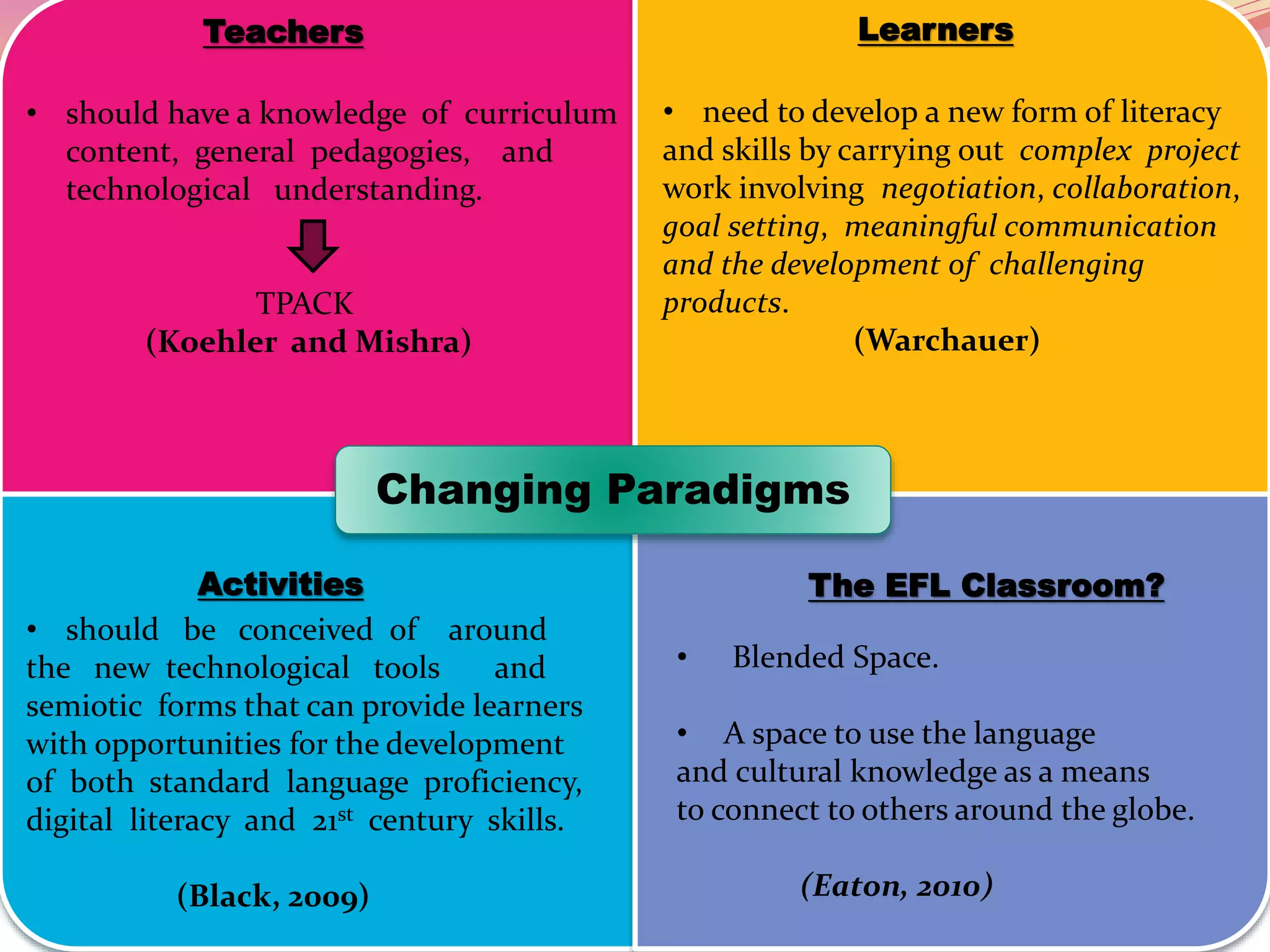
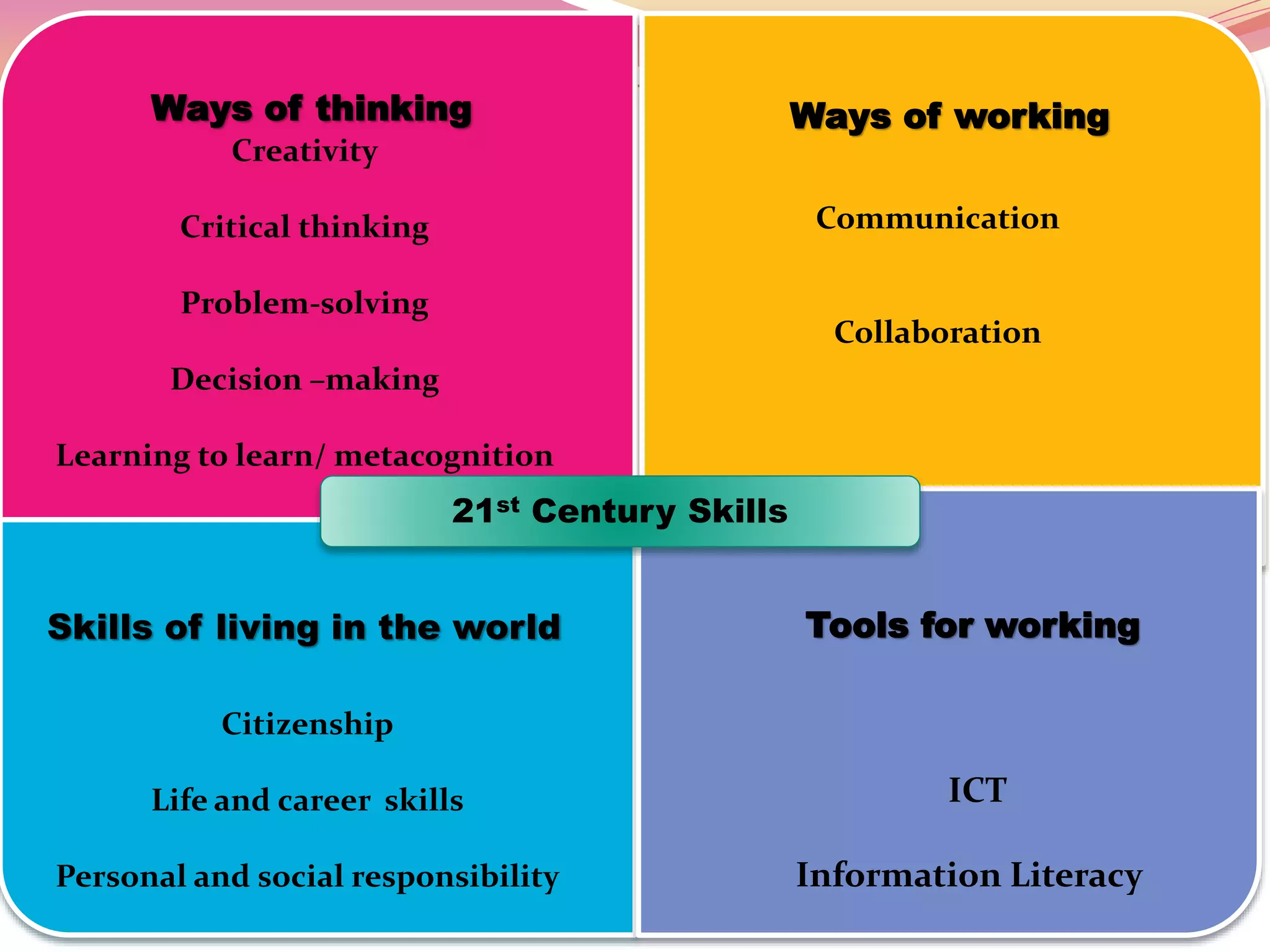
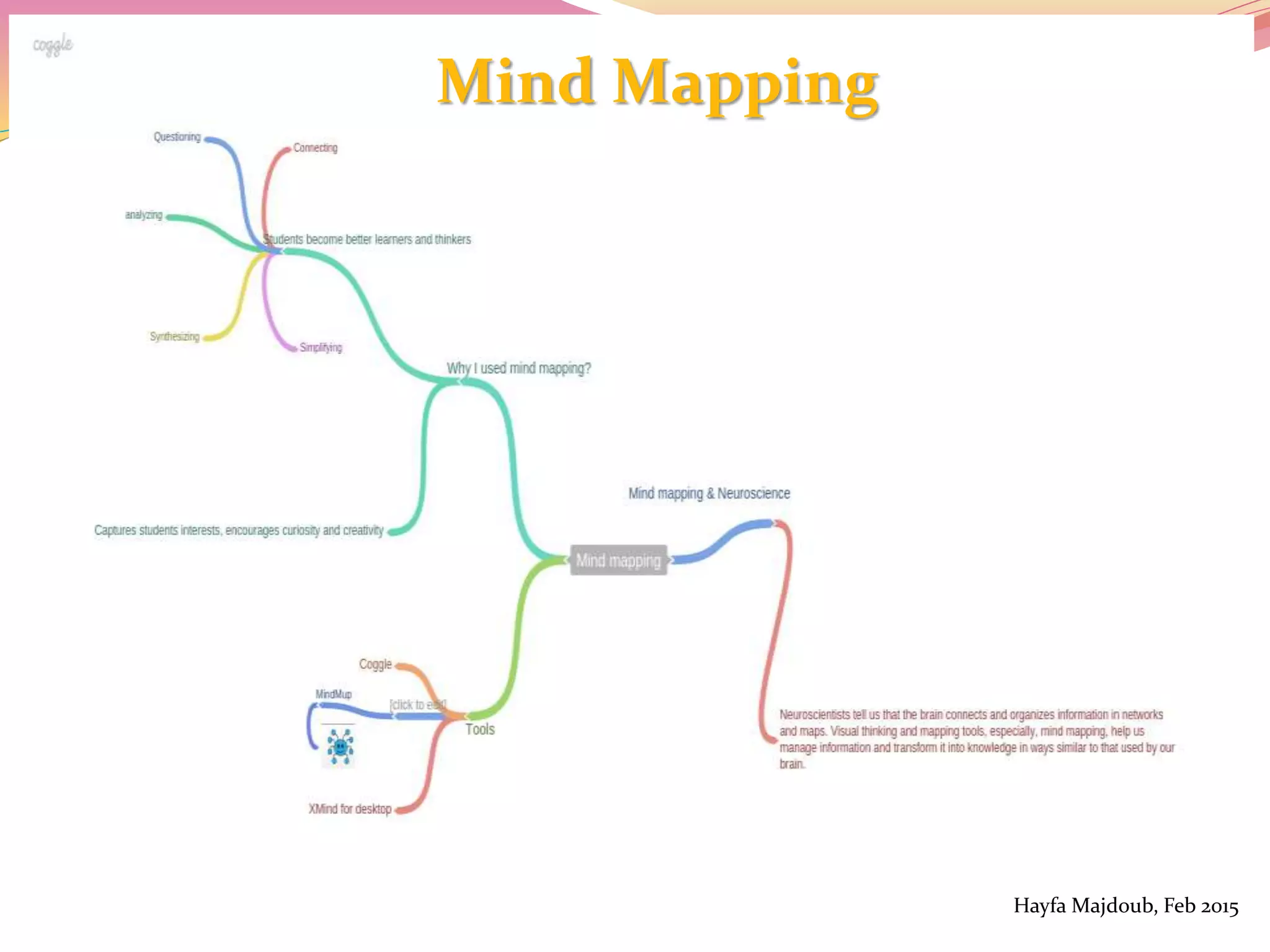
