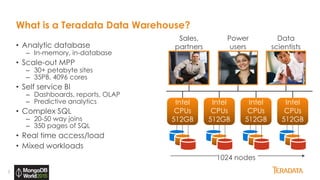
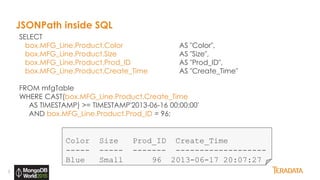
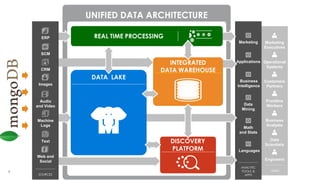
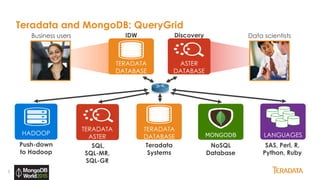
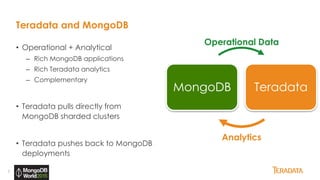
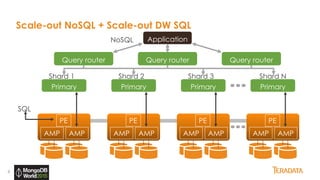
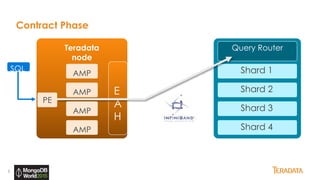
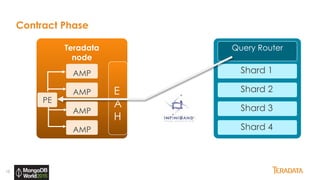
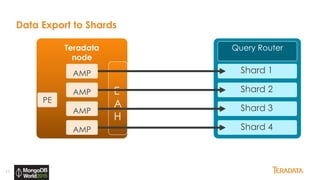
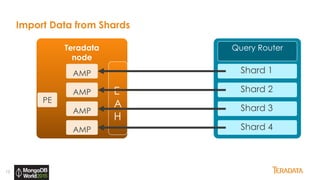
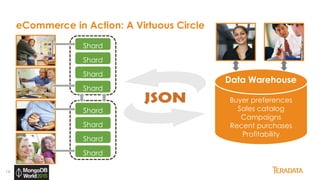
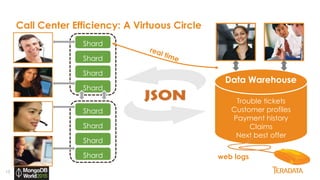
The document provides an overview of Teradata's integration with MongoDB through QueryGrid, emphasizing its capabilities in handling large-scale data analytics and operational data. It outlines the architecture, including the use of sharded clusters in MongoDB and Teradata's ability to perform complex queries and real-time analytics. The integration is designed to enhance both operational and analytical processes for various users, including data scientists and business analysts.