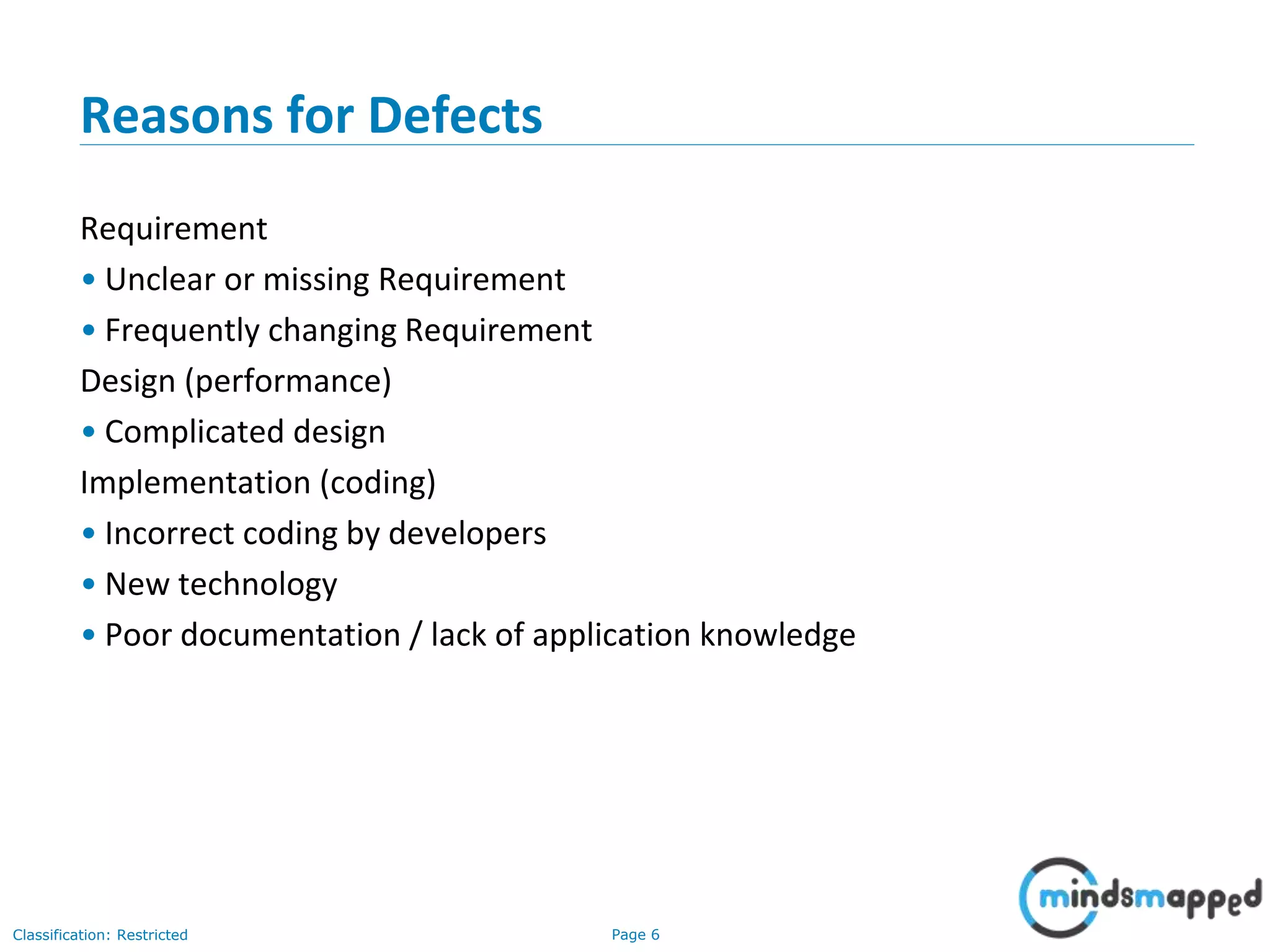
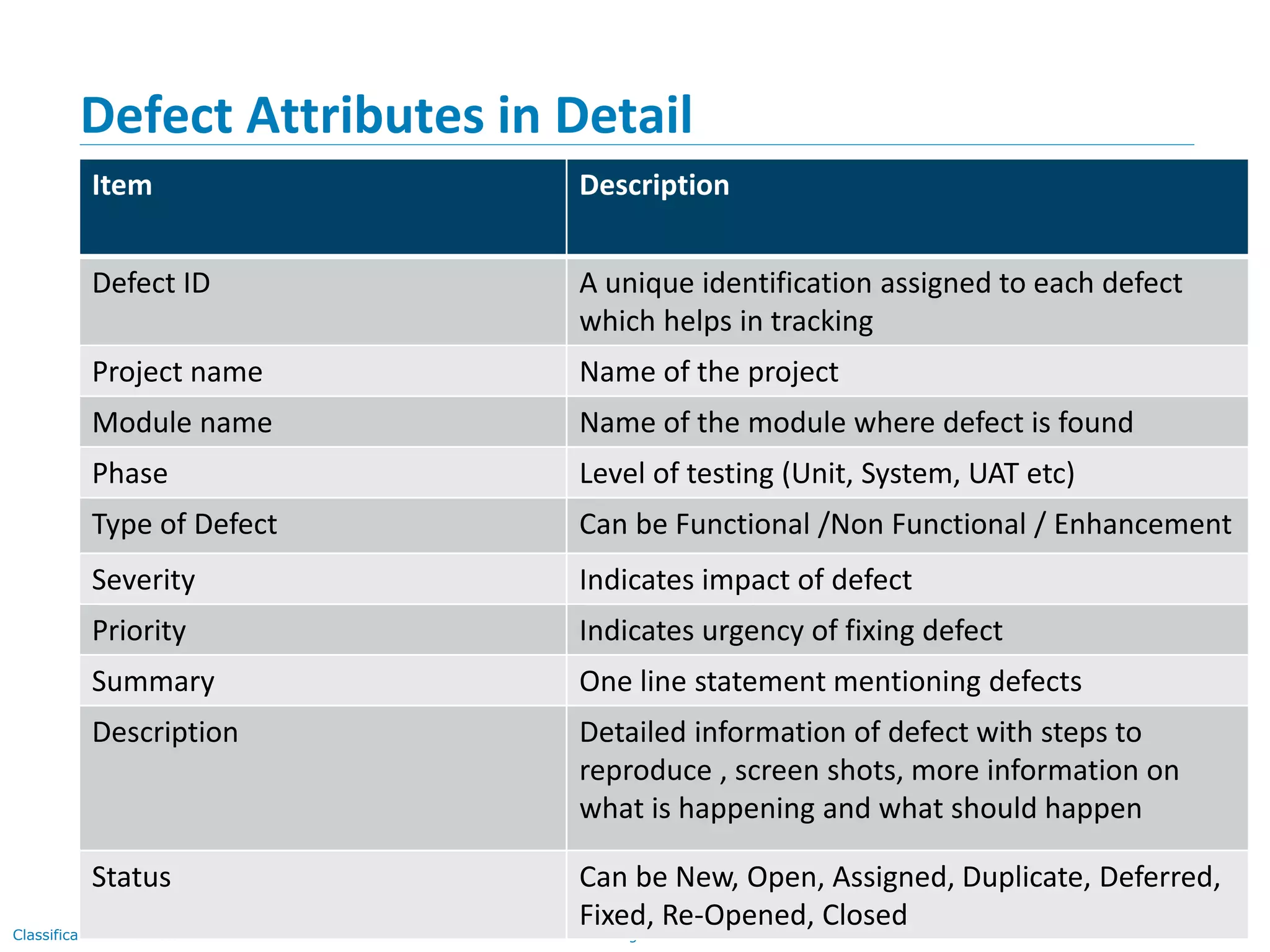
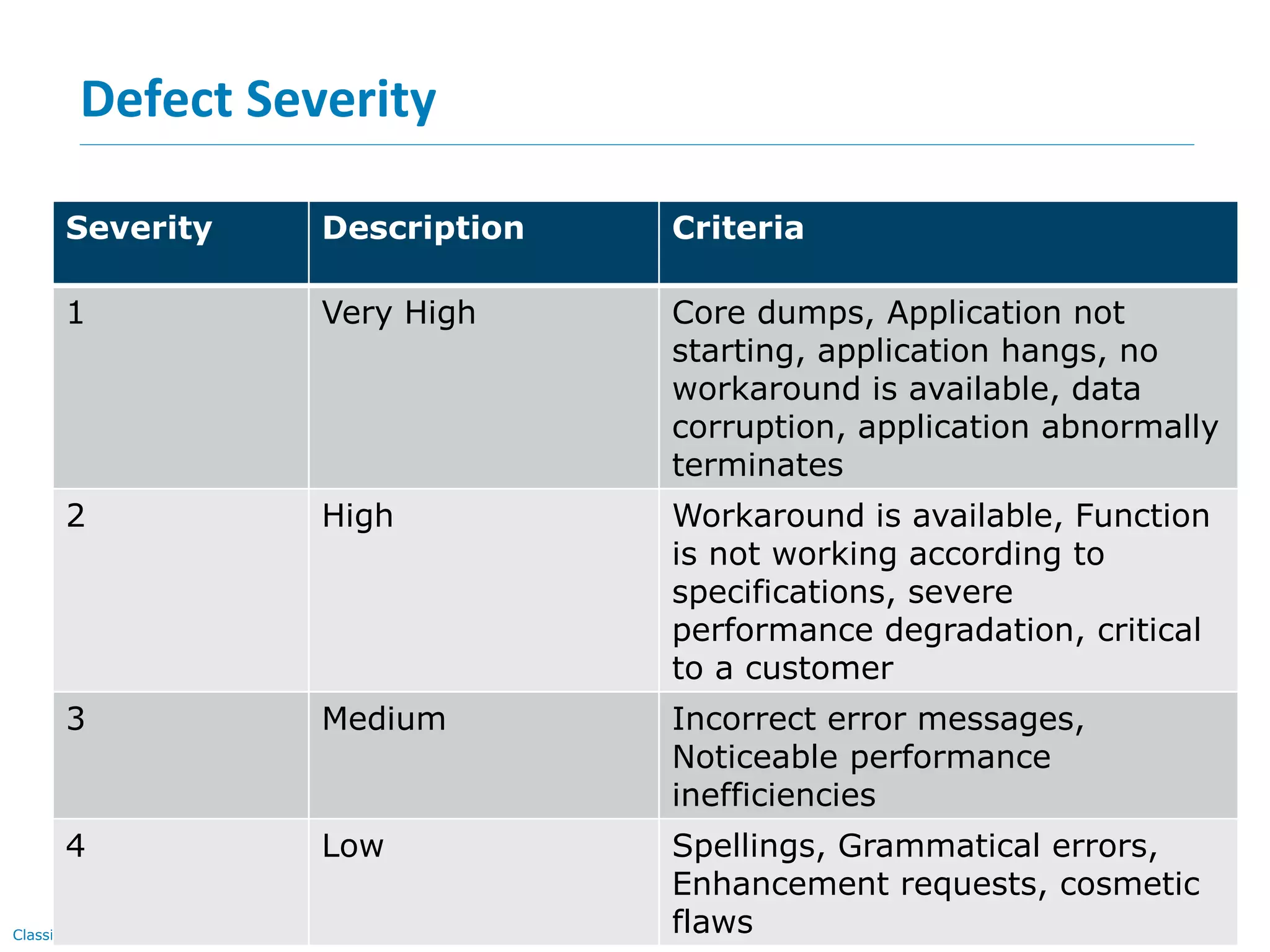
