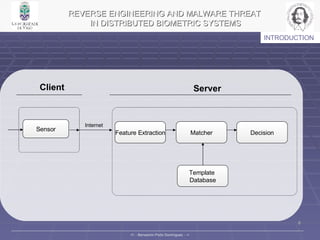
1. The document analyzes vulnerabilities in distributed biometric authentication systems from malware and reverse engineering attacks.
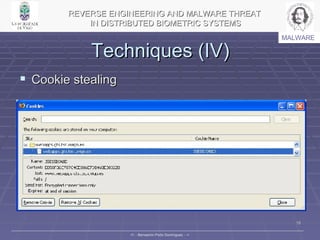
2. It studies how different types of malware like viruses, worms, and trojan horses could exploit such systems and reverse engineers a biometric face authentication prototype system.
3. The results showed the prototype system could be bypassed using spoofed images reconstructed from reverse engineering the template data distribution and feature extraction algorithms.