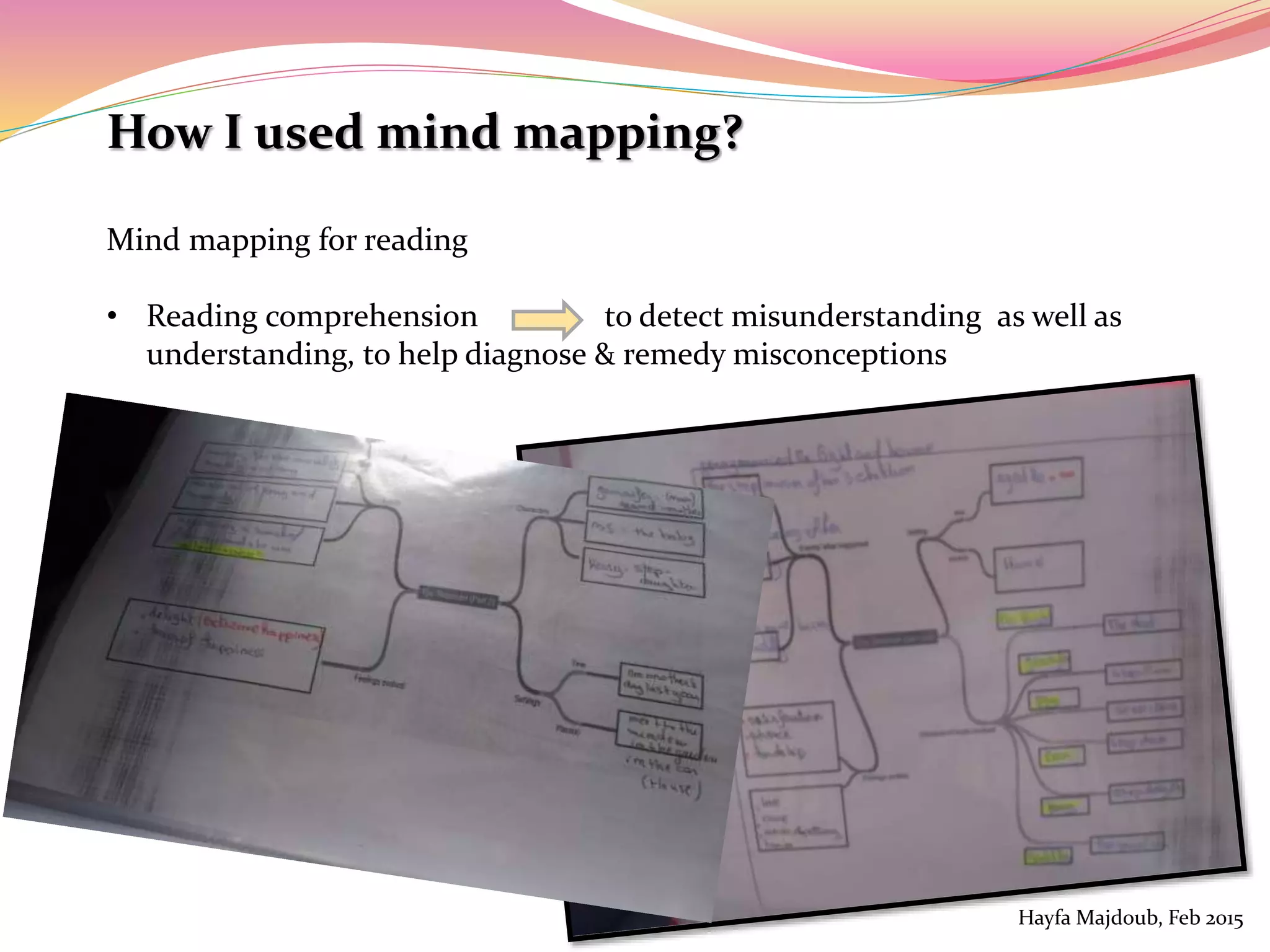
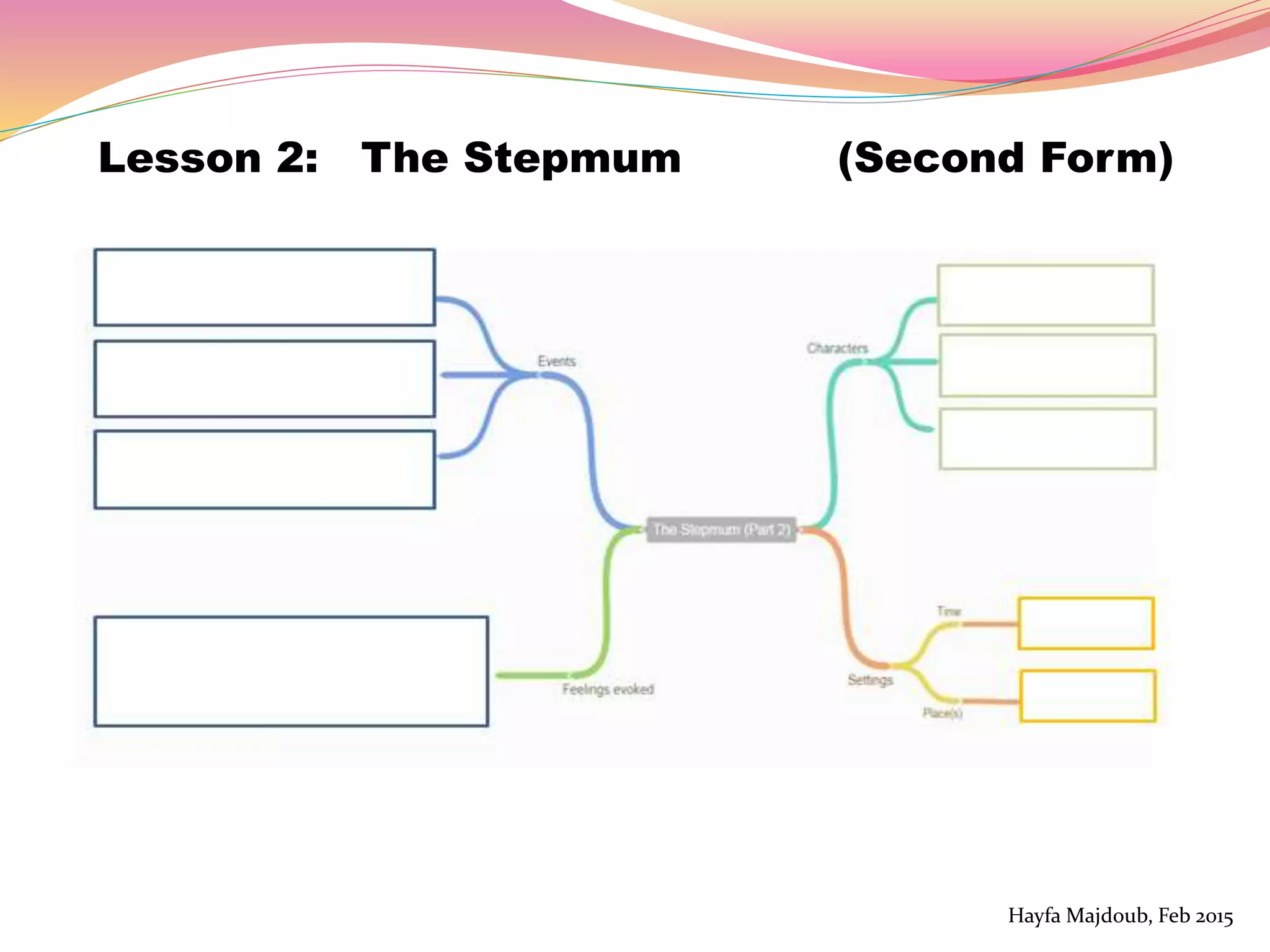