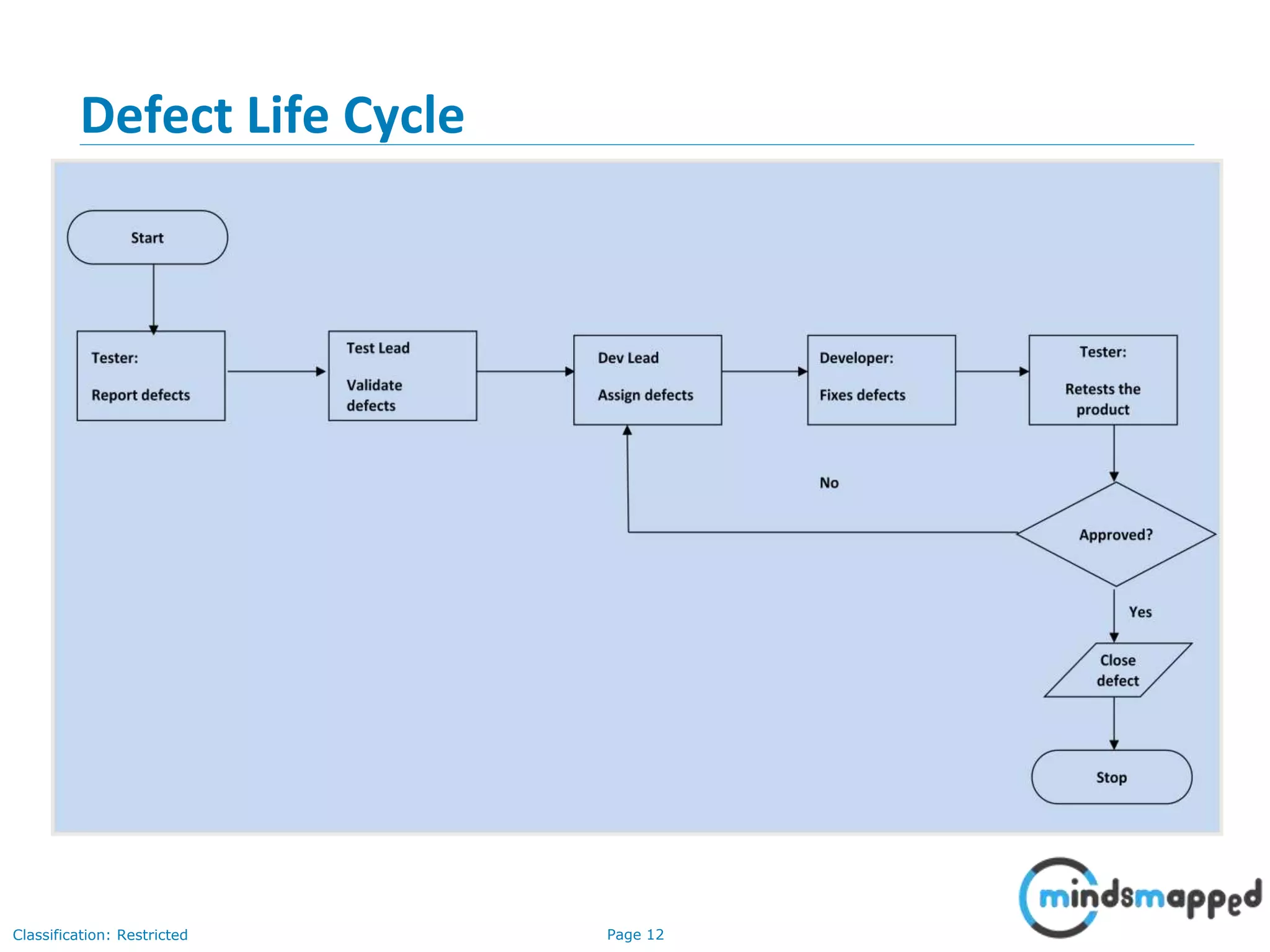
The document discusses quality assurance and software testing, focusing on defects, their identification, life cycle, and tracking tools. It outlines various defect scenarios, reasons for defects, attributes of defects, and their severity and priority. Additionally, it emphasizes the importance of defect tracking for resource allocation, process improvement, and overall application readiness.