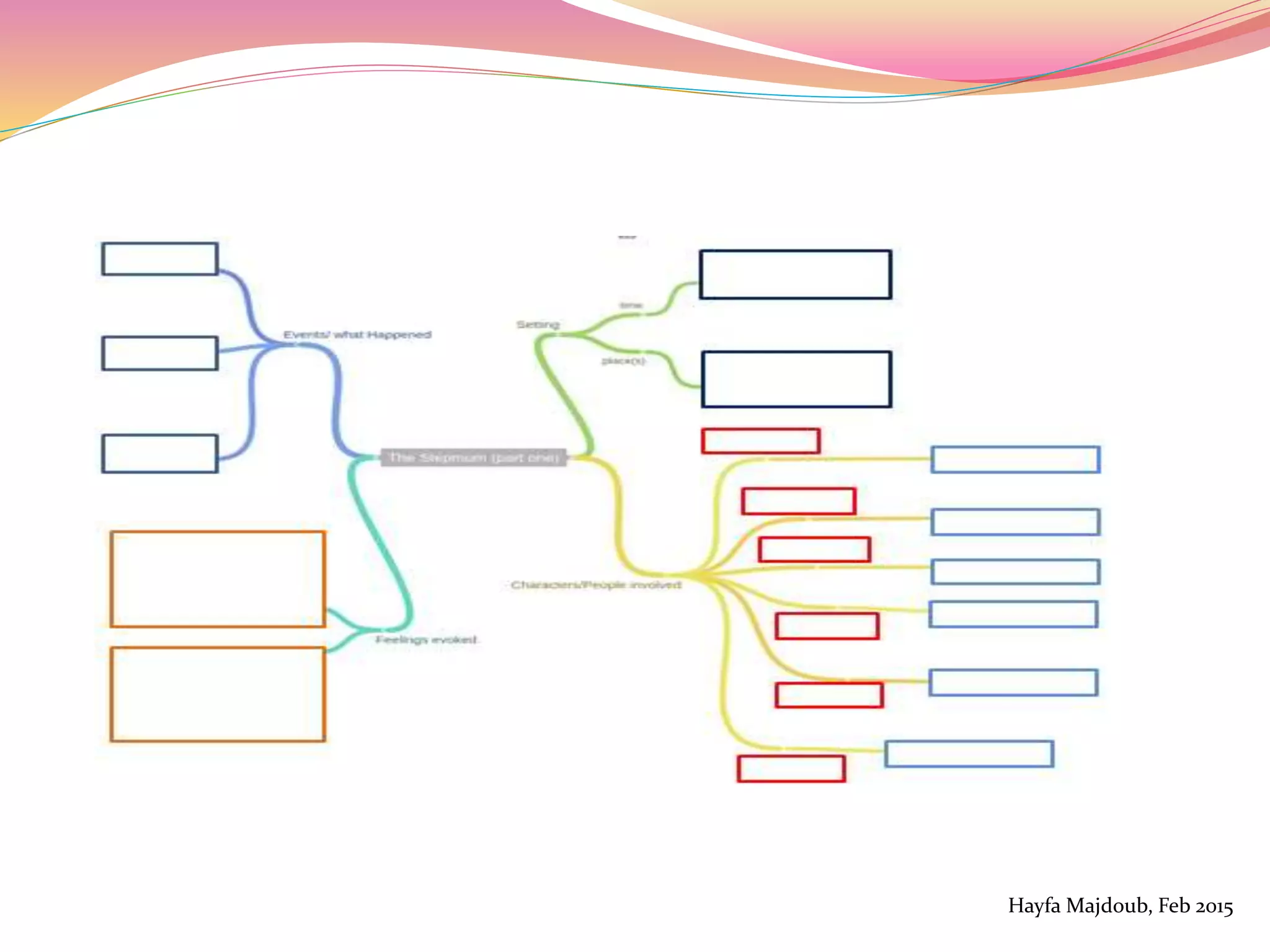
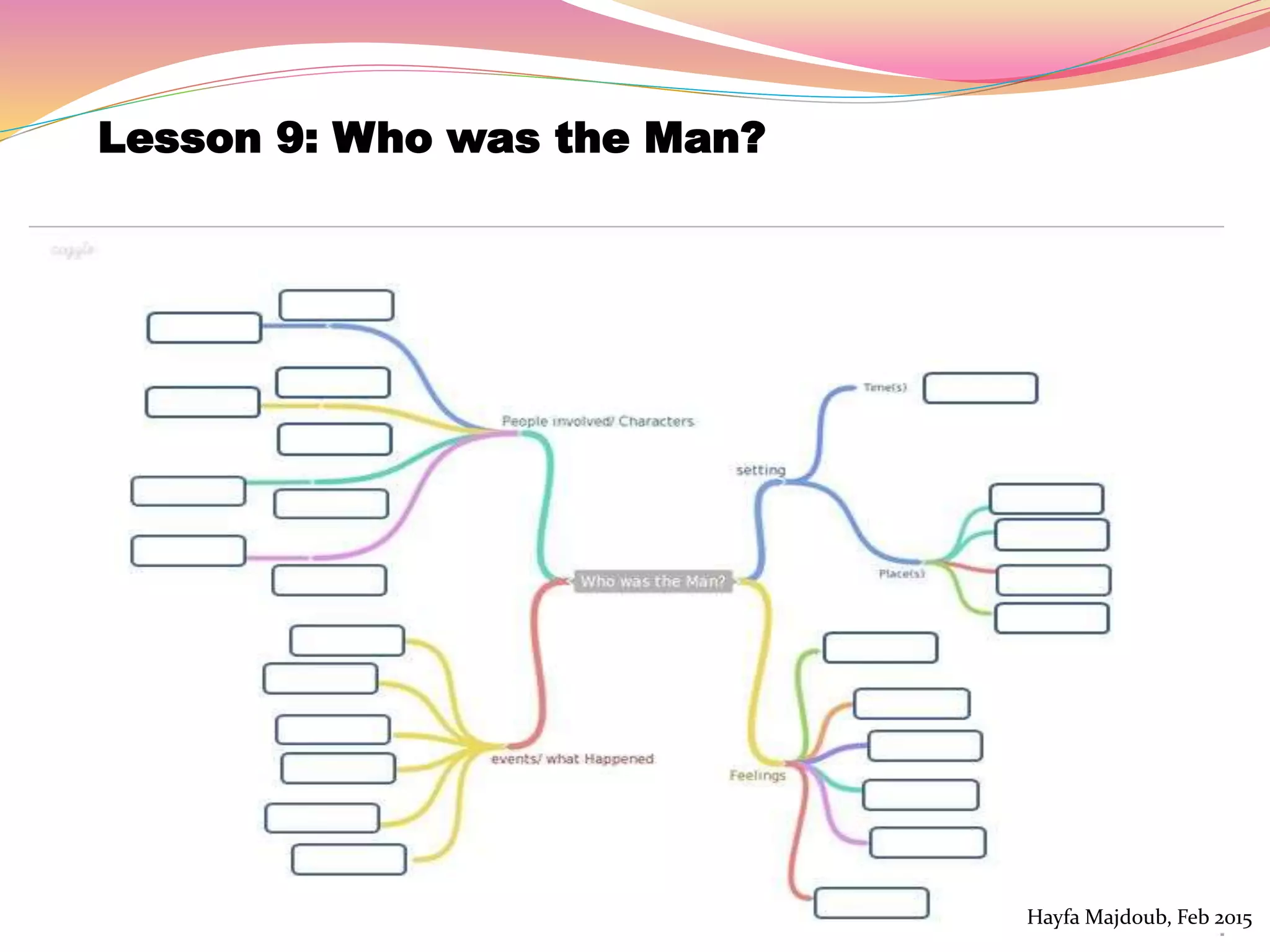
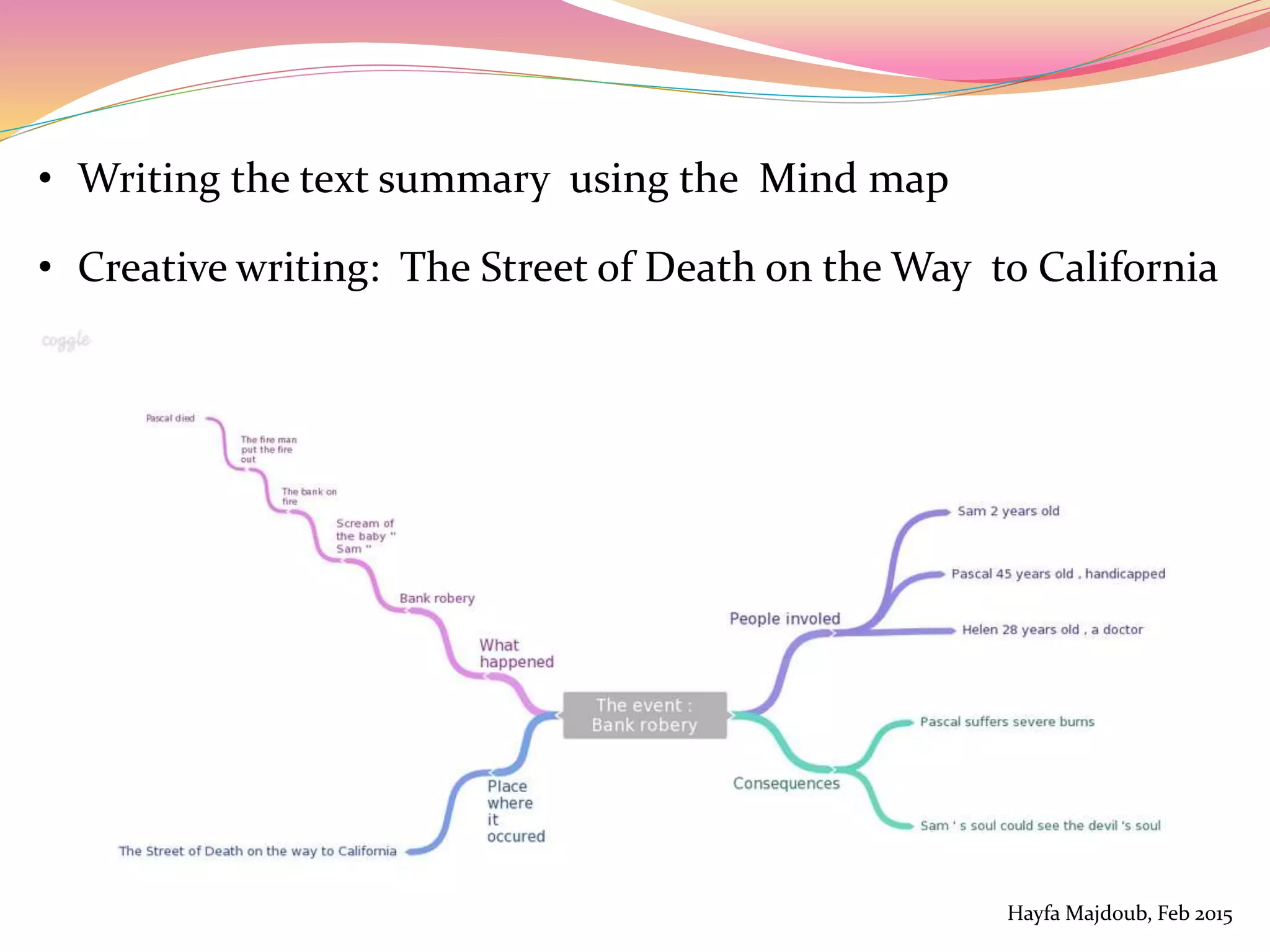
The document discusses the integration of Information and Communication Technology (ICT) in English as a Foreign Language (EFL) classrooms, emphasizing its importance for 21st century learners who require new skills and literacies. It presents various teaching strategies and activities that utilize ICT to enhance student engagement, promote autonomy, and develop critical thinking. The author shares personal experiences and outlines project-based learning methods that engage students in real-world issues while leveraging technology for collaborative learning.